¶ Introduction
This document describes how to properly configure your IVAO ATC Software Aurora according to your preferences for the version:
- Aurora version higher than 1.4.1.x
Advanced Aurora Functions Manual
There are some features of the Aurora that are not explained in this document. For some advanced functions, please refer to our ==Advanced Aurora Functions== document.
FAQs
- Check our Frequently Asked Questions in case you have any problems.
- For MacOS and Linux users also check our MacOS & Linux Manual for more information.
For Developers
¶ Manual Index
Introduction Overview important information about this Manual
Downloading and Installing Aurora How to Download Aurora
Quick Setup Aurora's First Steps
Sectorfiles Download your Division's Sectorfile
Main Window Aurora's Main Window Explanation
Aurora's Navigation Bar Aurora's Navigation Bar Sections & Options
Preferences Bar Learn about all the options in the Preferences Bar
Aircraft Context Menu What happens when you right-click a traffic?
Session Recorder Aurora's Built-in Function to Record ATC Sessions
Shortcuts Learn useful shortcuts for Aurora ATC Client
Authors
¶ Installation
-
Download Aurora from here
-
For Windows:
- Recommended: Install to default installation path
C:/Aurora
- Recommended: Install to default installation path
-
For MacOS or Linux (Beta):
- Refer to our dedicated MacOS & Linux Manual
-
Run Aurora
¶ Quick Setup
- Right click anywhere on the screen and select PREF BAR.
- Recommended: Configure your PREF BAR as shown in the image above. White font indicates the type of nav data that is turned on.
- These settings may vary depending on your division sectorfiles presets.
- Each button's function is explained here.
Check MacOS Aurora's Manual for more information regarding right-clicks on MacOS
¶ Sectorfiles
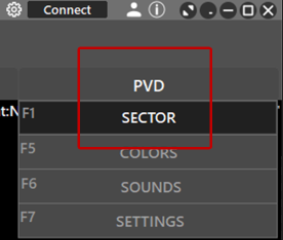
- Select PVD > SECTOR in the MENU BAR
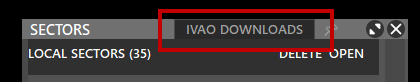
- Select IVAO DOWNLOADS
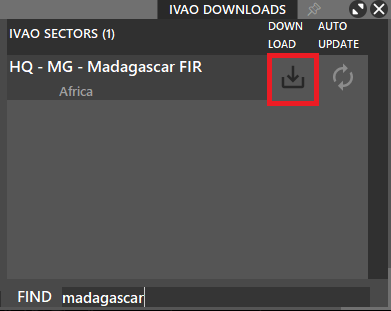
- In the bottom right find field, enter the FIR or country name of the sectorfile.
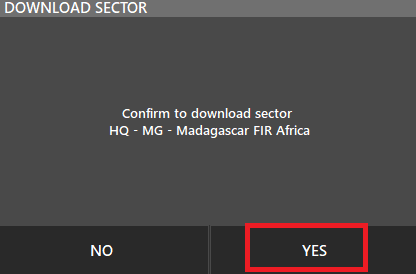
- Click yes in the confirmation dialog.
- Verify that the auto-update is enabled (green). When an update is available aurora will automatically download it for you.
- The new sectorfile will now appear on the left side
- Click the folder icon to load it.
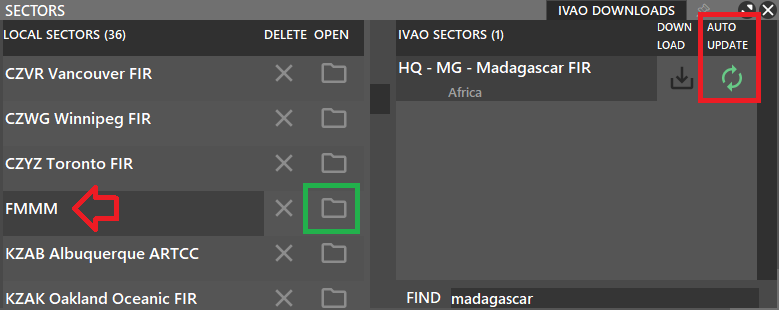
Tip: Sector screen will automatically close after loading sector files. If you wish to keep it open, use the pin on the top right.
¶ Main window
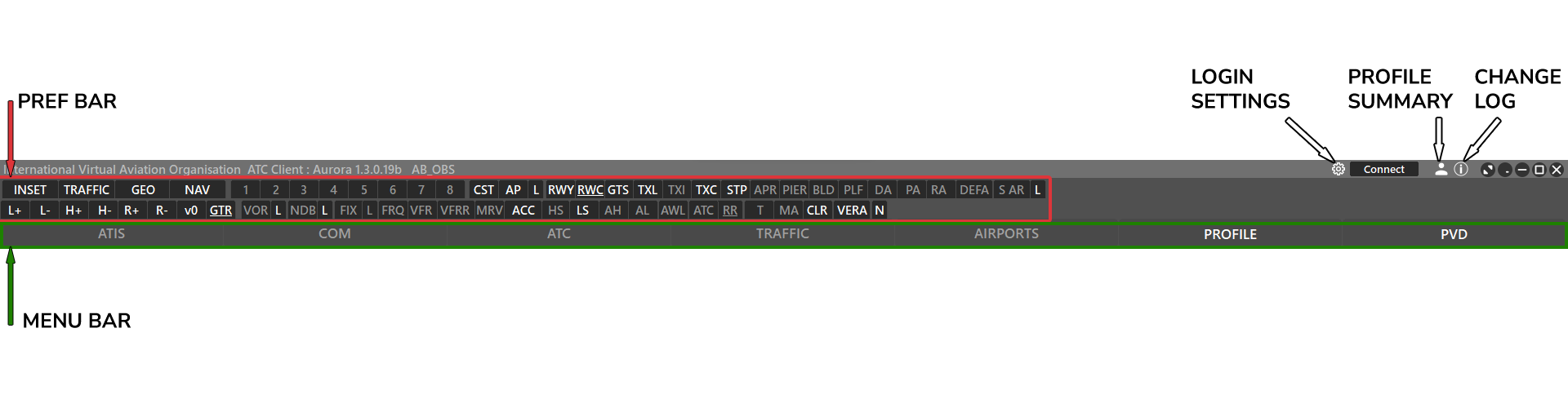
Aurora has three sections: title bar, nav bar, and the plan view display (PVD).
¶ Title Bar

- Aurora version
- Callsign, or last used profile (when offline)
- Login settings
- Connect / Disconnect
- Profile
- Changelog
- Fullscreen (covers taskbar)
- Minimize to tray icon
- Minimize to taskbar
- Fullscreen (windowed mode)
- Close
¶ Login / Logout
⚙️ The cog-wheel button will allow you to set your login settings.
🔽The dropdown icon opens a list of all possible ATC station that can be used.
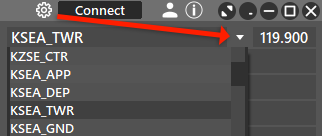
Once you have a login selected you can click Save, then click Connect to go online.

Hide SUP/ADM rating: Used by supervisors or network admins to have rating hidden when connected.
Connect to Artifice: Used for Tower views. Read more here in the artifice manual.
Connect voice: Must be selected in order for pilots to join your frequency. A voice server will automatically selected based on the lowest latency. Clicking on the dropdown icon reveals a list of voice servers and their latency measured in miliseconds (ms).

The 3 voice servers are:
ts-1.eu-west-2.ivao.aero located in europe.
ts-1.ap-southeast-1.ivao.aero located in southeast asia.
ts-1.sa-east-1.ivao.aero located in brazil..
Hoppie: Used to enter CPDLC logon code. Read more about it here.
¶ Title Bar (When Connected)

- Active position callsign
- Timer window
- Intercom window
- Disconnect button
¶ Timer
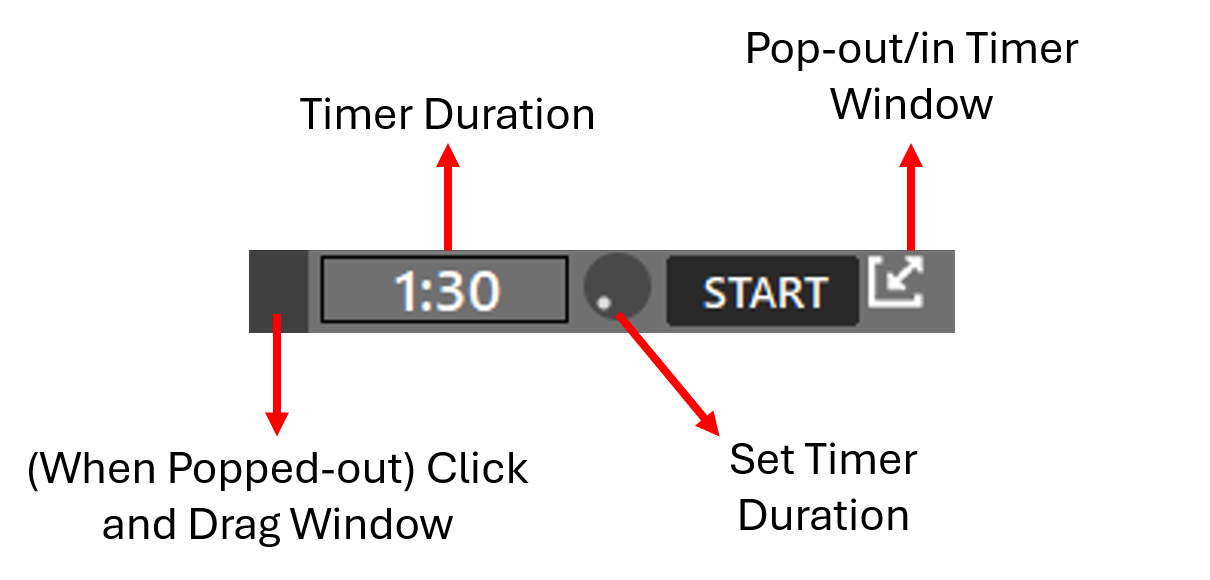
Timer Duration Wheel
- Using the mouse scroll wheel, the timer's duration can be set by adding intervals of 10 seconds up to 10 minutes.
Pop-out Button
- Using the pop-out button, the timer window can be moved by clicking and dragging the timer using the darker grey section at the left part of the timer window (when popped-out)
Timer Sound Configuration
- To set the timer beep frequency, duration and volume, check the sounds configuration panel here.
¶ Intercom
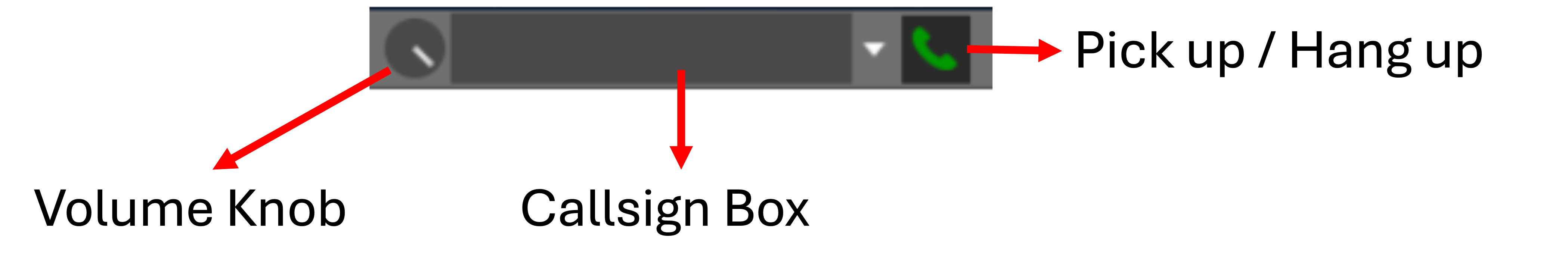
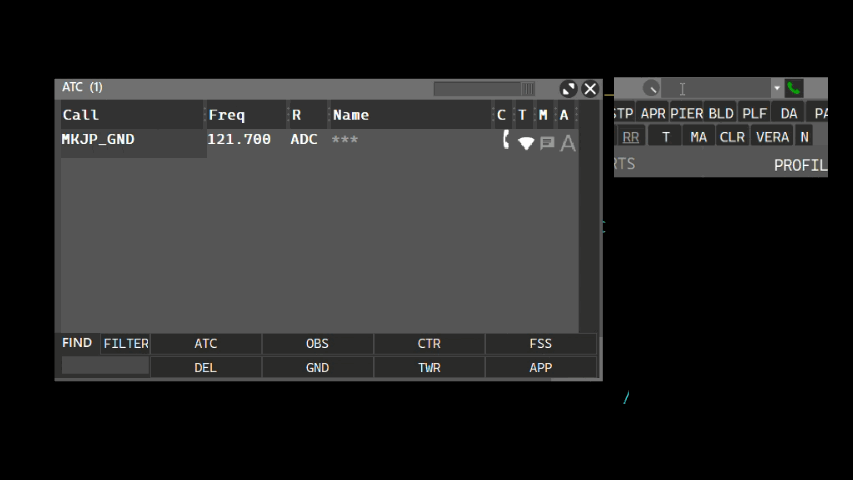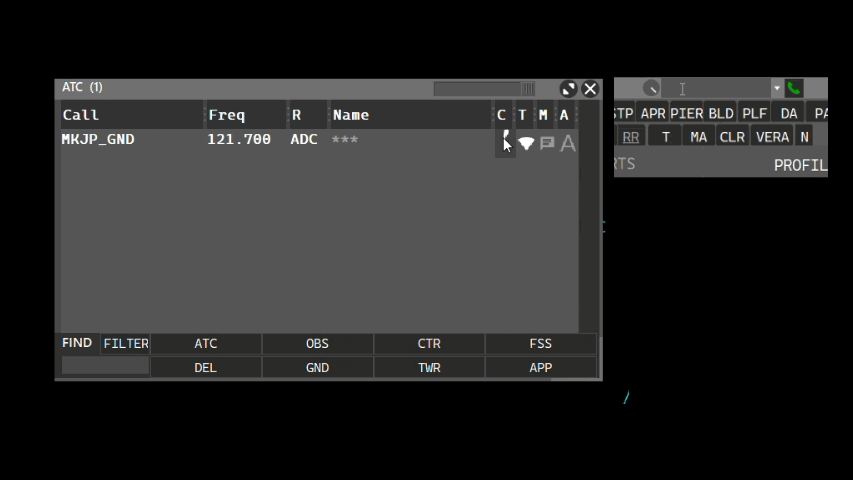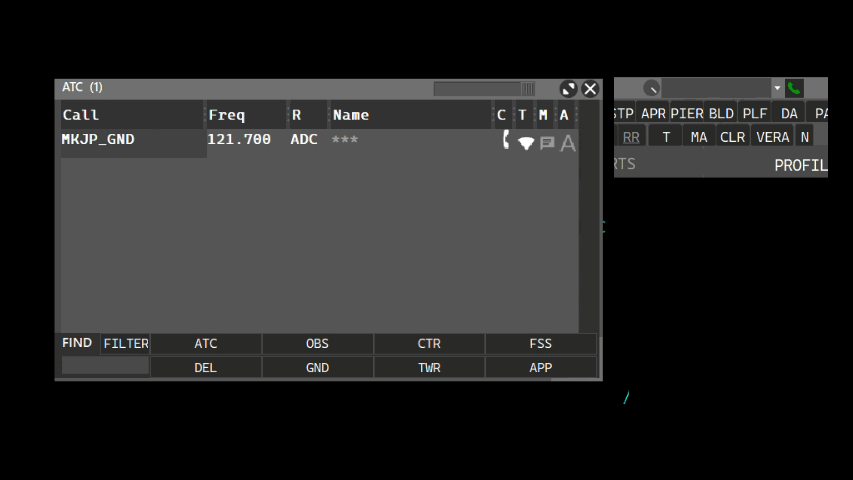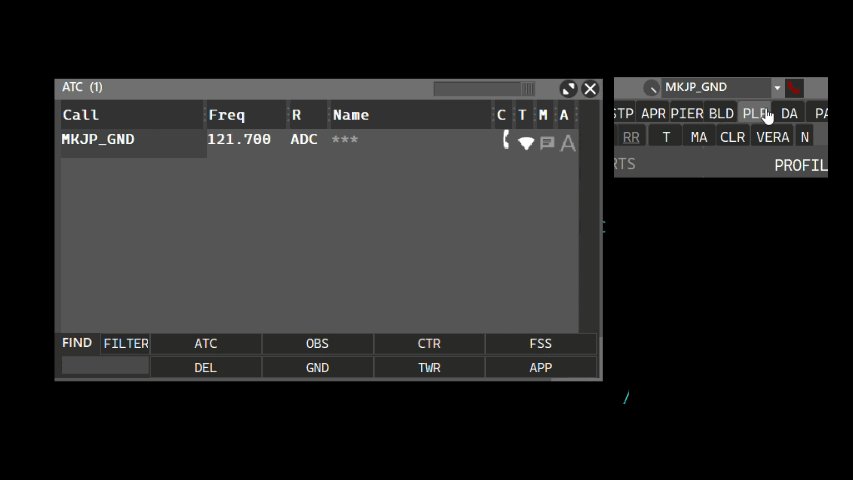
The intercom allows you to contact other connected ATC positions. The Intercom volume can be adjusted via the volume knob. Calling an ATC position can be made using the ATC window and clicking the phone button, or by typing the ATC position name on the callsign box, as shown:
- Using the callsign box:
- Using the ATC window:
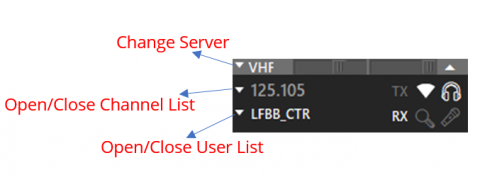
¶ VHF Window
VHF window only appears when connected.
