¶ Introduction
The purpose of a filed Flight Plan (FPL) is to provide specified information to air traffic services (ATS) units about:
- The type of aircraft used and some of its characteristics.
- An intended flight or portion of a flight of an aircraft and its flight rules.
- The equipment according to the operation the crew is going to conduct.
¶ ICAO Flight plan
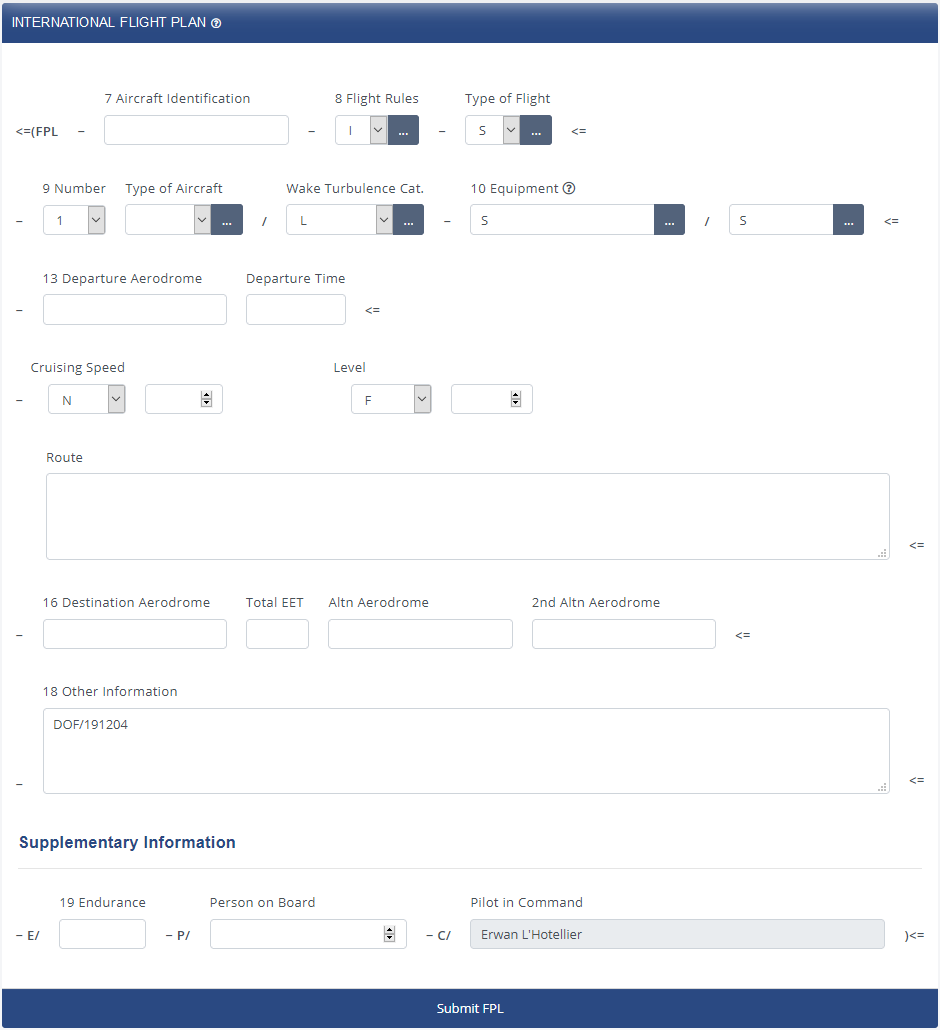
In the IVAO network, the format chosen for building the flight plan is the ICAO standard. This ICAO flight plan is presented like the figure below.
All pilots in IVAO must complete this flight plan before any flight
The Flight Plan shall include all information relevant to that specific planned flight. This includes:
- Item 7- Aircraft identification (Note: Aircraft identification means the radio call sign!)
- Item 8 -Flight rules and type of flight
- Item 9 -- Number of aircraft, type(s) of aircraft and wake turbulence category
- Item 10- Equipment on board
- Item 13 - Departure aerodrome ICAO code and planned time of departure
- Item 15 - First cruising speed and first cruising level or altitude
- Route to be followed
- Item 16 - Destination aerodrome ICAO code and total estimated elapsed time (EET)
- Item 17 - Alternate aerodrome(s)
- Item 18 -- Remarks and other equipment (emergency and survival)
- Item 19 - Fuel endurance and total number of persons on board
In IVAO a flight plan MUST ALWAYS be filed before any flight.
