¶ Introduction
Except some minor differences, both helicopter and aeroplane cockpits are very similar.
Basic flight instruments like air speed indicator, altimeter and variometer are completely the same for both types.
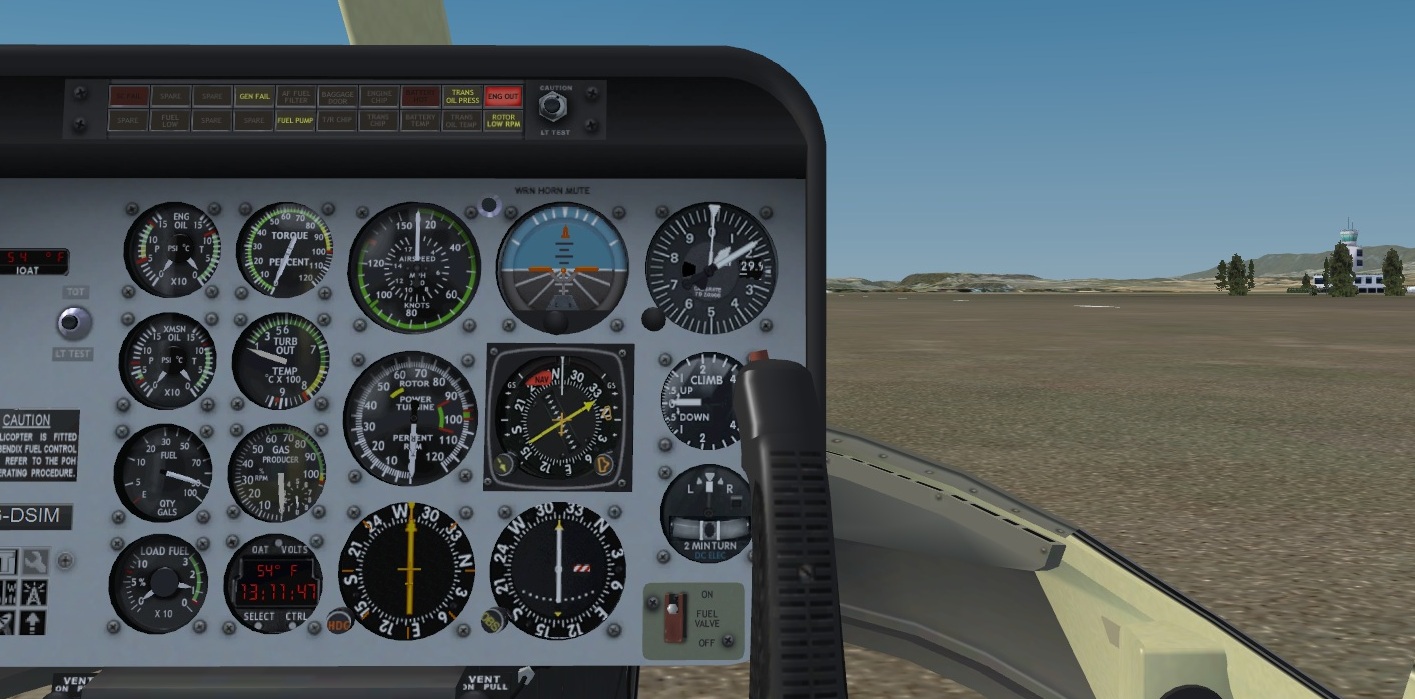
A typical helicopter cockpit contains:
Some old model helicopters only contain one Collective Pitch Control
- 2 Pairs of Antitorque Pedals
- An Overhead control panel
Overhead panel usually contains electrical panel, light panel, hydraulic panel, fire system, etc.
- Instrument panel
Instrument panel usually contains basic flight and navigation instruments, engine parameters, transmision parameters, etc.
- Interseat control panel
Interseat control panel usually contains radio control panels, autopilot panel, navigation panel, fuel control system
¶ Description
¶ Main Panel
As mentioned above helicopter flight instruments, navigation instruments and engine instruments are very similar to airplanes.
Helicopter cockpit configuration may vary between different models.