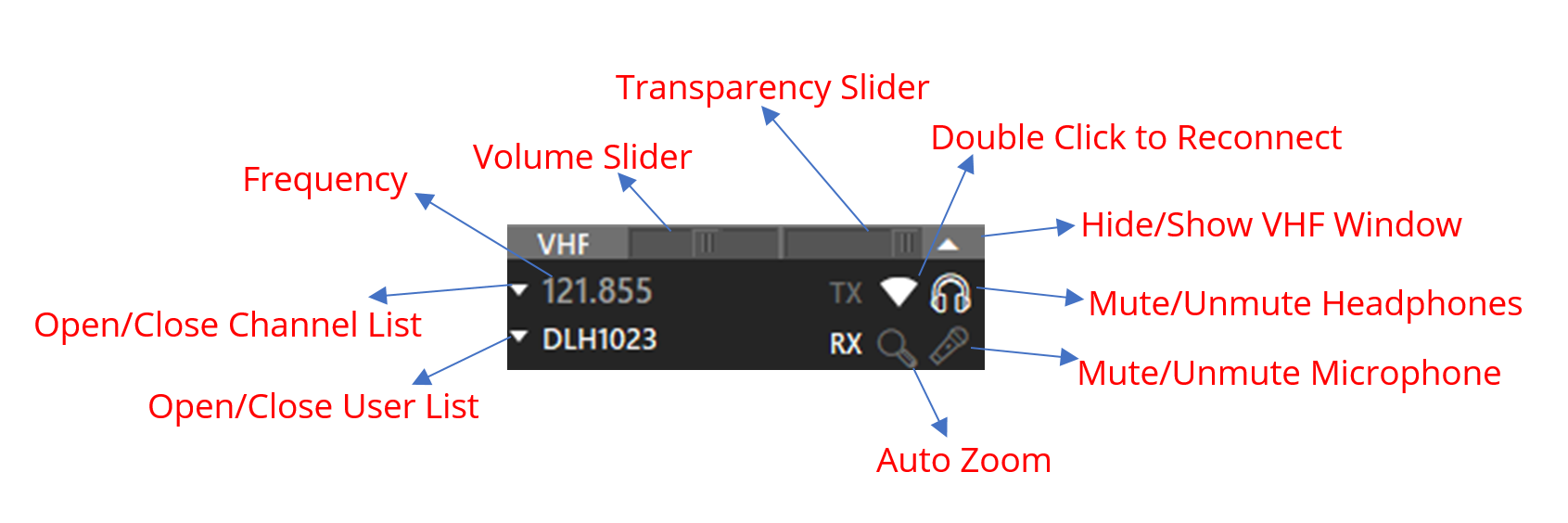
Auto Zoom (Magnifying glass)
Zooms to or Selects Traffic transmitting on frequency.
- Grey : Off
- White : Place rings around traffic on the radar screen
- Green : Select the aircraft
- Amber : Zoom on the traffic
TX & RX
- TX : Transmitting
- RX : Receiving
- BL : Frequency blocked if 2 or more talk at the same time. Click on BL to disable Block Tone.
- CA: Channel Admin(Assigned to whoever created the frequency channel) CA can kick, mute or grant other CA access by right-clicking a user in the channel list.
Radar Icon 
- Used to reconnect voice server. Double-click to reconnect.
User Lists
| Observer | ATC |
|---|---|
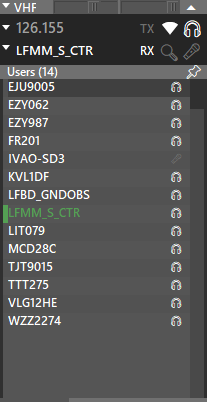 |
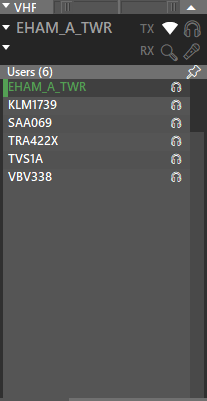 |
When online as Observer, instead of the station frequency, you might see the Station Name.
This means that this station is outside of your range.
You can use the pushpin on the User List to separate it from the VHF Window.
¶ VHF Audio Settings
Located under PVD > Settings > VHF Radio
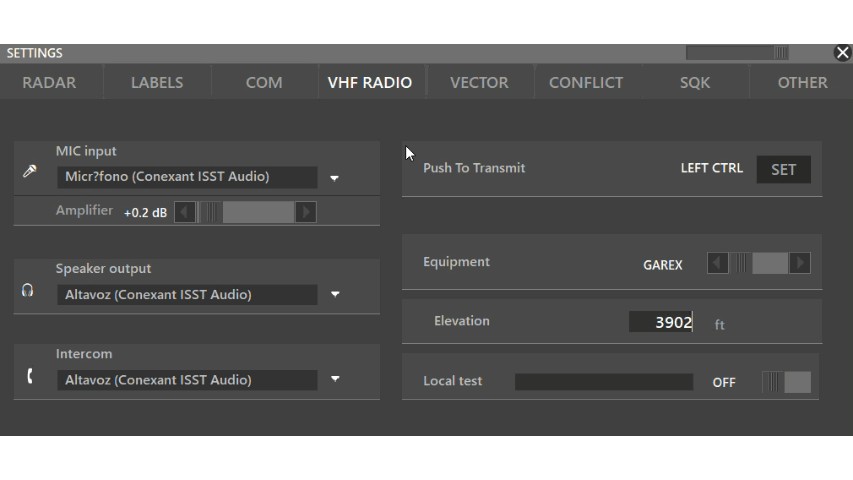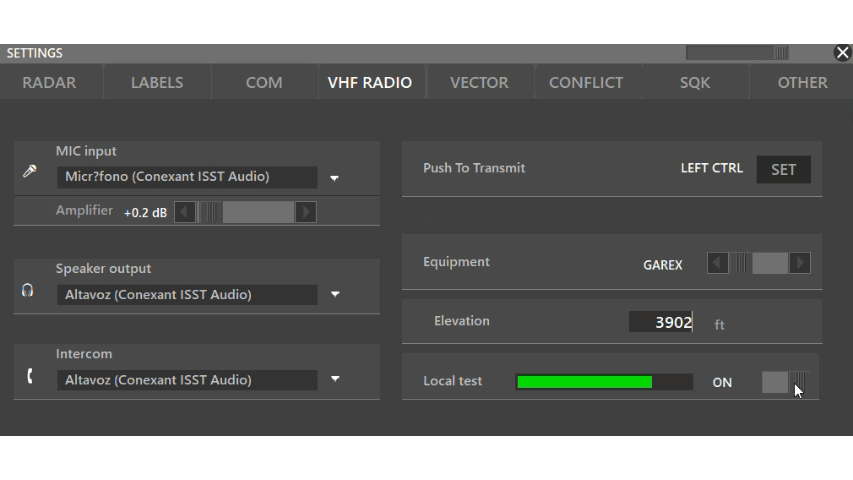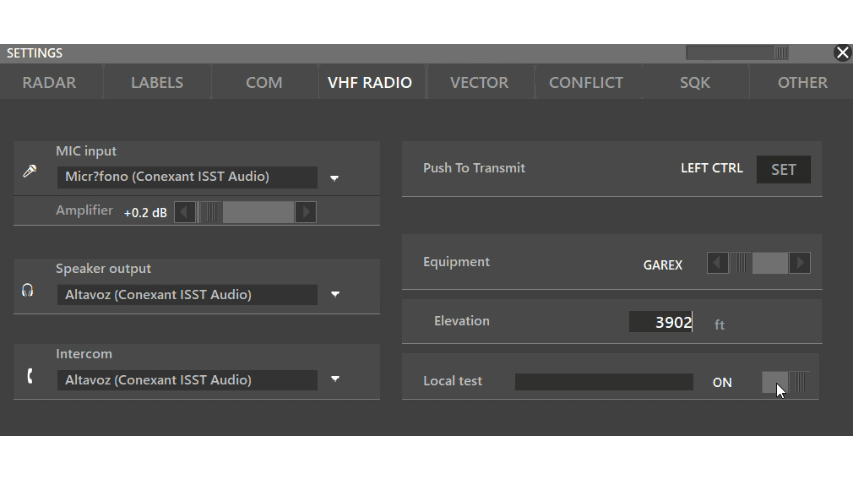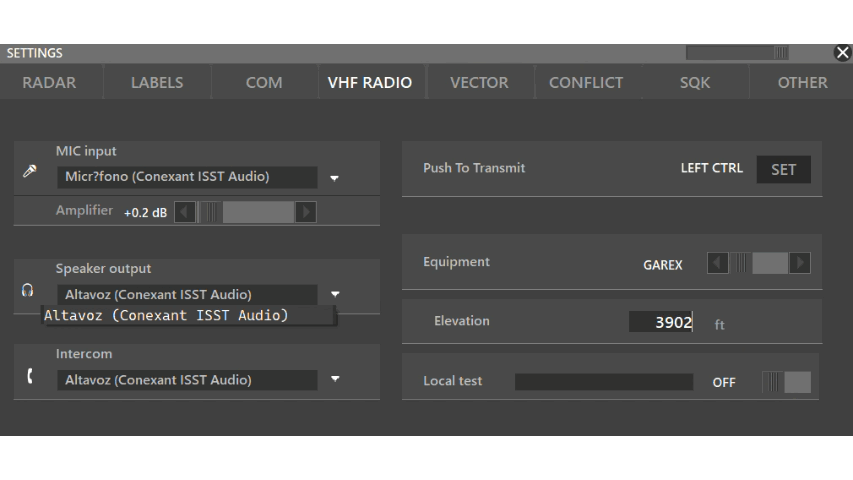
MIC Input: Select your microphone
Amplifier: Increases volume. Value is set in decibal and increases exponentially. We recommend to leave it at 0.0 and adjust your mic volume via the operating system.
Speaker output: Select your output device.
Intercom: Select your output device for ATC intercom calls
Push to transmit: set your push to talk keybind. Recommended for beginners are shift or control keybinds.
Equipment: Specify which radio type you wish to simulatoe for pilots hearing you.
Elevation: Simulate a higher antenna altitude.
Local test: Toggle on and press your push to talk to listen to your input device. A green bar should appear indicating the volume.
If you don't hear yourself and you don't see a green bar ➡️ Your input device is not working.
If you don't hear yourself but you see a green bar ➡️ Your output device is not working.
¶ Equipment Types
Each equipment has different filters so they sound different. You can try each one and choose the one you like the most, or browse through the list below and choose the real receiver used in the real world.
All receivers are used worldwide, below you can find the most popular uses.
GAREX
- GAREX is the receiver developed by the INDRA Company, most commonly used in Europe and some parts in Asia, South America and Africa.
- GAREX is commonly used in Ground and Area Control Centers, but this may change depending on country and airport.
- You can check out the Indra Navia Company Brochure for a list on installations.
- Source: Indra Navia Company Brochure 2017 pg. 10
General Dynamics
- General Dynamics is the receiver developed by NEXCOM, most commonly used in the United States.
JOTRON
- Jotron is the receiver developed by Jotron, the most popular receiver in the world.
- Jotron is commonly used in Tower and Approach Control, but this may change depending on the country and airport.
- Check out Jotron's website for a detailed list on airport installations.
PAE
- PAE is the receiver developed by Park Air, used worldwide in over 180 countries.
- PAE is commonly used in Tower and Approach control, but this may change depending on the country and airport.
¶ Aurora's Navigation Bar
This section is split into two seperate bars: Preferences and Menu.

- You may open/close these bars by using the right-click menu (bold when active):
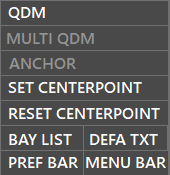
¶ Menu Bar
- ATIS
- COM
- ATC
- TRAFFIC
- AIRPORTS
- PROFILE
- PVD

¶ ATIS
What is ATIS?
Used to broadcast relevant airport or ATC facility information. Refer to the Training Documentation if you want to learn more about ATIS.