¶ Explanation of ICAO Flight Plan
To know each part of the Flight Plan (FPL), we will go through all the items in the FPL. The following is a sample Flight Plan form with full explanation of all possible fields.
The picture shows the layout used in IVAO based on the ICAO real flight plan.
¶ Aircraft Identification (up to 7 characters) -- Field 7
This item is the identification of the aircraft.
This identification is your chosen unique call sign on the IVAO Network.
It can be as follows:
- A registration marking of the aircraft as pronounced on the frequency : N704YA, OONZA
- An ICAO designator (trigram) of an operating company, followed by the flight number (plus letters) : BCS777, SLR05K
- A special military call sign given by authorities: BAF54, USAF112, FAF020
- (dash) must not be used in the call sign in an ICAO flight plan. A national registration marking is usually used for a general aviation VFR flight.
¶ Flight Rules (1 character) -- Field 8
This item is the flight rules chosen for the flight. This one letter type must be chosen in the following list:
- I when the whole flight will be under IFR
- V when the whole flight will be under VFR
- Y when the first part of the flight will be under IFR and later changed into VFR
- Z when the first part of the flight will be under VFR and later changed into IFR
The flight rules are Instrument Flight Rules (IFR) or Visual Flight Rules (VFR).
Short explanation of VFR and IFR:
- V = VFR: Visual Flight Rules means the pilot is required to be able to see ground reference except where the local authorities allow differently. It is the rule of "see and be seen". The ceiling and the visibility shall be compatible with the flight.
- I = IFR: Instrument Flight Rules means the aircraft instrumentation and the pilot abilities have to be certified. Instrument flight rules allow pilots to fly through clouds and in poor visibility. In most of the cases separation is provided by ATC in controlled airspace.
The pilot should specify in the appropriate route item the point or points where the change of flight rules is planned.
Example: GIBAL W616 LXR VFR DCT. This means the flight will depart IFR and remain IFR till LXR, after LXR the flight will continue VFR
Example: GIBAL/N0260F120 IFR W616 LXR. This means the flight will depart VFR and remain VFR till GIBAL, after GIBAL the flight will continue at a speed 260 kts at FL120, IFR.
¶ Type of flight (1 character) -- Field 8B
This item is the type of flight.
This one letter type must be chosen in the following list:
- S if scheduled services (commercial flight according time-table)
- N if non-scheduled Air Transport Operations (occasional commercial flight)
- G if General Aviation (non-commercial flight)
- M if Military
- X if other than any of the defined categories above (State Flight, Search And Rescue, ...)
¶ Number of aircraft (1 or 2 characters) -- Field 9
This item is the number of aircraft in the formation. In IVAO, this number shall be 1 except for formation flight with multiple aircraft.
Be careful, do not mix, fly with other aircraft, perform own navigation and make a visual separation between each other and a formation flight, that all aircraft must be close to each other and doing the same thing at the same moment.
¶ Type of aircraft (up to 4 characters) -- Field 9B
This item is the code of the aircraft you use in the IVAO Network. The aircraft is coded using the ICAO table provided.
If an aircraft type has no ICAO code, you must use ZZZZ in the type of aircraft cell and you must specify in Remarks (item 18) the full name of the used aircraft type preceded by TYP/
¶ Wake Turbulence Category (1 character) -- Field 9C
This item is the wake turbulence category of the aircraft chosen in the flight plan.
It is coded using one chosen letter with the following possibilities:
- H = heavy: for an aircraft type with a MTOM of 136.000 kg (300.000 lb.) or more.
- M = medium: for a MTOM less than 136.000 kg but more than 7.000 kg (15.500 lb.).
- L = light: for a MTOM of 7.000 kg or less.
For each aircraft type, the wake turbulence category is determined by its MTOM = Maximum Take-Off Mass. The actual mass of an aircraft does not change its wake turbulence category.
¶ Equipment -- Field 10A
Preceding the oblique stroke, this item is the equipment used, carried and serviceable for the current flight.