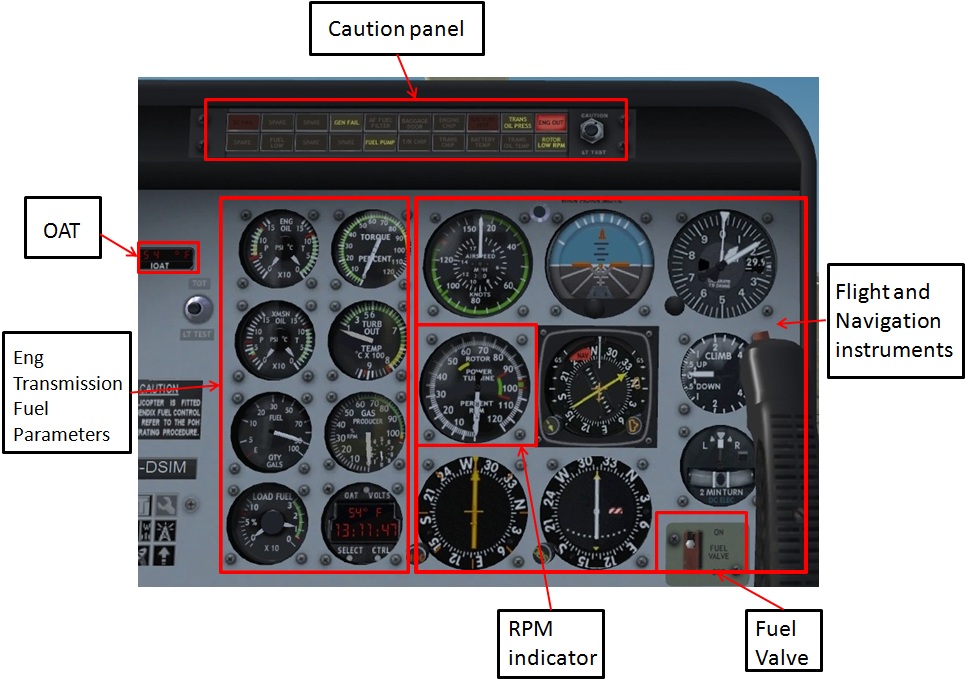

The main difference comes with engine instruments like the main gear box (MGB), intermediate gear box (IGB) and terminal gear box (TGB) pressure and temperature indicators.
The most significant difference which is also very important for the flight safety of the helicopter is the Torque indicator.

Another very important gauge is the RPM indicator. The RPM indicator indicates the amount of main rotor Revolutions Per Minute (RPM).
RPM gauges indicate the exact number or percentage (%) of turns per minute.

The RPM gauge of a helcopter is double functional instrument, the short needle marked with letter R and inner circle indicates main rotor RPM; the long needle marked with T and external circle indicates engine turbine RPM. Both have to be in the green area during flight.
Helicopter rotors are designed to operate in a specific RPM range to create necessary lift. If the RPM is lower than required, rotor blades would not be able to create the required lift; if it is higher than required, it would result in damage of rotating parts.
¶ Design
There are two types of cockpit design:
¶ Traditional Cockpit
Traditional cockpit includes lots of separate instruments. This type requires a lot of pilot attention by cross-checking all the instruments and observering parameters one by one.
The UH-1H and Bell 206 JetRanger are good examples of traditional cockpit presentation.

¶ Glass cokpit
A glass cockpit is an aircraft cockpit that features electronic (digital) flight instrument displays, typically large LCD screens, rather than the traditional style of analog dials and gauges. For example, the AS532 and H135.
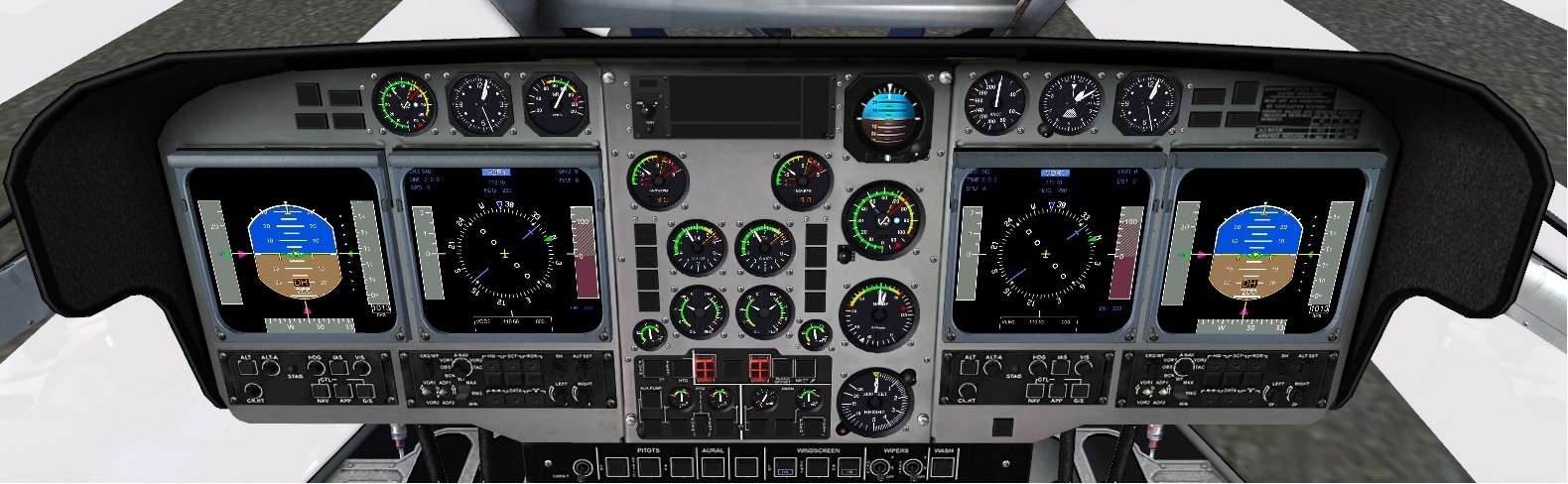
¶ Additional panels
¶ Overhead panel
Depending on the helicopter type, the overhead panel usually includes light, electrical, hydraulic and anti-ice sub-panels.