Can be retrieved via Altitude pilot client (text or audio), webeye, or via Aurora ATC list.
Only one ATIS is available for each aerodrome and the ATIS owner is determined by ATIS Priority. The sequence for an aerodrome is TWR > APP > GND > DEL. e.g if all four different ATC stations are online at an aerodrome, TWR will be responsible for the ATIS, if TWR closes, the ownership will transfer to APP.
If there is more than one TWR are connected, the first connected will have priority.
Approach positions have the option to leave/join the ATIS sequence.
Information: BLOCK ATIS for Trainers/examiners
ATIS Window

- ATIS Active: toggle ATIS on or off
- ATIS letter: starts at A and updates automatically each time the ATIS info is changed or weather report updates.
- STATIC: Set manual ATIS letter. Will not auto-update.
ATC Radio callisgn: Fetched from IVAO ATC database.
TMA ATIS: Terminal Maneuvering Area (TMA) can only be toggled by APP/DEP ATC. Used if multiple airports are serviced. Disables individual airport runway information. - ICAO airport code: Fetched from ATC callsign but can be changed. Used to get airport METAR.
- Arrival runways: Enter runways seperated by spaces.
- Departure runways: Enter runways seperated by spaces.
- Transition Level: Can be toggled on/off. Value must be indicated in flight levels.
- Transition Altitude: Can be toggled on/off. Value must be indicated in feet.
- Remarks: Located at the bottom right. ATC can enter custom remarks.
- Preview area: Located in the top right previews the entire ATIS information.
- Cancel: Close ATIS window without saving.
- Send: Save ATIS info.
Voice ATIS
- TWR/GND/DEL have the option to record airfield voice ATIS or use TTS. Read more here
¶ COM (Communications Box)
- Can be opened by toggling the COM button in the menu bar.
- It is recommended to keep it open at all times.
- Yellow flashing speech bubble indicates unread messages.
The COM Box may have up to eight tabs:
- The first tab is your MAIN frequency. You can change it by typing
//123.4anywhere in the com box. ATC frequencies are provided via sectorfiles upon position selection automatically. - The second and Third optional tab represent other frequencies that you can use to “monitor” text messages. For example, you can set UNICOM (122.800) or another ATC frequency. These additional frequencies can be set in PVD -> Settings -> COM window.
- D-LINK Telex/CPDLC communications.Only visible when online as ATC. Read more here.
- GUARD Guard frequency, 121.500. When a pilot changes his main frequency (COM1) to 121.500 and sends a text message, this message will be delivered to all near pilots, no matter the main frequency they have tuned, and to nearby online ATC. Avoid using this as much as possible. If you need to reach a pilot attempt it via private messages.
- ATC ATC chat only.
- BRDCST Broadcast messages. Supervisors/Admins can send messages to the whole network.
- MSG Server messages to you only.
- PRIVATE Private messages.
¶ ATC
When pressing the ATC button, it opens a new window, where we can see ATC or Observers online, near our station (based on Range and Center Point). Here, you have five (5) columns:
- Call, which is the Callsign
- Freq, which is the primary frequency of the station
- R, which means the ATC rating
- Name
- Options
- C : Controlling: if the ATC position is active, it will be white; therefore intercom is available. If observer, it will be grey.
- T : Transfer List: if marked (white), this station will be available in your transfer list and the position's fill color, if present in the sector file, will be shown.
- M : for creating a chatbox
- A : to request ATIS of the station, as a private message
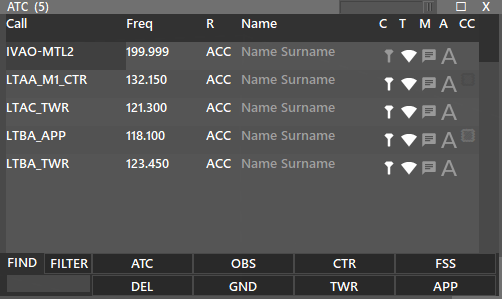
On the title of the window, you can see the total number of connections being displayed. In this case (5).
You can use the filtering options to customize your ATC window.
When using the FIND box:
- If FILTER is selected, It will filter the ATC positions and only display those matching with your search.
- If FILTER is not selected, It will search for the exact phrase and highlight ATC positions matching your search.
- For example, if you wish to only see airport EHAM positions. Then, you should have the FILTER on and write EHAM to the find box. (left picture)
- Or, if you wish to highlight EHAM positions. Then, you should have the FILTER off and write EHAM to the find box. (right picture)
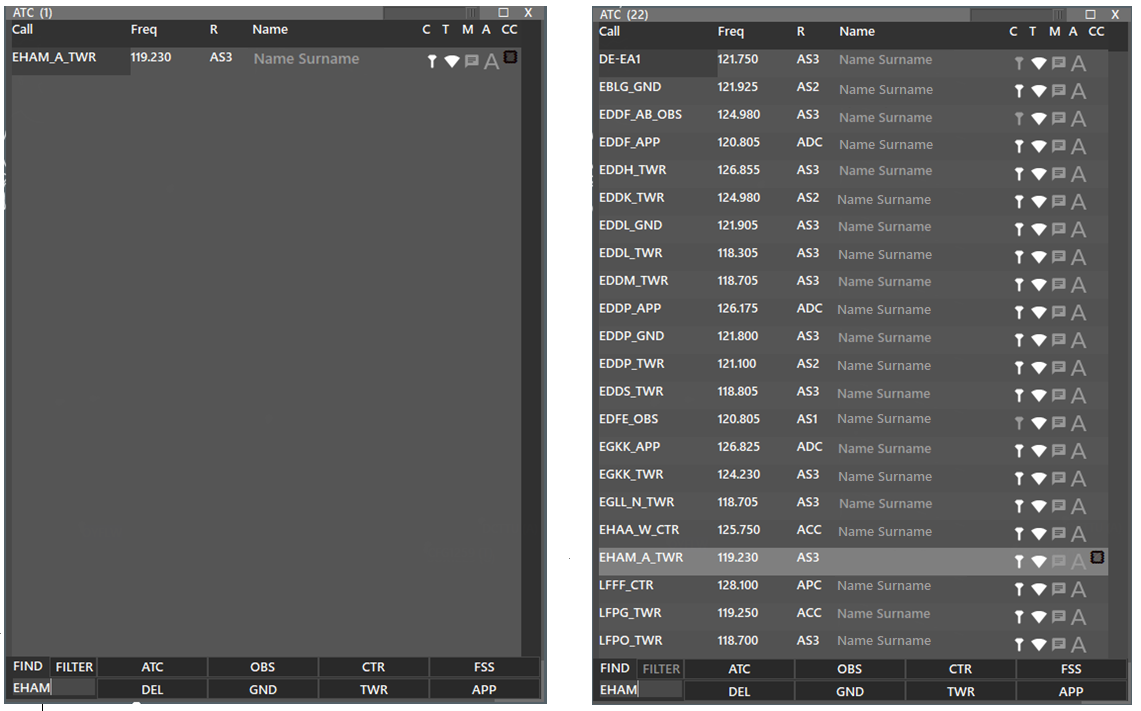
You can filter multiple stations by putting a space between.
- So writing AM BK EH will filter all positions for EHAM, EHBK and EHEH
- Multi Filter will not work when FILTER option is off. You can only search for exact phrases.
¶ TRAFFIC
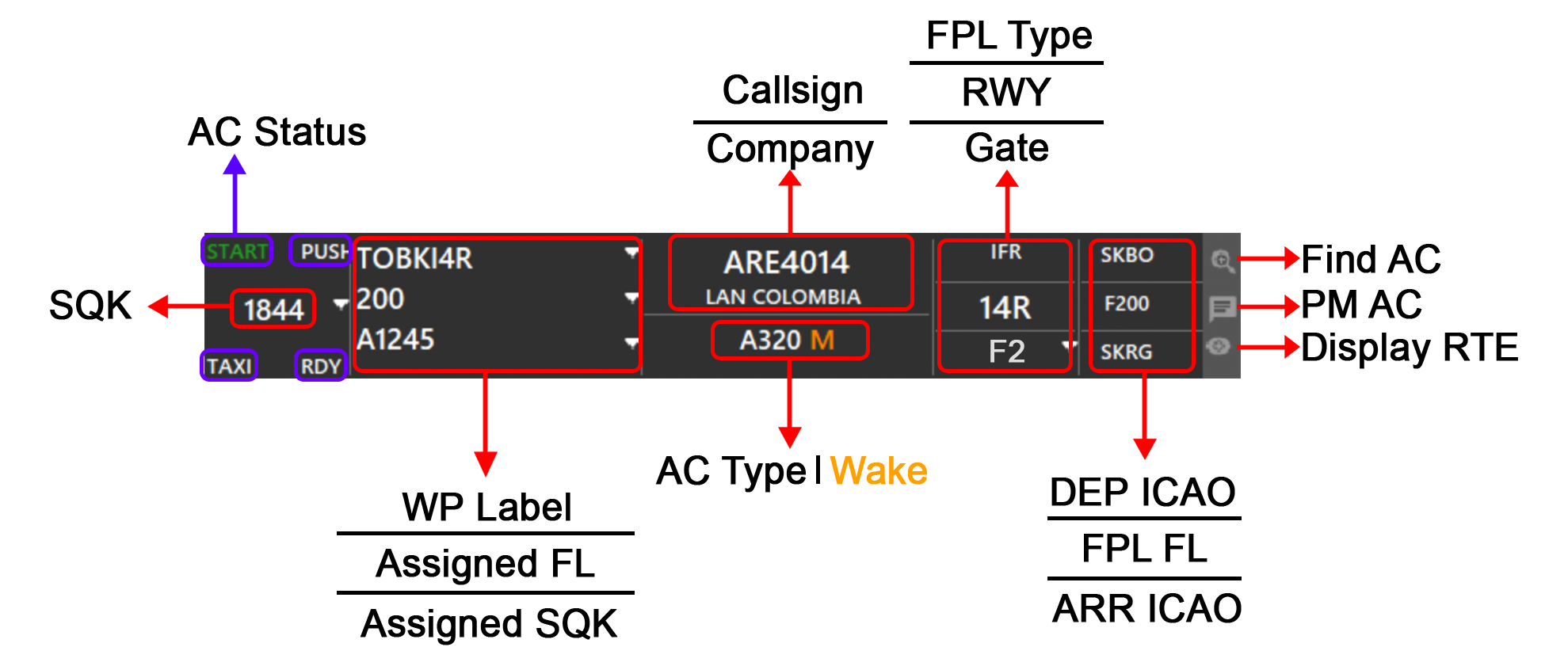
In this window, we have a general/basic flight strip display with information regarding the selected aircraft.
The first column shows EGPE as the destination, I as IFR flight, then 4301 for the transponder code selected by the pilot.
The second column shows F260 as the final Flight Level (FL), B738 M as aircraft type and category, N0454 as speed, and EGPK as the alternate airport.
The third column shows VAF771 as the aircraft callsign, and SKY FRIEND as a reminder for the radio callsign, EGFF as the departing airport, and 1455 as the departure time.
The fourth column shows the Flight Plan (FPL) route, and underneath is the other info or remarks section (Item 18 of FPL).
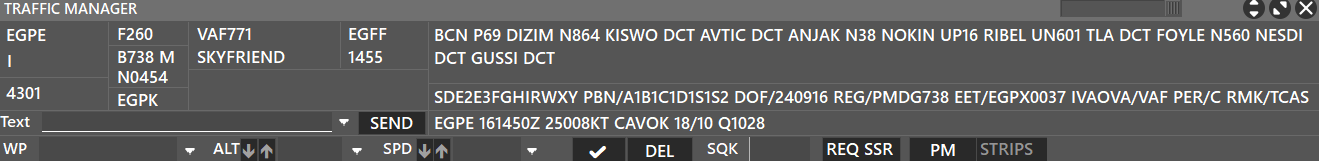
In addition to the above description, at the bottom there is a row where ATC can write information into the aircraft TAG:
- WP as waypoint or text, with a maximum of XX characters.
- ALT as Altitude
- SPD as Speed
Writing information in any of these boxes, and then pressing the “tick” button or just hitting “enter” on the keyboard, will send the information. When pressing the “DEL” button, all information will be removed from the aircraft tag.
There is a SQK box, meaning Squawk (Transponder), where ATC can assign a transponder code, so when selecting a new aircraft, and hitting the REQ SSR button, the client will automatically assign a new transponder code, based on the last one used.
The PM Button will open a private chat tab in the COM window, to talk with the pilot in private.
The STRIPS button expands the TRAFFIC window and will display aircraft based on the buttons selected below: DEP for Departures, ARR for Arrivals, OVER for Overfly, and UNCO for uncontrolled (not assumed). All this will be based on what is selected in the AIRPORTS window.
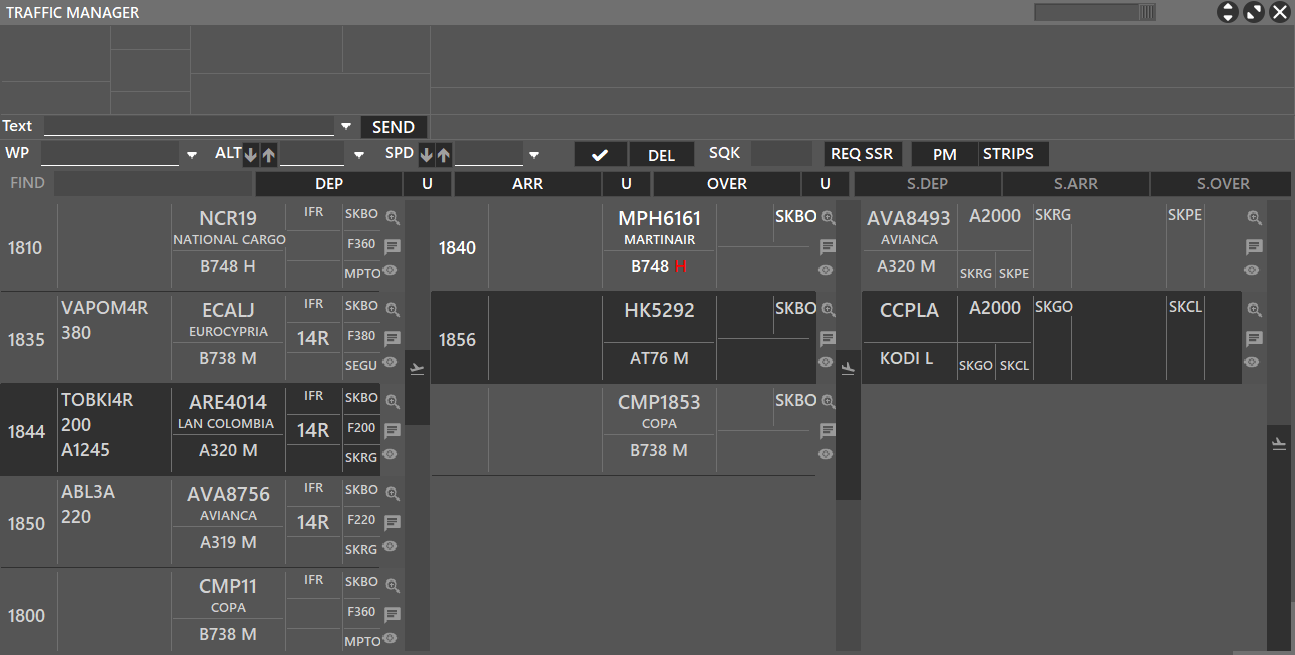
On the Traffic Manager window, you can see three columns. Each representing DEP (Departure), ARR (Arrival) or OVER (Overfly) based on your controlled airports from the Airports Menu.