For VFR flight, we present only the usable options for your type of flight and/or your available equipment in a light aircraft used for VFR flight. (Note that light VFR aircraft can be equipped with some IFR equipment).
| Eq | Description |
|---|---|
| D | Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) is a transponder-based radio navigation technology that measures distance between the equipment on ground and an aircraft by timing the propagation delay of VHF or UHF radio signals. |
| F | Automatic Direction Finder (ADF) is a radio-navigation instrument that automatically and continuously displays the relative bearing from the aircraft to a suitable radio station. |
| G | Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). The term GNSS encompasses all the satellite navigation systems such as GPS, GLONASS, GALILEO |
| I | An Inertial Navigation System (INS) or Inertial Reference System (IRS) or Inertial Reference Unit (IRU) is a navigation aid that uses a computer, motion sensors (accelerometers) and rotation sensors (gyroscopes) to continuously calculate the position, orientation, and velocity (direction and speed of movement) of a plane without the need for external references.. |
| L | Instrument Landing System (ILS) is a ground-based instrument approach system that provides precision guidance to an aircraft approaching and landing on a runway. |
| N | It shall be specified if no COM/NAV approach aid equipment for the route to be flown is carried, or the equipment is unserviceable. |
| O | VHF Omni directional Range (VOR) is a type of radio navigation system for aircraft. The system relies on ground based transmitters which emit signals to a VOR receiver inside the aircraft. The navigation signal allows the aircraft receiving equipment to determine a magnetic bearing from the station to the aircraft. |
| S | It shall be specified if standard COM/NAV/approach aid equipment for the route to be flown is carried and serviceable. If the letter S is used, standard equipment is considered to be VHF RTF,VOR and ILS unless another combination is prescribed by the appropriate ATS authority. S= O+L+V |
| V | Very High Frequency (VHF) RadioTelephone (RTF). Radio equipment onboard the aircraft. |
| Y | Very High Frequency (VHF) with 8.33 kHz spacing channel: it was decided in 1994 to introduce a further channel split from 25 to 8.33 kHz. Subsequently, 8.33 kHz was introduced above FL245 in the ICAO EUR Region from October 1999 and above FL195 from the 15 March 2007. At the time of writing Eurocontrol is working on the second phase of the mandate contained in the Commission Regulation (EC) No 1265/2007 which is the deployment of 8.33 kHz channel spacing to the airspace below FL195. The current date planned for the deployment is 2018. |
¶ Equipment SSR -- Field 10B
After the oblique stroke, this item is the SSR (transponder) equipment used, carried and serviceable for the current flight.
IVAO pilot interface shall be considered as mode S transponder equipment in IVAO.
If you do not know which transponder type is serviceable on your aircraft, please use "S" type as the default one.
For VFR flight, we present only the usable options for your type of flight and/or your available equipment in a light aircraft used for VFR flight. (Note that light VFR aircraft can be equipped with some IFR equipment).
| Eq | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Transponder - Mode A (4 digits - 4096 codes) |
| C | Transponder - Mode A (4 digits - 4096 codes) and Mode C |
| H | Transponder Mode S, including aircraft identification, pressure-altitude and enhanced surveillance capability. Mode S: Whilst traditional Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) stations interrogate all aircraft within their range, Mode S (Select) establishes selective and addressed interrogations with aircraft within its coverage. Such selective interrogation improves the quality and integrity of the detection, identification and altitude reporting. |
| I | Transponder Mode S, including aircraft identification, but no pressure-altitude capability. Mode S: Whilst traditional Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) stations interrogate all aircraft within their range, Mode S (Select) establishes selective and addressed interrogations with aircraft within its coverage. Such selective interrogation improves the quality and integrity of the detection, identification and altitude reporting. |
| L | Transponder Mode S, including aircraft identification, pressure-altitude and extended squitter (ADS-B) and enhanced surveillance capability. Mode S: Whilst traditional Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) stations interrogate all aircraft within their range, Mode S (Select) establishes selective and addressed interrogations with aircraft within its coverage. Such selective interrogation improves the quality and integrity of the detection, identification and altitude reporting. |
| N | It indicates that no surveillance equipment for the route to be flown is carried or the equipment is unserviceable. |
| P | Transponder Mode S, including pressure-altitude, but no aircraft identification capability. Mode S: Whilst traditional Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) stations interrogate all aircraft within their range, Mode S (Select) establishes selective and addressed interrogations with aircraft within its coverage. Such selective interrogation improves the quality and integrity of the detection, identification and altitude reporting. |
| S | Transponder Mode S, including both pressure-altitude and aircraft identification capability Mode S: Whilst traditional Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) stations interrogate all aircraft within their range, Mode S (Select) establishes selective and addressed interrogations with aircraft within its coverage. Such selective interrogation improves the quality and integrity of the detection, identification and altitude reporting. |
| X | Transponder Mode S, with neither pressure-altitude nor aircraft identification capability. Mode S: Whilst traditional Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) stations interrogate all aircraft within their range, Mode S (Select) establishes selective and addressed interrogations with aircraft within its coverage. Such selective interrogation improves the quality and integrity of the detection, identification and altitude reporting. |
¶ Departure Aerodrome and planned time of departure (4 + 4 characters) -- Field 13
This item is the ICAO code of the departure aerodrome. The ICAO code is noted using maximum 4 letters.
