¶ Introduction
Due to the reduction in pressure-sensing accuracy of barometric altimeters with increasing altitude, there was a need above a certain flight level (FL) to increase the prescribed vertical separation minimum (VSM) of 300 m (1 000ft).
In 1966, an increased VSM of 600 m (2000ft) was established above FL 290 on a global basis. ICAO provisions stated that a reduced VSM could be applied under specified conditions within designated portions of airspace on the basis of regional air navigation agreement.
In 1982, ICAO and worldwide navigation offices started a study about the feasibility of a reduction of the Vertical Separation Minima (VSM) above FL290 from 2000 feet to 1000 feet.
The principal benefits of the reduced VSM were:
- A theoretical doubling of the airspace capacity above FL290
- The opportunity for aircraft to operate closer to the optimum flight level (fuel economy)
¶ Definition
Vertical separation minimum named VSM in airspace is:
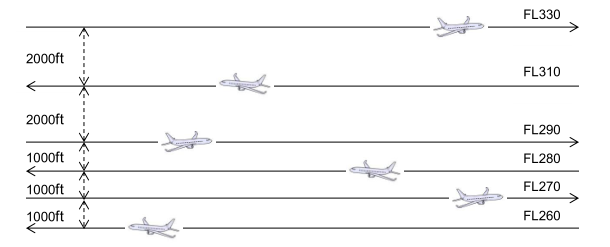
- 300m or 1000ft below FL 290
- 600m or 2000ft above FL 290
Except where, on the basis of regional agreement, a value of less than 600 m (2000ft) but not less than 300m (1000 ft) is prescribed for use by aircraft operating above FL290 within designated portions of the airspace.
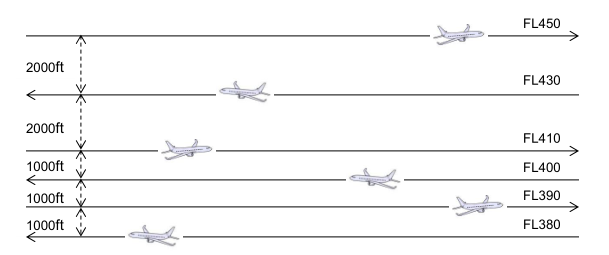
The reduced vertical separation minimum named RVSM is the reduction of the vertical separation minimum to 300m or 1000ft between FL290 and FL410:
- 300m or 1000ft below FL410
- 600m or 2000ft above FL410
Flight crew indicates RVSM approval by filing a "W" in field 10 of the ICAO model flight plan.
¶ Regulation
¶ Implementation
An aircraft shall not fly on an altitude based on the reduced vertical separation minimum (RVSM) unless that minimum is approved by the national regulation in the flied airspace (RVSM Approval).
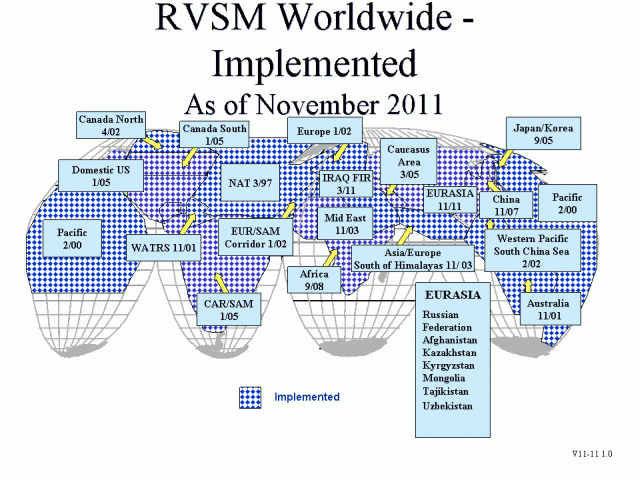
Between 1997 and 2005, RVSM was implemented in all of Europe, North Africa, Southeast Asia, North America, South America, and over the North Atlantic, South Atlantic, and Pacific Oceans.
After 2011, near all worldwide airspace has chosen RVSM including China, Russia and Africa.