- For each window, you can use the U button on the right of each section to choose to display or not display Uncontrolled Traffics. Meaning assumed traffics.
If U button is Bold, this means Uncontrolled Traffic will be displayed.
- You can also activate/deactivate each column by pressing the respective button from above or separate them from the TRAFFIC MANAGER window by pressing S.DEP, S.ARR or S.OVER, each meaning Separate Departure, Arrival or Overfly windows.
The overall fields of the traffic strips are the following:
¶ DEP COLUMN
On the title of the OUTBOUND window you can see the total number of aircrafts being displayed.
In this case (6).
¶ ARR COLUMN
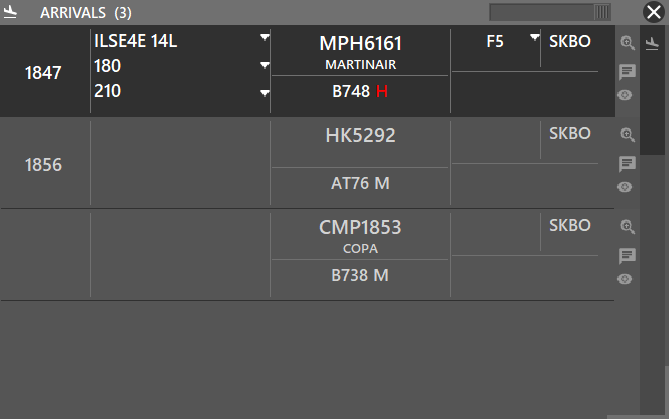
On the title of the INBOUND window you can see the total number of aircrafts being displayed.
In this case (3).
¶ OVER COLUMN

On the title of the OVERFLY window you can see the total number of aircrafts being displayed.
In this case (2).
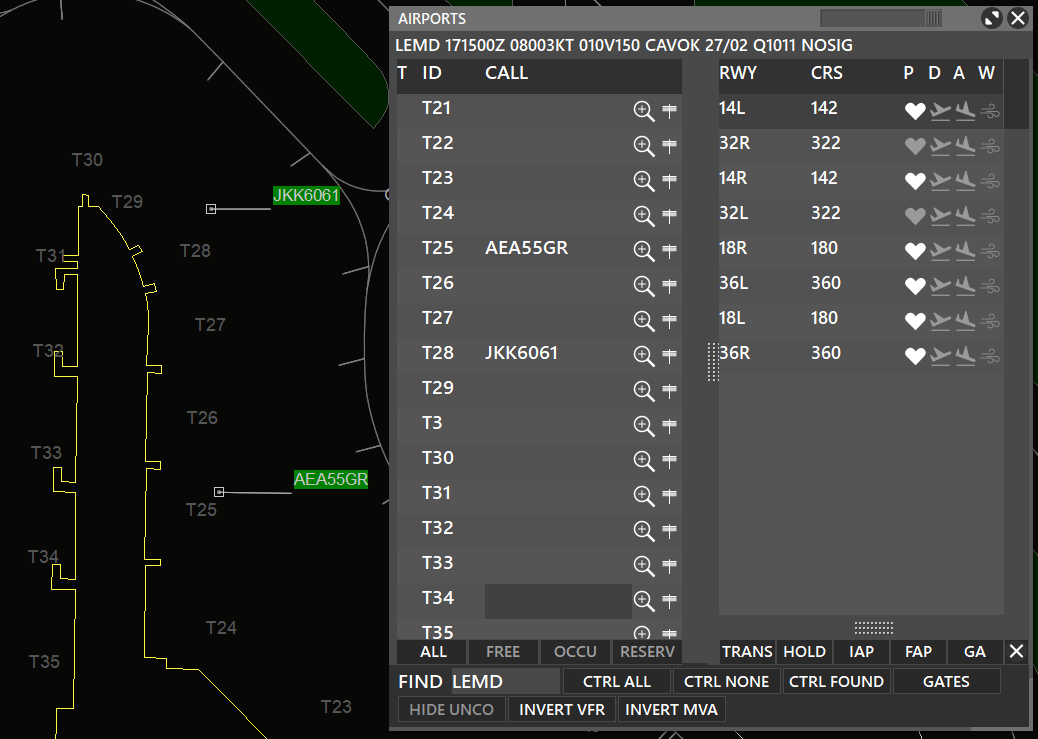
¶ AIRPORTS
The window is split into two main columns, where the one on the left displays airports, based on sector file information. When an airport is selected in the list underneath, full METAR for that station (if available) will be displayed. In addition, for those stations with a valid METAR, QNH and wind information will be shown.
When controlling an airport, or more, first you must select that airport “as controlled” by clicking the funnel in the C column. You can select the “crossed runways” icon (R), to let the system choose the active runway automatically. The magnifying glass icon (Z) will focus the main radar screen over that airport. The V column is for toggling on the VFR waypoints for that airport and the M column for toggling the MRVA.
By selecting a controlled airport, Aurora will autofill procedures that are typed on the WP section of the traffic window. This is useful to make succesful cordinations between postions.
The right column is split into two sections. The top section refers to runways of the selected airport (on the left). RWY indicates Runway number, CRS indicates Runway course (magnetic). P shows advise on which runway should be selected for the active runway (automatically selected by the system), D is where you can set the departure runways and A to select the arrival runways.
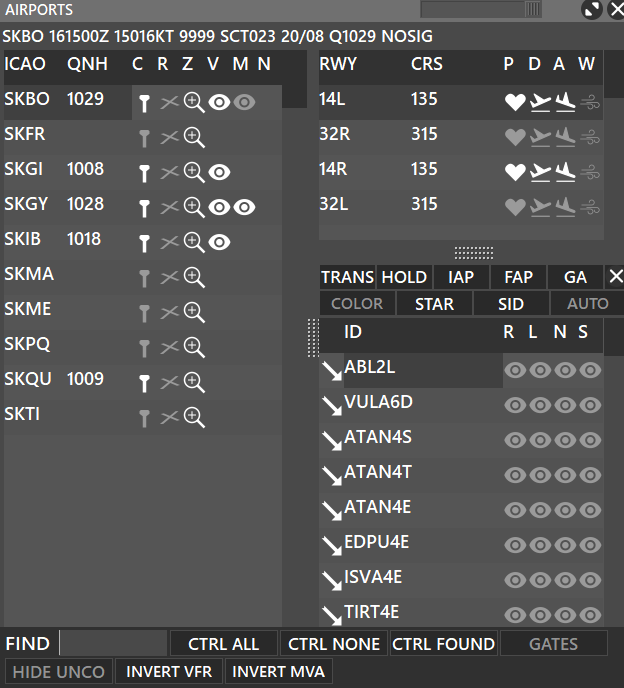
On the bottom of the screen, you can see 7 buttons and a FIND box:
- You can use the FIND box to search for airports.
- CTRL ALL will select all airports controlled, on the C column.
- CTRL NONE will deselect all controlled airports, on the C column.
- CTRL FOUND will select the airport in the FIND box and select it as controlled, on the C column.
- GATES will display the gates of the airport and aircraft on the gates, you can assign gates to traffics by clicking the sign icon.
- HIDE UNCO will hide uncontrolled airports, so you will see only controlled airports.
- INVERT VFR will hide the selected VFR procedures and show the ones that were previusly hidden.
- INVERT MVA will hide the selected MVA and show the ones that were previusly hidden.
When assigning GATES to aircraft, you can remove any gate assignment by deselecting any aircraft that was selected and press the sign icon.
- T column, left of the Gate ID, shows the Type of Gate. L for Light, M for Medium, H for Heavy or S for Super.
¶ Gates Window
Aurora's Gates window automatically detects when an aircraft is on an specific gate and is displayed on the Gates Window. Also, you can assign a gate for an arriving traffic and it would be also displayed on this window.
At the bottom of this window you will see 4 buttons to filter the gates depending on their availability:
- ALL: will show all the gates
- FREE: will show all free gates
- OCCU: will show occupied gates
- RESERV: will show reserved gates
¶ Procedures Window
Between the runways and arrival/departure procedures window, you will see 10 buttons:
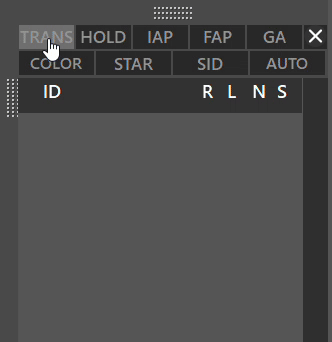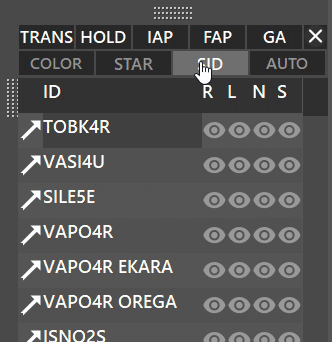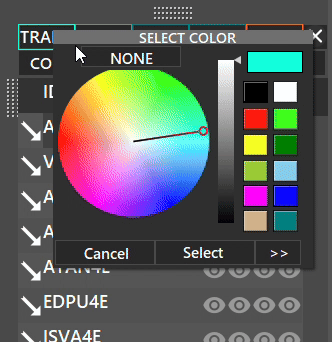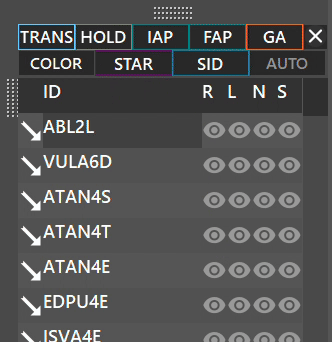
On the first row:
- TRANS : Displays TRANSITION procedures when active, for the selected runway.
- HOLD : Displays HOLDING procedures when active, for the selected runway.
- IAP : Displays INITIAL APPROACH procedures when active, for the selected runway.
- FAP : Displays FINAL APPROACH procedures when active, for the selected runway.
- GA : Displays GO AROUND procedures when active, for the selected runway.
- X: When pressed lets you separate the procedures tab into a separate window.
On the second row:
- COLOR: By holding SHIFT while clicking the COLOR button, it lets you display custom colors for procedures.
- SID: Displays SIDs procedures when active for the selected runway.
- STAR: Displays STARs procedures when active for the selected runway.
- AUTO: Activates automatic filtering for the active runways.
The COLOR function is used in some real ATC positions to differenciate between procedures of different airports.
¶ AUTO Button
AUTO button activates automatic filtering for the active runways:
- When AUTO filtering is enabled;
- Depending whether the runway is selected for Departure or Arrival, you will see:
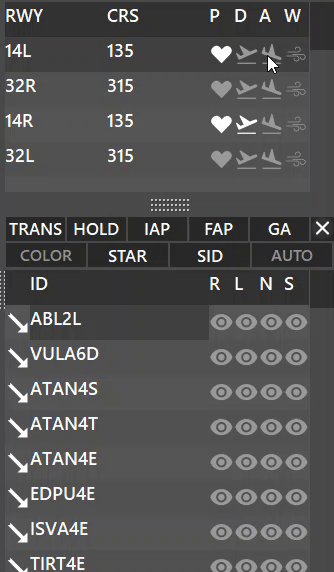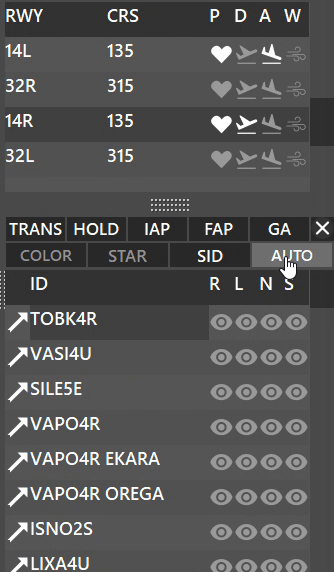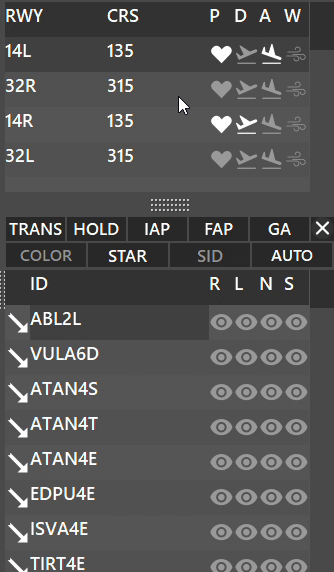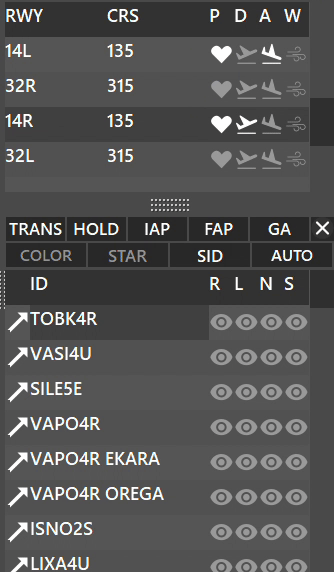
¶ PROFILE
Profiles are text files where different settings are saved, to make save setting everything again, the next time you log on. When pressing this menu option, a dropdown list with three (3) options is shown:
- Open, lets you select a profile.
- Save (Key Shortcut: F4), lets you save the current profile (the name of the profile will be the station callsign currently used).
- Supervisor (Key Shortcut: F3), opens the Supervisor module (Appendix to this document).
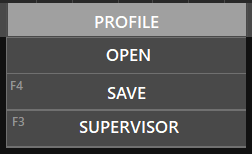
It’s important to note, that the system will not save the profile when exiting, so make sure to press F4 each time you make an important change (FIX selection, zoom, etc), so the profile will be saved.
¶ PVD
¶ SECTOR (F1)
Opens the Sector File window where you can download (right column), load (left column folder icon), delete (left column X icon) or enable/disable Auto Update of your desired Sector File.