In IVAO, the ICAO code is mandatory. No IATA or Airfield names are allowed.
If no location identifier is assigned, you must use the special code ZZZZ and the exact name of your airfield in plain language should be specified in the 'other information' item, preceded by DEP/ text.
The Estimated Off-Block Time (known as departure time) is the estimated time at which the aircraft will commence ground movement associated with departure. It is coded using 2 digits for the hour followed by 2 digits for the minutes.
All hours must be calculated in UTC time for all countries.
¶ Cruising Speed (maximum 5 characters) -- Field 15
This item is the cruising speed for the first or whole portion of the flight.
The cruising speed is the True Air Speed expressed in one of the three possible units:
- N = Knots: N followed by 4 digits which will be the speed in knots (N0220 = 220KT)
- M = Mach: M followed by 3 digits which will be the mach number without the dot character (M079 = 0.79 Mach)
- K = km/h : K followed by 4 digits which will be the speed in kilometres per hour (K0350 = 350km/h)
ICAO provision is to apply a Mach number notation only above FL250.
The speed value K or N is selected for the first part of the flight. If the required value changes en- route, the speed/level field for level changes should be stated in the route next to a fix.
Mach number is only given for flights in those airspaces where ATC prescribes (big example: North Atlantic.) There is no Flight Level above which Mach must be filed.
¶ Cruising Level or altitude (maximum 5 characters) -- Field 15B
This item is the cruising altitude or flight level for the first or whole portion of the flight.
The cruising altitude or flight level is expressed in one of the three possible units:
- F = flight level: followed by 3 digits expressed in hundreds of feet above transition altitude.
(Example: F130 = 13000ft). - A = altitude: followed by 3 digits expressed in hundreds of feet below transition altitude.
(Example: A025 = 2500ft). - S = standard metric level: followed by 4 digits expressed in tens of meters above transition altitude
(Example: S1130 = 11300m) - M = metric altitude: followed by 4 digits expressed in tens of meters below transition altitude
(Example: M1130 = 11300m) - VFR = VFR level: it is used when no specific VFR altitude chosen.
The letters S and M are used only in some countries. It depends of the local regulations.
Note that "VFR" level is usually set when a VFR flight is performed below 3000ft where altitude is free to use.
¶ Route
This item is the route followed by the aircraft during its flight.
Aircraft routing types used in flight planning are:
- Airways
- Navigational Aids
- Direct to fixes or geographical points (55N030W)
- SIDs and STARs (only for IFR)
For a VFR flight, it can be filled with the items above and/or the commonly used visual reference points to indicate the intended flight path. (See the appropriate VFR navigation charts.)
In real life, for a local VFR flight, the route in the flight plan is not mandatory. The pilot is not obliged to send his route.
On IVAO, even for a local flight, this item can't remain empty. The words "VFR" or "local flight" or "traffic patterns" can be used only for a local VFR flight (i.e Inside a CTR/CTA)
A route may be composed of segments of different routing types.
¶ Arrival Aerodrome and Estimated En-Route Time (4 + 4 characters)
This item is the ICAO code of the arrival aerodrome. The ICAO code is stated using maximum 4 letters.
In IVAO, the ICAO code is mandatory. No IATA or Airfield names are allowed.
If no location identifier is assigned, you must use the special code ZZZZ and the exact name of your airfield in plain language should be specified in the 'other information' item, preceded by DEST/ text.
The Estimated Elapsed Time (EET) is the time calculated:
- Between take-off time and the estimated time overhead the arrival aerodrome calculated for VFR flight rules
- Between take-off time and the estimated time at the expected IAF for IFR flight
It is coded using 2 digits for the hour followed by 2 digits for the minutes.