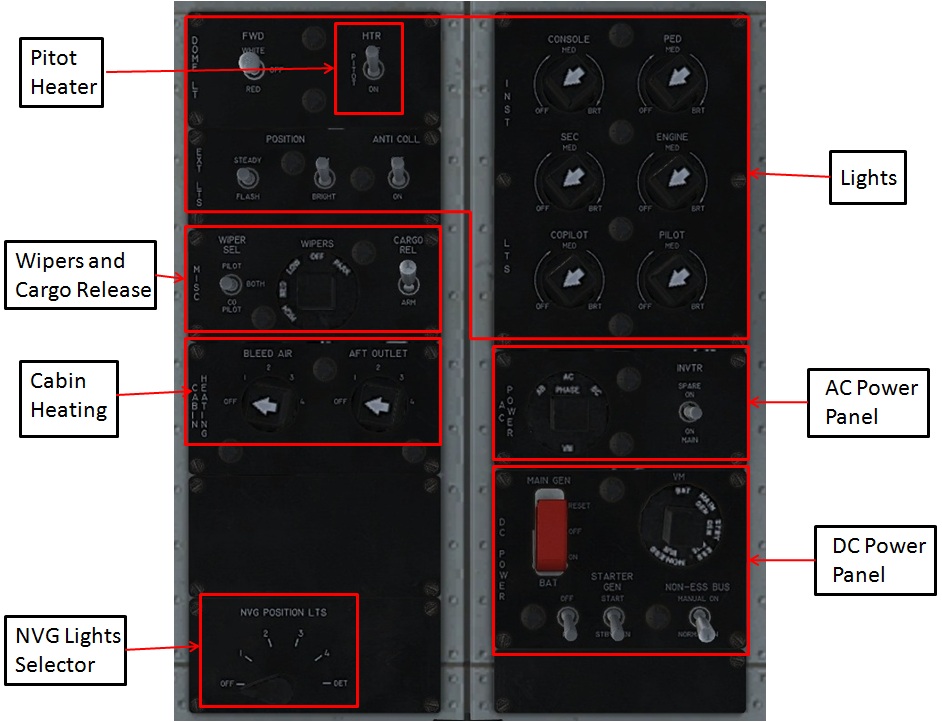 ![mainoh3.jpg]
![mainoh3.jpg]
"NVG lights" means that this helicopter is designed for flying with Night Vision Goggles with dimmed internal and external illumination
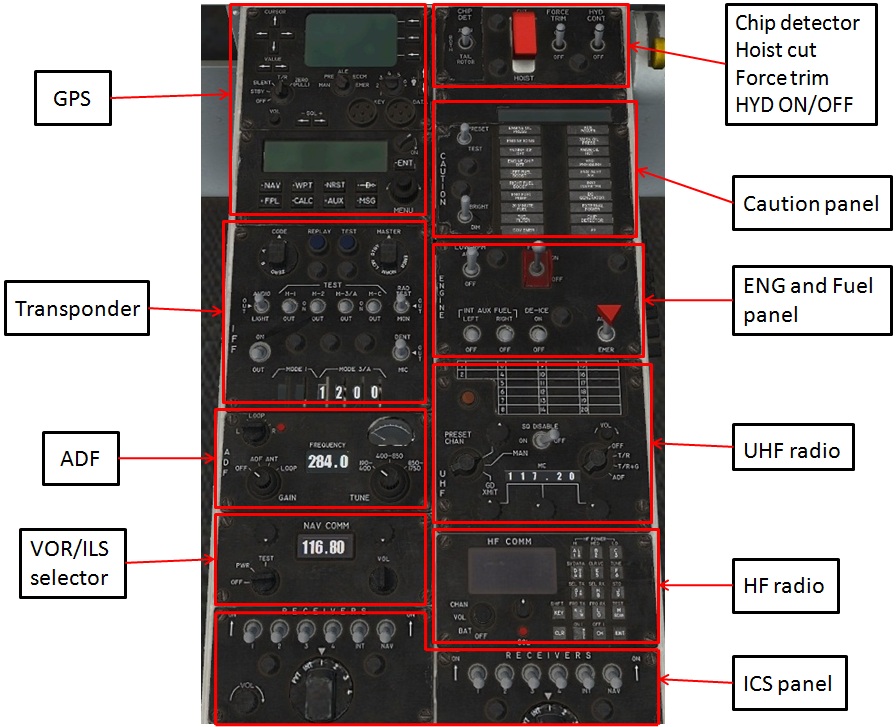
¶ Interseat console
Depending on the helicopter type, the interseat console usually includes radio, Internal Communication System (ICS), fuel, GPS, Auto Pilot and landing gear sub-panels.
- None
- None
- VID 241036 - Creation
- VID 496402 - Wiki.js integration