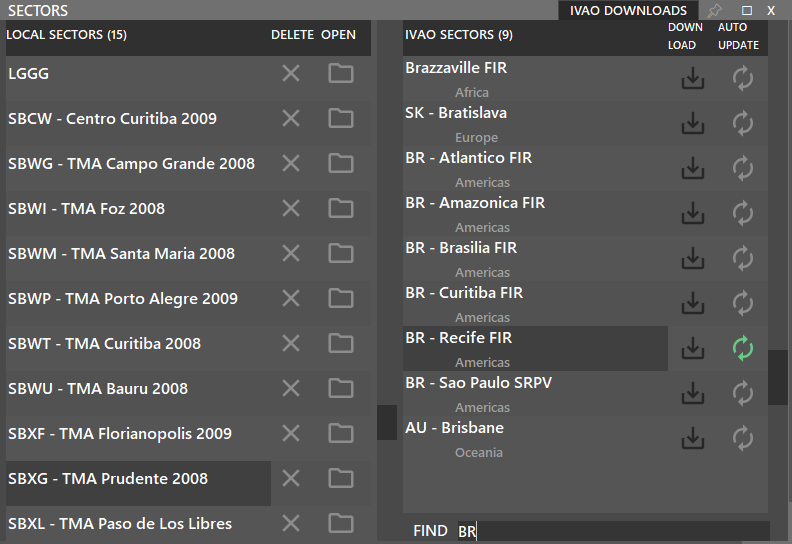
Sector screen will automatically close after opening sector files. If you wish to keep it open, use the pushpin on the top right.
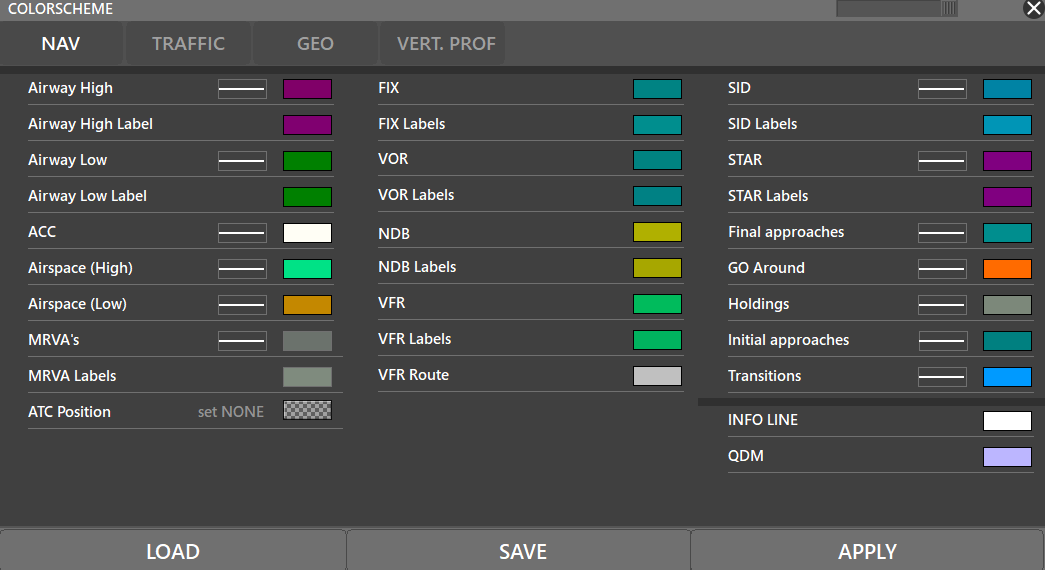
¶ COLORS (F5)
Opens the Color Scheme editor where you can define different colors, open and save profiles. Remember to press “APPLY” for changes to take effect.
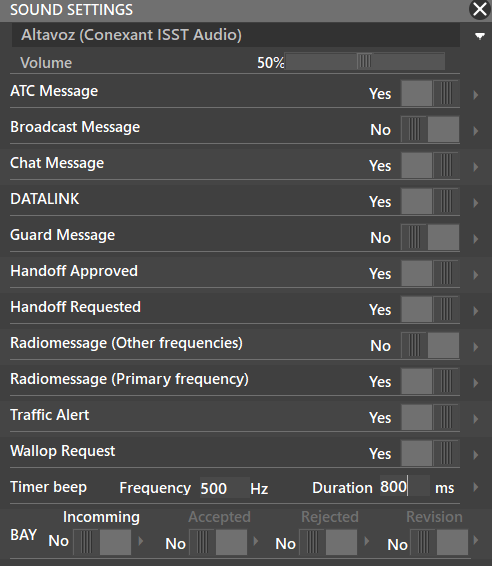
¶ SOUNDS (F6)
Opens the Sound settings where you can choose your Output Device, mute/unmute sounds or decrease/increase volume of notifications. In the case of the timer, you can change the tone (frequency in Hz) and its duration.
These sounds refer to the files in the Sounds folder, with specific filenames.
¶ SETTINGS (F7)
Here you can change the main settings, all of them are explained below. For a full explanation into these settings refer to our detailed documentation about Aurora's Settings.

¶ RADAR
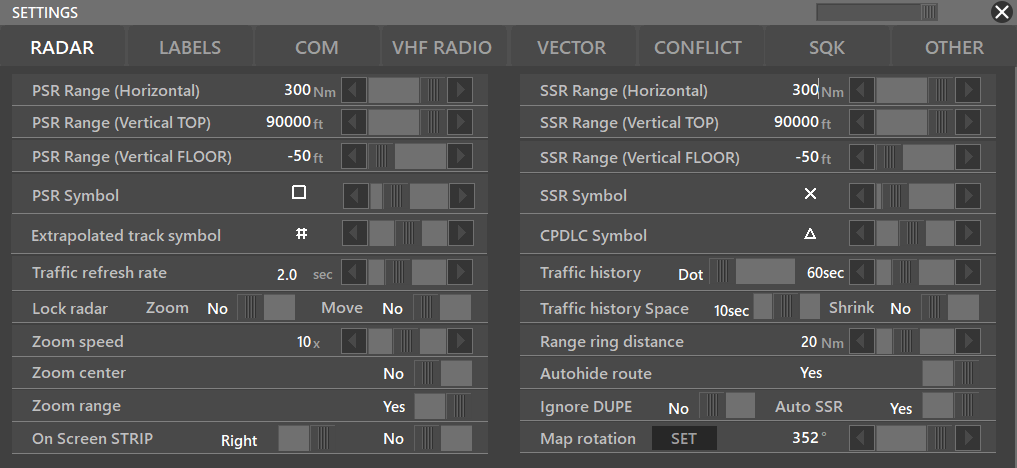
- PSR Range (Horizontal): Different intervals for each position: DEL = 0-10nm, GND = 0-10nm, TWR = 0-100nm, APP = 0-200nm, CTR = 0-1000nm, OBS = 0-300nm
- PSR Range (Vertical TOP): 500ft-60000ft
- PSR Range (Vertical FLOOR): -200ft-60000ft
- PSR Symbol: Symbol of Aircraft displayed when captured by the PSR
- Extrapolated track symbol: Symbol of Aircraft when multiple surveillance systems are in use
- Traffic Refresh Rate: Minimum can be set differently for each position: DEL = 1 second, GND = 1 second, TWR = 0.5 seconds, APP = 0.5 seconds, CTR = 1 second, OBS = 1 second
- Zoom Speed: 1x-20x
- Zoom Center: Yes/No
- Zoom Range: Yes/No
- On Screen STRIP: Left/RightNo/Yes
- SSR Range (Horizontal): Limited for each position: DEL = 0-10nm, GND = 0-10nm, TWR = 0-100nm, APP = 0-200nm, CTR = 0-1000nm, OBS = 0-300nm
- SSR Range (Vertical TOP): 500ft-60000ft
- SSR Range (Vertical FLOOR): -200ft-60000ft
- SSR Symbol: Symbol of Aircraft displayed when captured by the SSR
- CPDLC Symbol: Symbol of Aircraft displayed when CPDLC communication is established
- Traffic history dots: Lets you choose the symbol you want for the traffic history' path
- Traffic history space: 0 s 200 s
- Shrink: Yes/No (Older dots will get smaller each time)
- Range ring distance: 5 nm-50 nm
- Autohide route: Hides route of previously selected aircraft when selecting a new aircraft
- Ignore DUPE: Ignores “DUPE” situations
- AUTO SSR: When activated will self assign a SQK to 1 of the DUPE traffic
- Map Rotation: Suggested for Ground Radar, lets you adjust the sector file rotation. ==When the radar is rotated the QDM function works as well==.
First set the angle you want to rotate the screen, then click SET - Lock radar zoom/move: Locks the radar screen to a fixed position
Display Aircraft Icon on Ground Radar
On some real world ATC positions, ground aircraft are displayed as a plane icon, which might be useful because it also represents the traffic heading on ground. To do this, you have to change the PSR Symbol until you find the airplane icon.
¶ LABELS
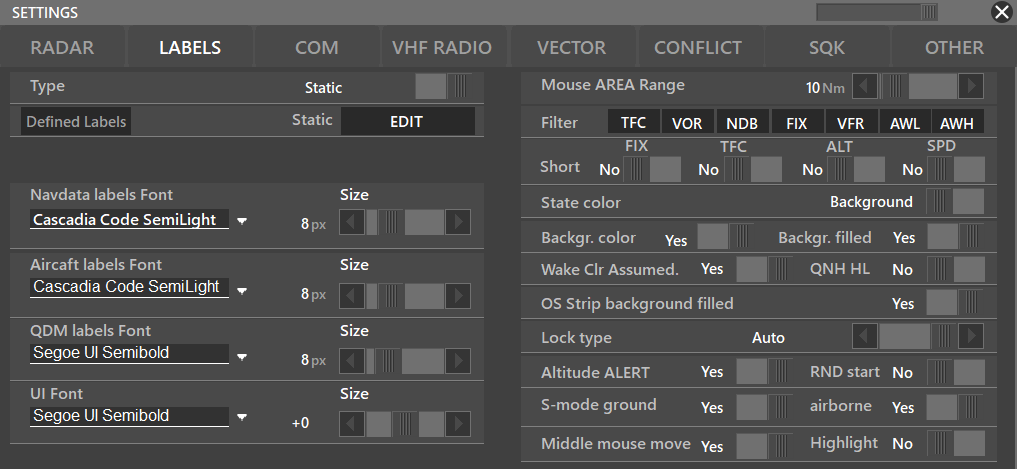
- Label Type: Dynamic/Static
- Static Labels Editor: Check the information posted on the Advanced Aurora's Functions Manual regarding the label editor
- Mouse AREA Range: Refers to MA option in Preferences Bar, NAV preferences.
- Mouse AREA filter: Filters which information is going to be displayed by the mouse range
- Short FIX: Reduces a normal 5 character fix into a 3 character one. (AMVES → AMV)
- Short TFC: Reduces the length of a traffic callsign
- State color: Depending on whether the traffic is an arrival, departure, or overfly, it will switch between displaying the color on the background or the label.
- Background color filled: Will fill the background of the callsign depending on the traffic status (ARR, DEP, OVERFLY)
- OS Strip background filled:
- Lock type: Position of Aircraft Label; Distance, Position, Auto.
- Altitude ALERT: Alerts if the traffic is not on the assigned altitude (the altitude assigned using the traffic window)
- S-mode equipment on-ground: Lets you activate SSR radar on ground. (Useful for GND positions where traffics don't have a SQK code at the beginning)
- S-mode equipment airborne: Forces the SSR activation when airborne
- QNH HL: Settings Autohighlight QNH (If activated on the label editor)
¶ COM
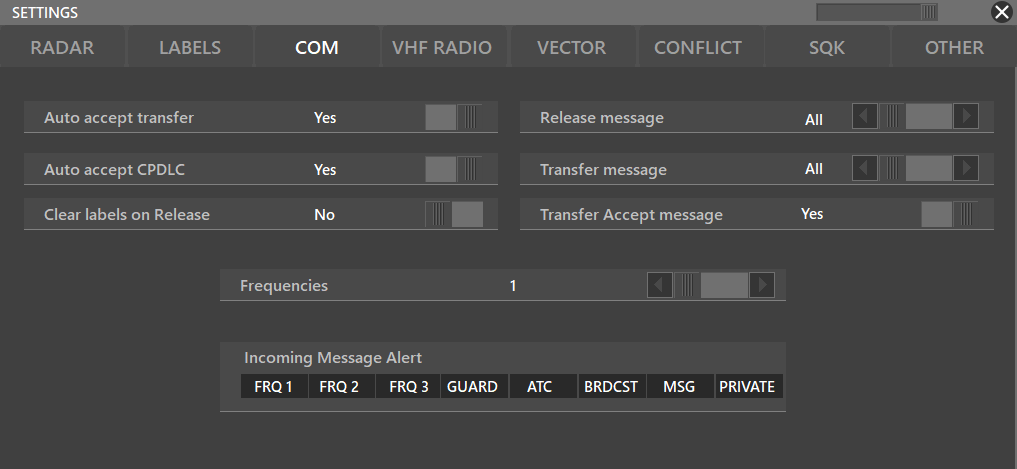
- Auto accept transfer: YES/NO; lets you choose when another connected ATC position transfers a traffic if you have to manually accept it, or automatically it's accepted when transfered
- Frequencies: 1 to 3 in the COM window
- Release message: All, None, No voice. This allows choose if a release message such as CALLSIGN, Switch to UNICOM 122.800, good day. is going to be send when a traffic is released
- Transfer message: All, None, No voice. This allows to choose if a message such as CALLSIGN, Switch to EDDF_GND 121.975 is going to be send when a traffic is transfered
- Transfer Accept message: Yes/No
- Clear labels on Release: Yes/No. When (Yes) is selected, all the previous labels like WP, ALT or SPD are going to be erased for the next ATC position or when released to UNICOM.
¶ VHF RADIO

- MIC input: Input Device for Voice Communications.
- Speaker Output: Output Device for Voice Communications.
- Elevation: Elevation of the Radio Station, sets automatically for airport positions.
- Push to Transmit: Set your preferred button for Push to Talk.
- Equipment: JOTRON, GAREX, General Dynamics, PAE. Check Equipments
- Local Test: Test your voice.