All hours must be calculated in UTC time for all countries.
¶ Alternate Aerodrome -- Field 16C
This item is the ICAO code of the alternate aerodrome. The ICAO code is stated using maximum 4 letters. The alternate aerodrome is used when your aircraft cannot land in the destination airport.
In IVAO, the ICAO code is mandatory. No IATA or Airfield names are allowed.
If no location identifier is assigned, you must use code ZZZZ and the exact name of your airfield in plain language should be specified in item 18, the 'other information' item, preceded by ALTN/ text. An alternate is optional for VFR flight rules unless local authorities require such.
¶ Other Information -- Field 18
This item includes all other information needed for the flight which is not present in the other items.
Example of some important remarks: If you have no FMC, please insert "RMK/NOFMC" If your aircraft has no RNAV capabilities, please insert "STS/ RNAVINOP" If your aircraft is not RVSM, please insert "STS/NONRVSM"
If any other necessary information is required, then in the preferred sequence shown below, the form of an appropriate indicator should be stated, followed by an oblique stroke and the information to be recorded.
IVAO recommended practices (NOT applicable for IVAO exams): If you are a Newbie in the IVAO network, please insert "RMK/IVAO Newbie" in this item. If your call sign of your company is not well known to ATC, please insert "CS/company_radio_call"
Here are the options for items to be inserted for a flight (the number of items has been reduced for this level to the minimum useful for a VFR flight):
Be advised that the following remarks have very little use on IVAO.
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| STS/ | Reason for special handling by ATS, e.g. a search and rescue mission, as follows: ATFMX, FFR, FLTCK, HAZMAT, HEAD, HOSP, HUM, MARSA, MEDEVAC, NONRVSM, SAR and STATE. Other reasons for special handling by ATS shall be denoted under the designator RMK/. |
| DEP/ | Name and location of departure aerodrome, if ZZZZ is inserted in Item 13, or the ATS unit for which supplementary flight plan data can be obtained if AFIL is inserted in Item 13. |
| DEST/ | Name and location of destination aerodrome, if ZZZZ is inserted in Item 16. |
| DOF/ | Date Of Flight departure in a six figure format: YYMMDD. |
| REG/ | The nationality or common mark and registration mark of the aircraft, if different from the aircraft identification in Item 7. |
| TYP/ | Type(s) of aircraft preceded if necessary without a space by number(s) of aircraft and separated by one space if ZZZZ is inserted in Item 9. Ex: TYP/2F15 5F5 3B2 |
| OPR/ | ICAO designator or name of the aircraft operating agency, if different from the aircraft identification in item 7. |
| ORGN/ | The originator's 8 letter AFTN address or other appropriate contact details, in cases where the originator of the flight plan may not be readily identified, as required by the appropriate ATS authority |
| ALTN/ | Name of destination aerodrome alternate aerodrome(s), if ZZZZ in inserted in Item 16. |
| RMK/ | Any other plain language remarks when required by the appropriate ATS authority or deemed necessary. |
¶ Supplementary Information
This information is not filed with the flight plan, but is kept at the unit where the plan was filed. In case of emergency, the supplementary information will be transmitted to the appropriate rescue agencies.
¶ Endurance
After E/ group, you fill the fuel endurance in hours and minutes (4 digits). It means the range of your aircraft in terms of flight hours.
¶ Persons on Board (POB)
After P/ the total number of persons (passengers and crew included) on board, when required by the appropriate ATS authority.
¶ Pilot in Command (PIC)
After C/ Pilot in command), your real name and surname are filled automatically with you account except on IVAO pilot interface software where you need to fill it manually.
¶ Example of flight plan
¶ Flight VFR from Calais to Kortrijk-Wevelgem with DR400
(FLP-FWBTS-VG
-DR40/L-S/S
-LFAC1600
-N0120VFR DCT LEQ DCT OKT DCT -EBKT0120 LFQQ
-OPR/PVT REQ/1 TOUGH AND GO AT LFQQ RMK/TRAINING FLIGHT)
- None
- VID 150259 - Creation
- VID 450012 - Wiki Integration
- VID 150259 - Update December 2019
- VID 496402 - Wiki.js integration
- VID 514786 (TDM) - Update 2024