¶ Aircraft equipment
An operator shall ensure that aeroplanes operated in RVSM airspace are equipped with:
- Two independent altitude measurement systems (altimeters) using independent pressure sensors
- An altitude-deviation alerting system
- An autopilot fitted with an altitude hold function
- A secondary surveillance radar (SSR) transponder with altitude reporting synchronized with the altimeter being the source for the autopilot.
¶ Separation in RVSM airspace
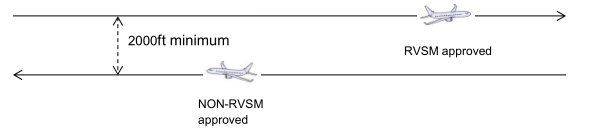
Within RVSM airspace (between FL290 and FL410 inclusive), the vertical separation minimum is 1000ft (300m) between RVSM-approved aircraft.

But, in this world we also have some non-RVSM approved aircraft. These aircraft can be state aircraft, military aircraft, vintage aircraft (DC6, DC7, B707).
Within RVSM airspace, the vertical separation minimum is 2000ft (600m) between non-RVSM approved state aircraft and any other aircraft operating within RVSM airspace.
Within RVSM airspace, the vertical separation minimum is 2000ft (600m) between non-RVSM aircraft operating as general air traffic (GAT) and any other aircraft operating within RVSM airspace.
There is no exemption for state aircraft to operate as GAT within RVSM airspace with a 1000 ft vertical separation minimum without an RVSM approval.
State aircraft which are exempted from having to meet the RVSM Minimum Aircraft System Performance Specification (MASPS) shall request special handling by filling "STS/NONRVSM" in Field 18 of the ICAO flight plan.
Formation flights are to be considered non-RVSM compliant and are not permitted within RVSM airspace with a 1000 ft vertical separation minimum.
¶ Approval for RVSM Operations
Flight crew shall indicate RVSM approval flight by filing a "W" in field 10 of the ICAO model flight plan (equipment).
It is a violation of ICAO procedures for a non-approved aircraft to file a W.
An important element of the certification process is the confirmation of the aircraft height keeping performance across the entire operational flight envelope. Flight crews must be trained in appropriate procedures in RVSM airspace.
The flight envelope covers all combinations of speed, altitude and weight/atmospheric pressure ratio that the aircraft would expect to operate across in RVSM airspace.
¶ Contingency procedures when unable to maintain RVSM
The pilots shall notify ATC of any equipment failure, weather hazards such as severe turbulence etc., which may affect the ability to maintain the cleared level or the RVSM requirements.
When an aircraft operating in RVSM Airspace encounters severe turbulence due to weather or wake vortex which the pilot believes will impact the aircraft's capability to maintain its cleared flight level, the pilot shall inform ATC. ATC is required to establish either an appropriate horizontal separation minimum, or an increased vertical separation minimum of 2000ft.
Where a meteorological forecast is predicting severe turbulence within the RVSM Airspace, ATC shall determine whether RVSM should be suspended, and, if so, the period of time, and specific flight level(s) and/or area.
When notified by ATC of an assigned altitude deviation of more than 300ft (90 m), the pilot shall take action to return to the cleared level as quickly as possible.
¶ RVSM related phraseology
| Event | Phraseology |
|---|---|
| ATC wishes to determine the RVSM status of a flight | CONFIRM RVSM APPROVED |
| Pilot response in case that the flight is RVSM approved | AFFIRM RVSM |
| Pilot response in case that the flight is not RVSM approved | NEGATIVE RVSM |
| Pilot of State aircraft responding that the flight is not RVSM approved | NEGATIVE RVSM STATE AIRCRAFT |
| ATC refuses to issue a clearance into RVSM Airspace | UNABLE CLEARANCE INTO RVSM AIRSPACE |
| Pilot reporting severe turbulence / weather affecting ability to maintain RVSM height keeping requirements | UNABLE RVSM DUE TURBULENCE |
| Pilot reporting equipment degradation below RVSM requirements | UNABLE RVSM DUE EQUIPMENT |
| Pilot ready to resume RVSM after equipment/weather contingency | READY TO RESUME RVSM |
- ICAO documentation Annex 2 - Rules of the Air - 10th Edition July 2005
- VID 150259 - Creation
- VID 150259 - Wiki integration
- VID 200696 - Update April 2020
- VID 496402 - Wiki.js integration