¶ VECTOR
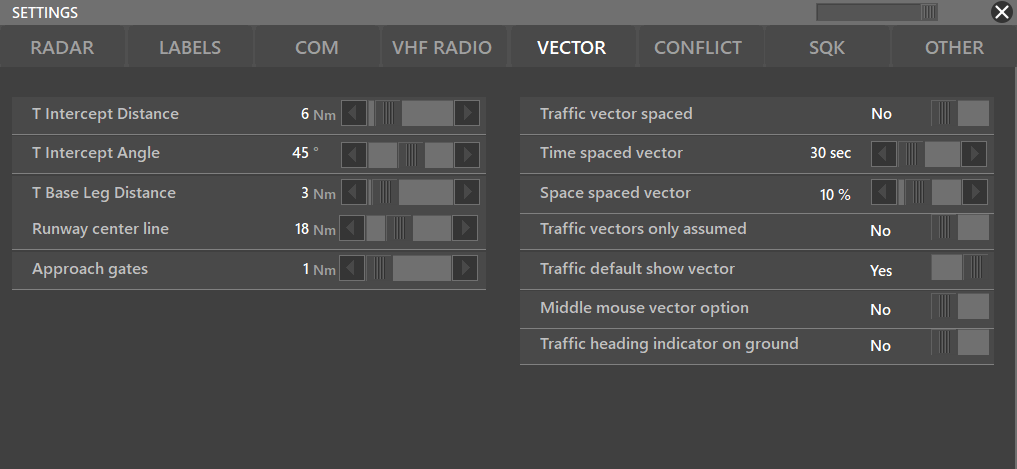
- T Intercept Distance: Changes the lenght of the Y legs
- T Intercept Angle: Changes the angle between the T legs
- T Base Leg Distance: Changes the lenght of the Base leg of the T
- Runway center line: Changes the lenght of the main runway centerline with small ticks every 1 NM
- Traffic vector speed:
- Time spaced vector:
- Space spaced vector:
- Traffic vectors only assumed:
¶ CONFLICT
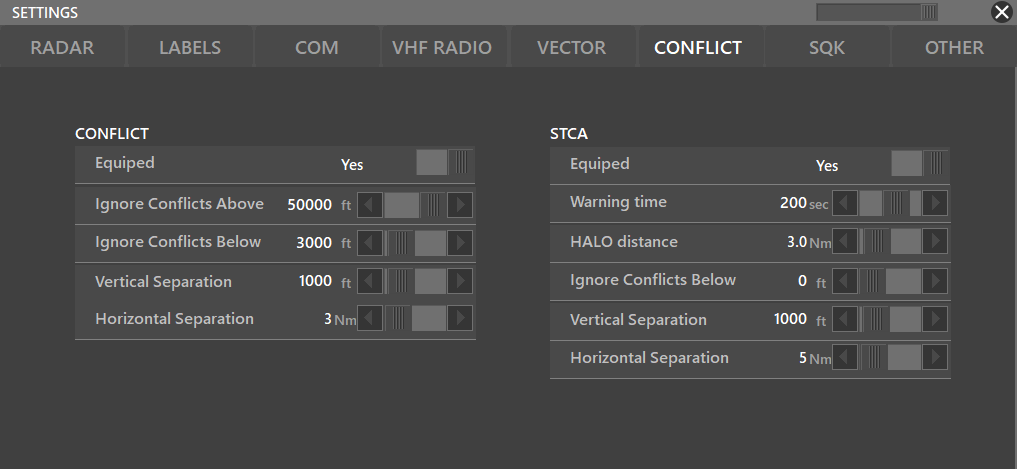
¶ CONFLICT
- Equipped: Yes/No
- Ignore Conflicts Above/Below: Lets you select where traffict conflicts are going to be ignored (Useful to ignore CA in VFR traffic patterns)
- Vertical Separation: Lets you choose what would be the minimum vertical separation before the CA triggers
- Horizontal Separation: Lets you choose what would be the minimum horizontal separation before the CA triggers
¶ STCA
Stands for Short Term Collision Allert and will predict traffic collisions beforehand.
- Equiped: Yes/No
- Warning Time: Depending on the traffics' course, altitude and speed; lets you how much time before the predicted collision the STCA will trigger.
- HALO distance: Lets you select how big the HALO will be (where the predicted collision might take place)
- Ignore Conflicts Below: Lets you select where traffict conflicts are going to be ignored
- Vertical Separation: Lets you choose what would be the minimum vertical separation before the STCA triggers
- Horizontal Separation: Lets you choose what would be the minimum horizontal separation before the STCA triggers
¶ SQK
This settings section lets the user select bewteen SERIES mode or CUSTOM mode, for more detailled information about CUSTOM mode, refer to Aurora's Advanced Functions Manual.
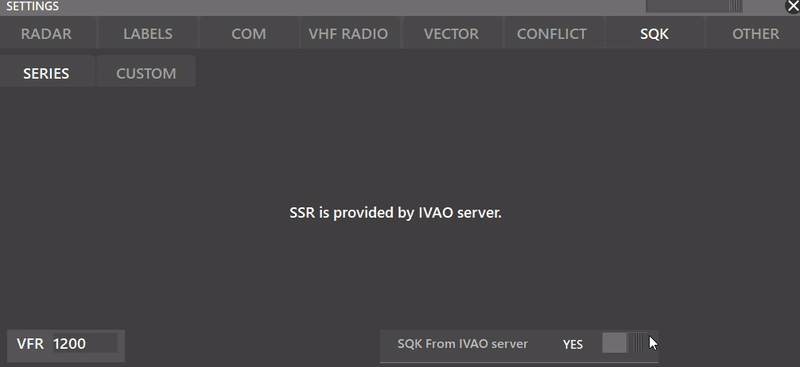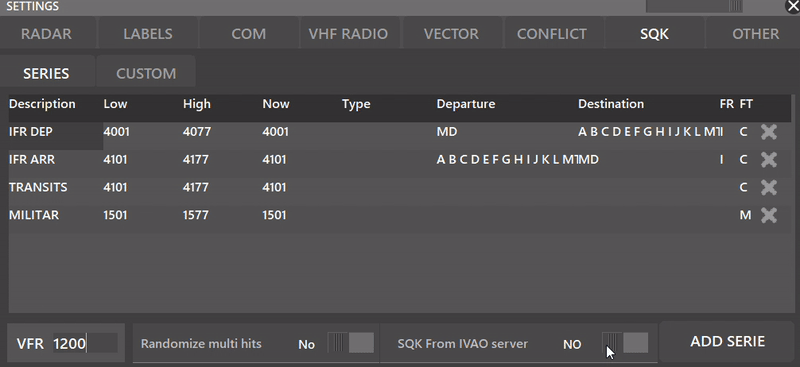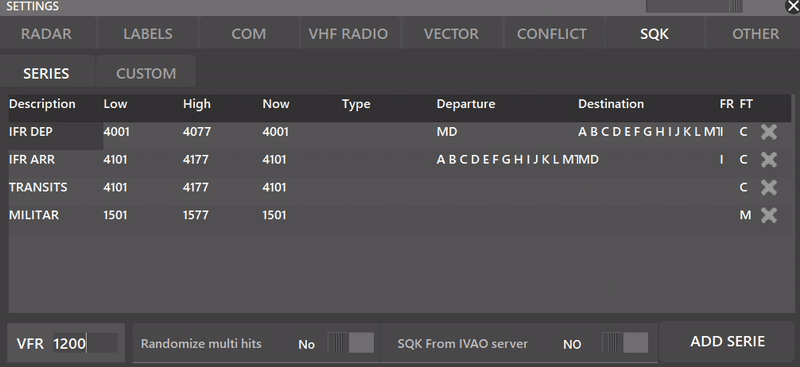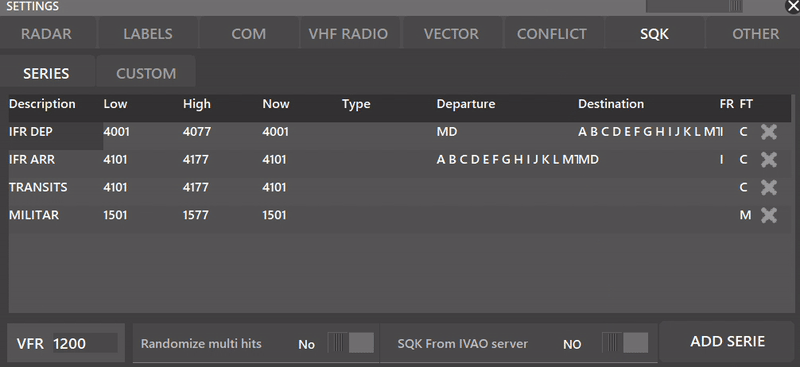
- VFR: Depending on the country, you can set a VFR SQK (Usually 1200 or 2000)
- SQK From IVAO Server:
Depending whether the SQK From IVAO server is selected or not, you can make your own SQK series with the built-in SERIES mode in Aurora. The following settings appear when NO is toggled.
- ADD SERIE: Lets you create a new SQK Series
- Randomize Multi Hits: When YES is selected, Aurora will randomize the SQK code inside the SERIES interval.
It is recommended for active division's users to select the option: SQK From IVAO server to YES.
¶ OTHER
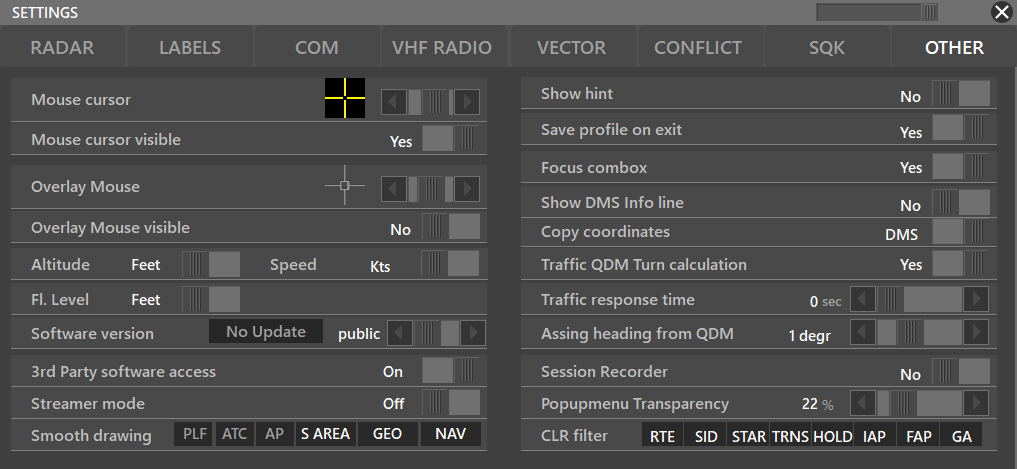
- Mouse cursor: Lets you change the color of your Aurora's mouse cursor
- Mouse cursor visible: Hides or shows your mouse cursor on Aurora's radar
- Overlay Mouse: Lets you change the Aurora's overlay mouse style
- Overlay Mouse Visible: Yes/No
- Speed Unit / Altitude Unit / FL Unit
- 3rd Party software access: If you are using a 3rd party add-on, your add-on might request this function to be enabled
- Software Version: (Staff Only) Lets you switch between the Public/Beta/Alpha versions
- Streamer mode: When enabled, it will hide personal names from the ATC and FlightPlan window
- Show Hint: Displays purpose of buttons when mouse over
- Save profile on exit: Yes/No
- Focus combox: When enabled, it will always focus on the combox. Meaning, when you type something, even on the radar screen, it will show on the combox.
- Traffic QDM Turn calculation: When enabled if you QDM a traffic, Aurora will also display the predicted turn path.
- Traffic response time
- Assing Heading from QDM: Lets you round the QDM's heading; therefore, when clicked, it will set the QDM's heading into the WP box label. Check our Aurora's Advanced Functions Manual
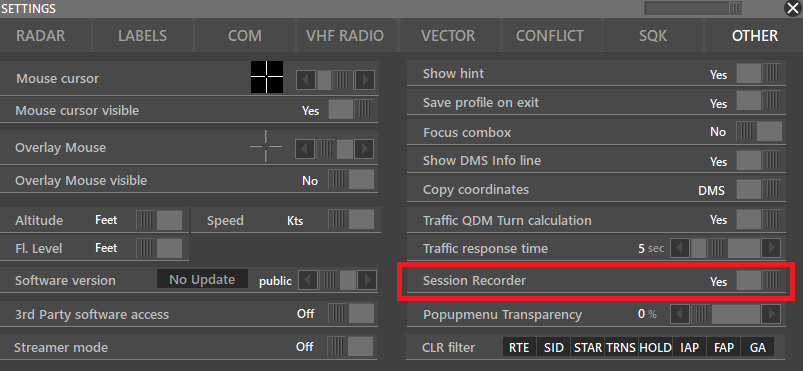
- Session recorder: Yes/No
- Popupmenu Transparency
- Copy coordinates: Decimal/DMS (Degrees, minutes, seconds) To use this feature, you can press CTRL + C and it will copy your mouse's coordinates.
- Smooth drawing: PLF/ATC/AP/S AREA/GEO/NAV; Depending on how fast your computer is you can use smooth drawing. When this is enabled it will draw smooth and you can use alphablend value.
- Assign HEADING from QDM: OFF state for Heading assign via QDM
Streamer Mode
Keep in mind that if you are streaming or recording, you have to comply with IVAO's rules, specifically 2.1.12. See here for more information.
¶ SYMBOLS (Coming Soon...)
On development...
¶ Preferences Bar
This bar has four (4) main sections where you may also extend these sections by selecting these different buttons.
¶ INSET (CTRL + 1-8)
This button, when enabled (BOLD), lets you open up to 8 new radar windows, so for example when controlling a large area, with multiple airports, you can open an INSET and zoom to each airport. You can use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + 1 to 8.
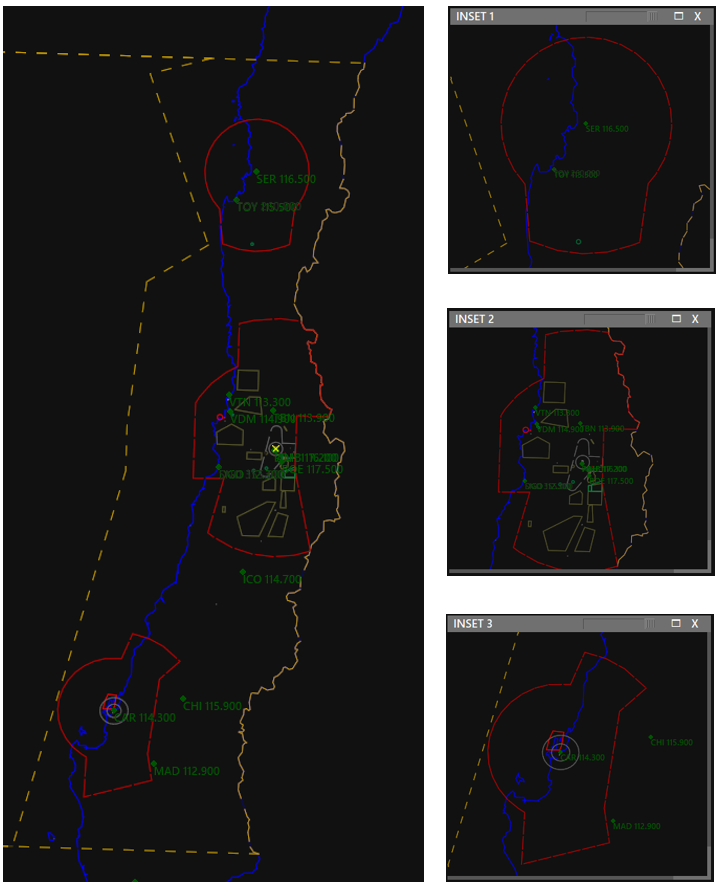
¶ PREF BAR IN INSET

The PREF bar in an INSET has 3 sub-tabs.
- GEO:
Lets you activate/deactivate different GEO settings
- NAV:
Lets you activate/deactivate different NAV settings
- OTHER:
Lets you activate/deactivate other settings such as:
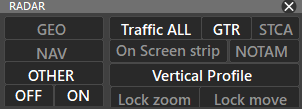
- Pressing TFC will filter aircrafts that are shown in INSET to: ALL/AIR/GROUND/OFF
- Inside an INSET window, you can select Vertical Profile from the PREF BAR to use that window as vertical profile
Also remember you can drag insets into other monitors
You can also lock your INSET window by selecting Lock Zoom or Lock Move
¶ Vertical Profile
Vertical Profile will display aircraft on different levels and show their path according to their assigned Flight Levels on the flight strip.
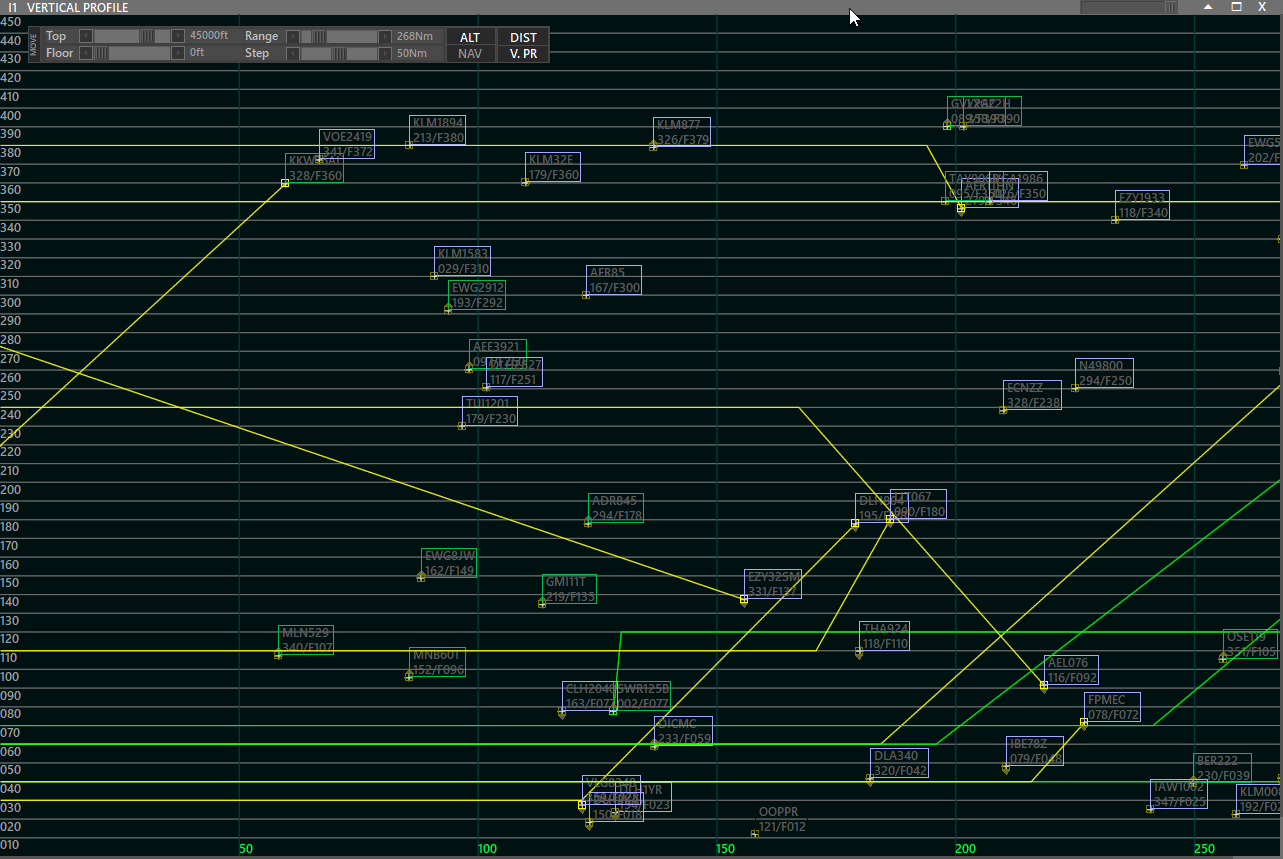
- On this screen, you can filter traffic that uses fixes/navaids and airways by pressing the NAV button.
- It is also possible to filter the traffic depending on Range and Altitude.
- Step is the distance between perpendicular lines.
¶ TRAFFIC (CTRL + T)
This button, when enabled (BOLD), lets you work with labels of aircraft, HALO radius, Range Rings distance and aircraft speed vectors.
¶ Label Position
- L+ = Moves the aircraft label away from the plane.
- L- = Moves the aircraft label towards the plane.
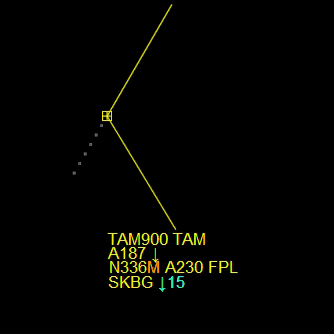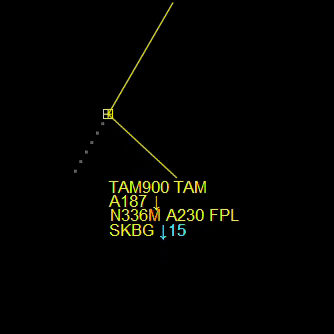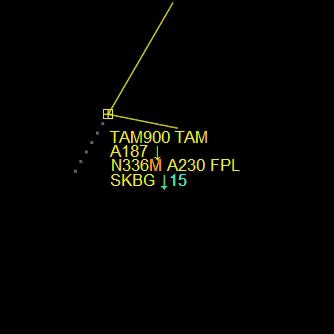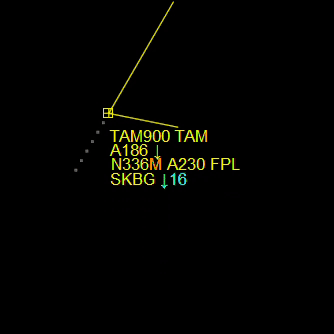
Also, you can move the aircraft labels using the “Mouse Wheel button” or holding SHIFT.
¶ HALO
- H+ = Increase HALO
- H- = Decrease HALO
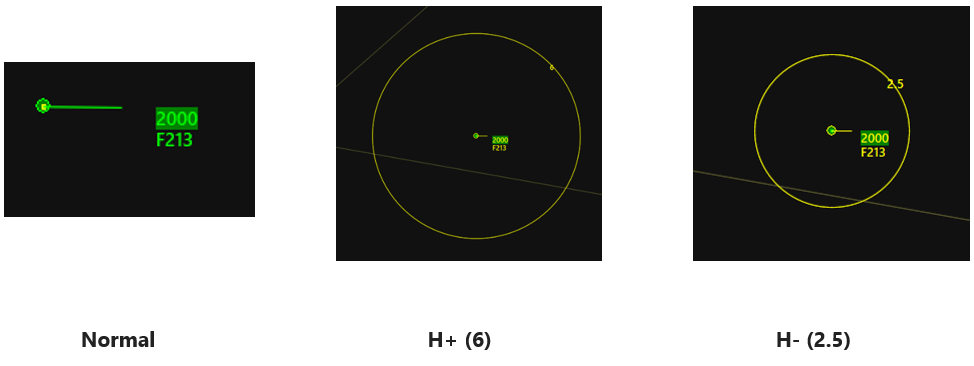
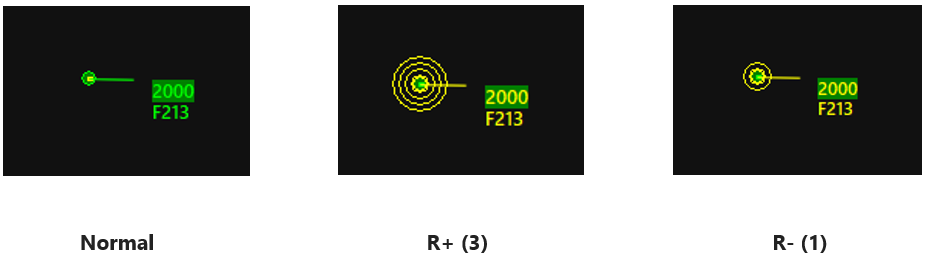
¶ Rings
- R+ = Add Ring
- R- = Remove Ring
¶ Speed Vectors
- 0 = Set Speedvector off.
- 1 = Set Speedvector to 1 minute.
- 2 = Set Speedvector to 2 minutes.
- 4 = Set Speedvector to 4 minutes.
- 8 = Set Speedvector to 8 minutes.
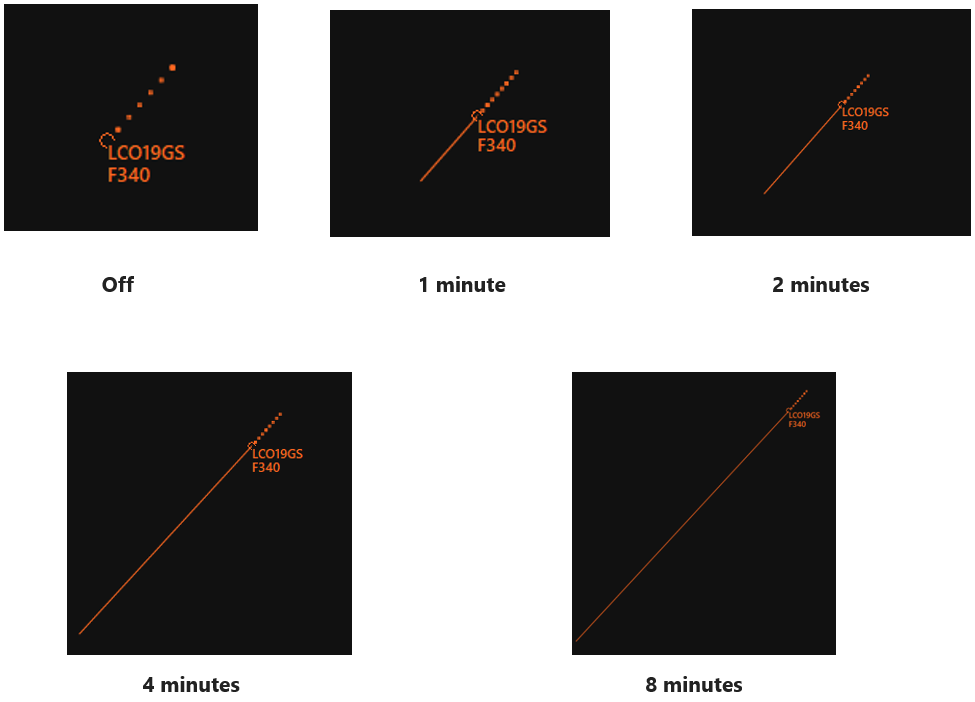
You can use the Spaced Traffic Vector function to have spaces, indicating 30 seconds, 1 minute or 2 minutes on the speedvector of Traffic.
This can be activated from PVD>SETTINGS>VECTOR>Traffic vector spaced, time spaced vector and space spaced vector.

¶ GTR - Ground Traffic
GTR button shows or hides ground traffic. When GTR is disabled, if you press SHIFT + GTR, It will display ONLY the assumed ground traffic.
¶ FLTR - Traffic Filter
This function allows to filter traffic separatelly on the PSR or SSR depending if the traffic is an inbound or an outbound.
To configure this filter you have to press SHIFT when clicking the FLTR button; the following window will appear:
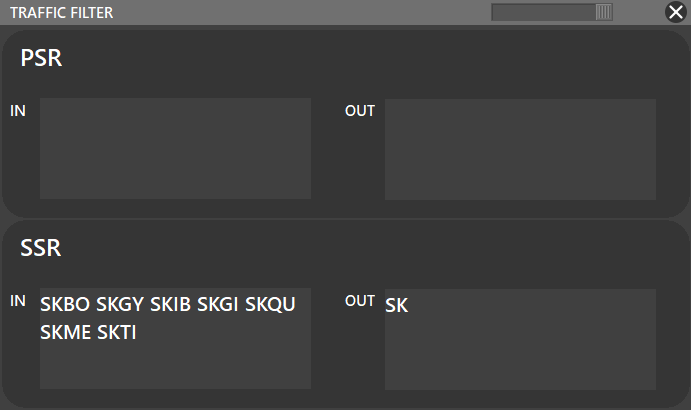
As you can see there is not any filter for the PSR, only for the SSR. In this case scenario, the SSR radar will only display traffics INBOUND: SKBO, SKGY, SKIB, SKGI, SKME, SKTI; and all the traffics OUTBOUND ==SK== airports. Chek this Wikipedia Article about ICAO country codes.
¶ LIST - Traffic Lists
List function allows the user to display custom lists as shown:
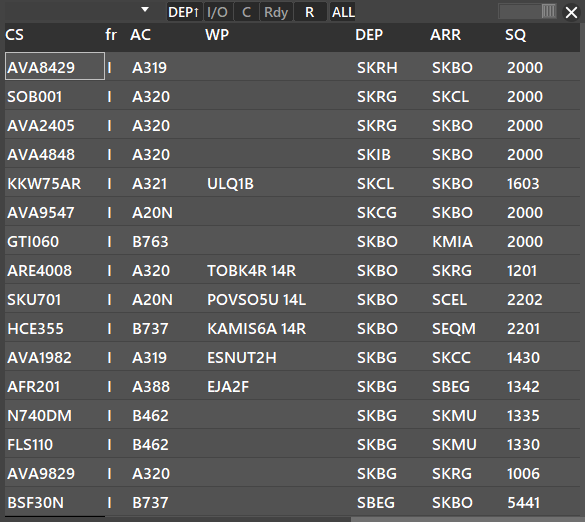
By pressing SHIFT + Click the LIST button you can acces the Traffic List Structure Manager Window where you can create custom lists.
For more information about lists, how to create them, and the Traffic List Structure Manager Window refer to Aurora Advanced Functions Manual.
¶ eSSR - SQK Traffic Filter
This button allows you to hide a specific label if a traffic match rule defined in SQK custom is made. To use the eSSR function, you first need to create a CUSTOM SQK series in the PVD SQK CUSTOM. To learn all about CUSTOM SQK series refer to our Aurora Advanced Functions Manual.
¶ GEO (CTRL + G)
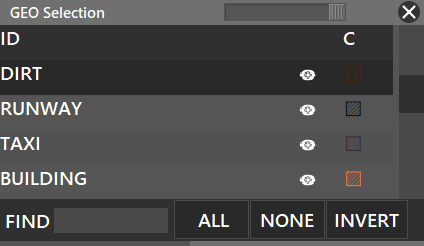
This button, when enabled (BOLD), lets you display or hide some information of the Sector File (radar screen content) like Airports, Runways, Buildings, etc.

By pressing SHIFT + GEO, if defined in your sectorfile by your division's ATC Ops Dept., you can see a list of where you can enable/disable or change the color of certain things.
¶ CST (CTRL + SHIFT + C)
- Shows or Hides Coast Lines
¶ ELEV
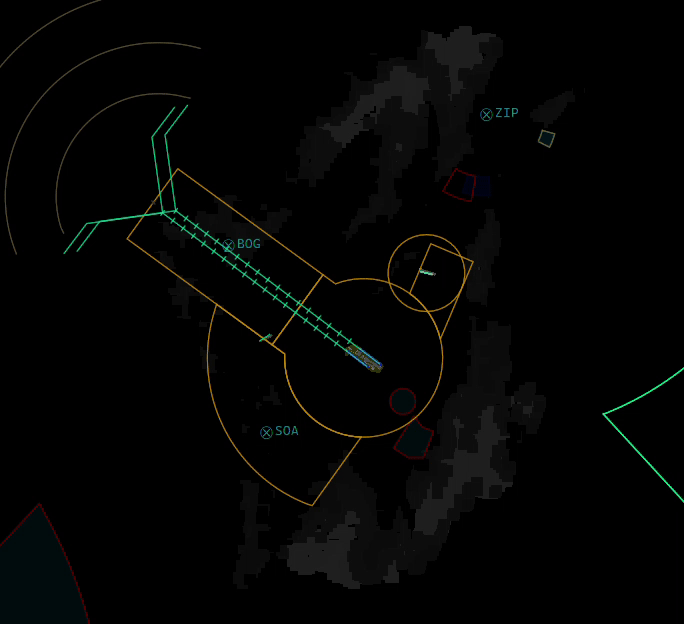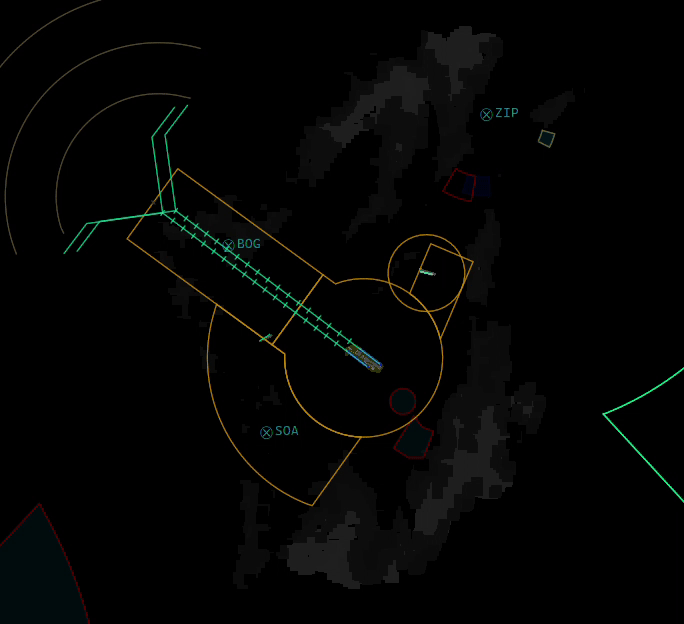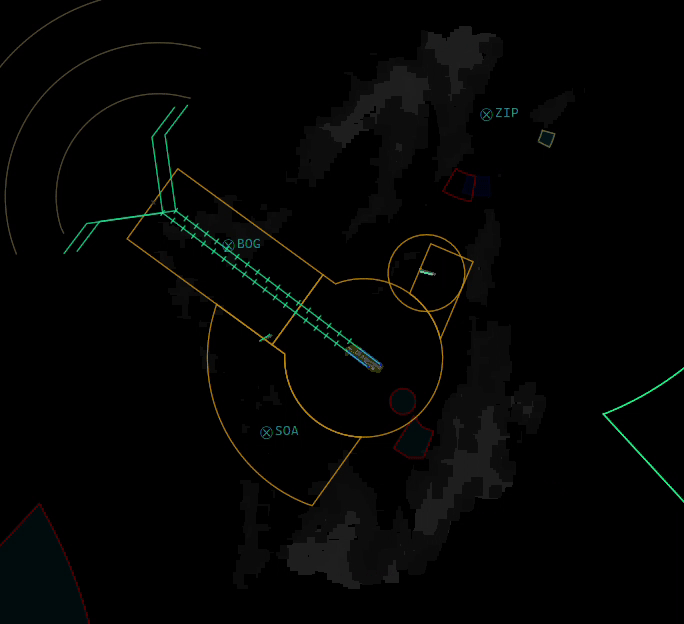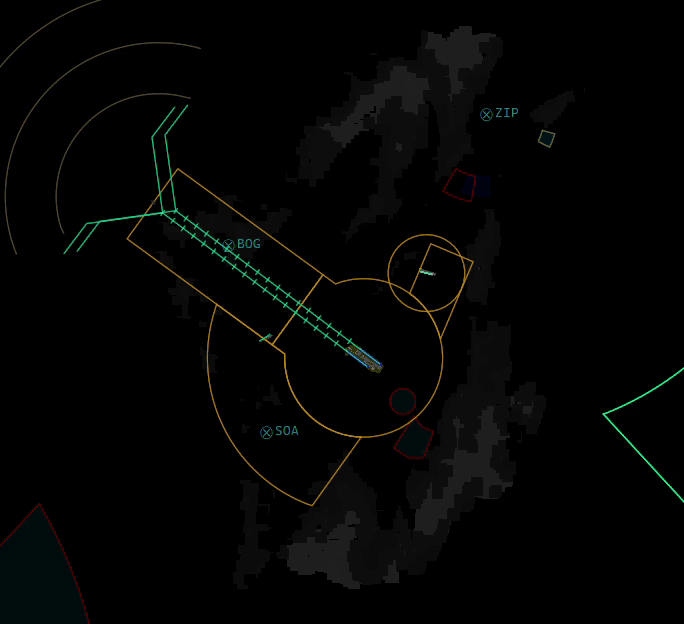
- Shows or Hides Elevation profiles (only if they are defined by your division's sectorfile)
- You can also SHIFT + Click the ELEV button to select or deselect individual elevation profiles
¶ AP (CTRL + A)

- Shows or Hides Airport names
¶ RWY
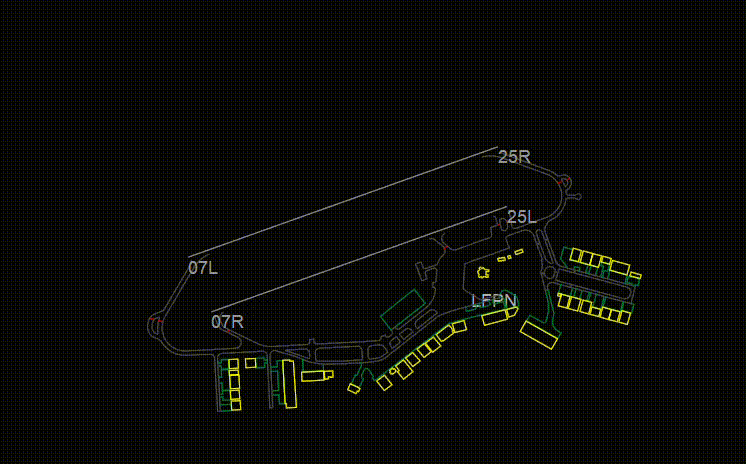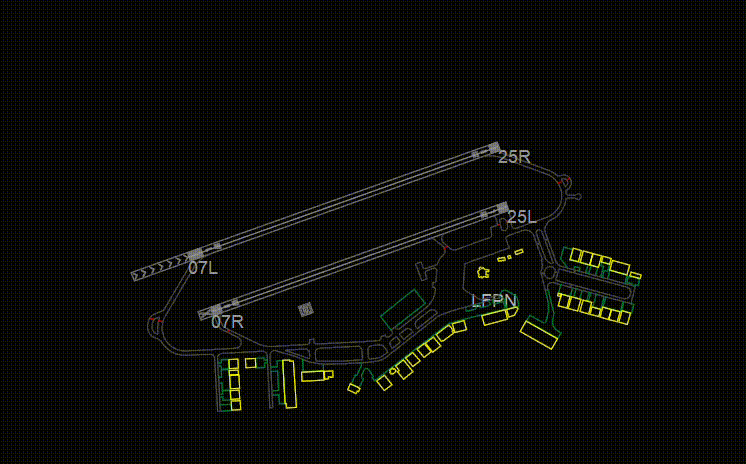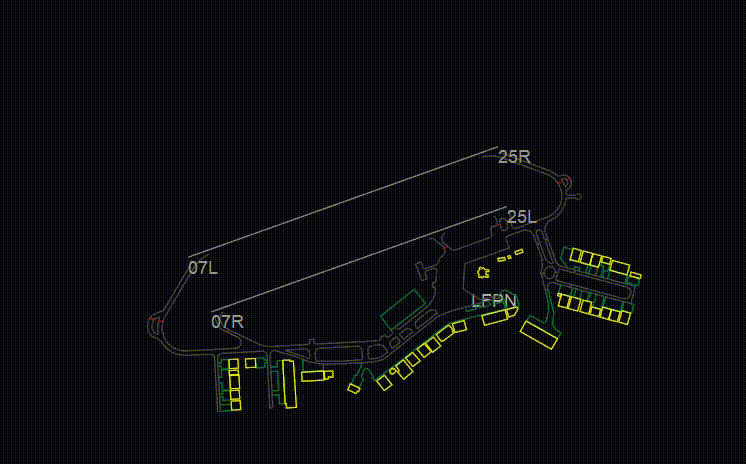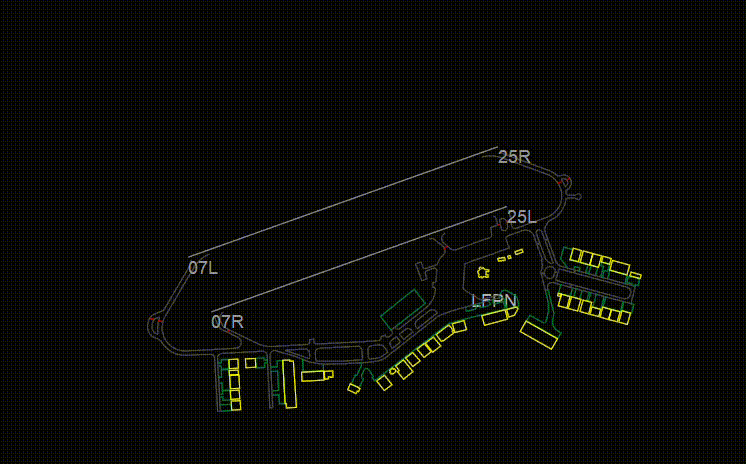
- Shows or Hides Runways
¶ RWC
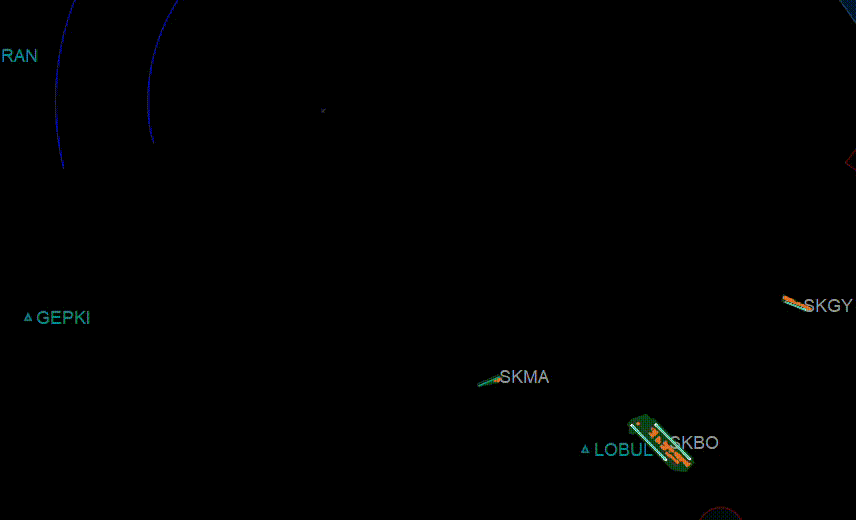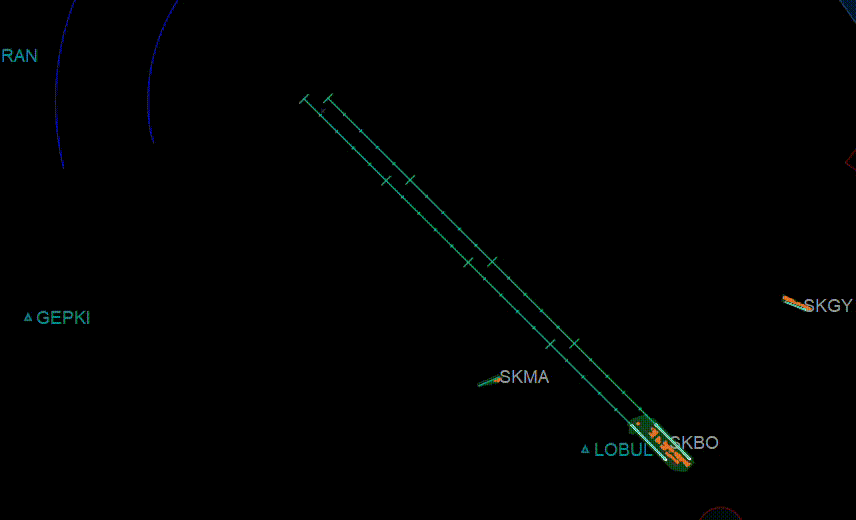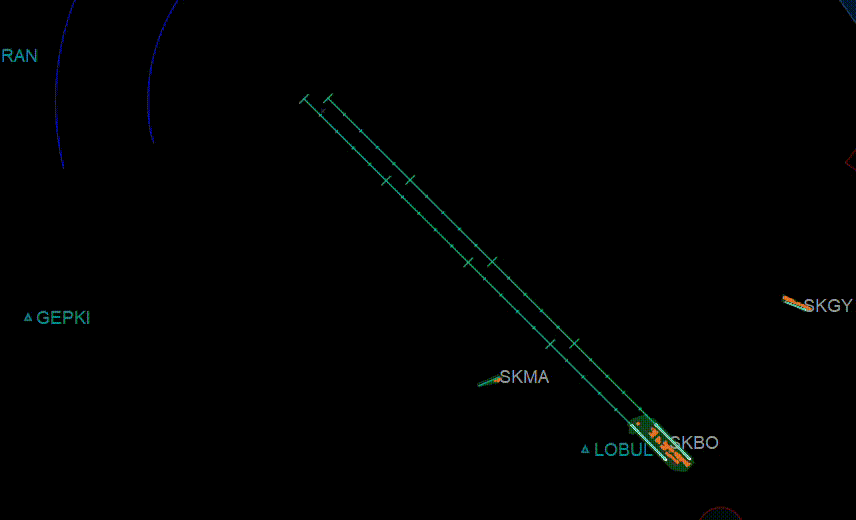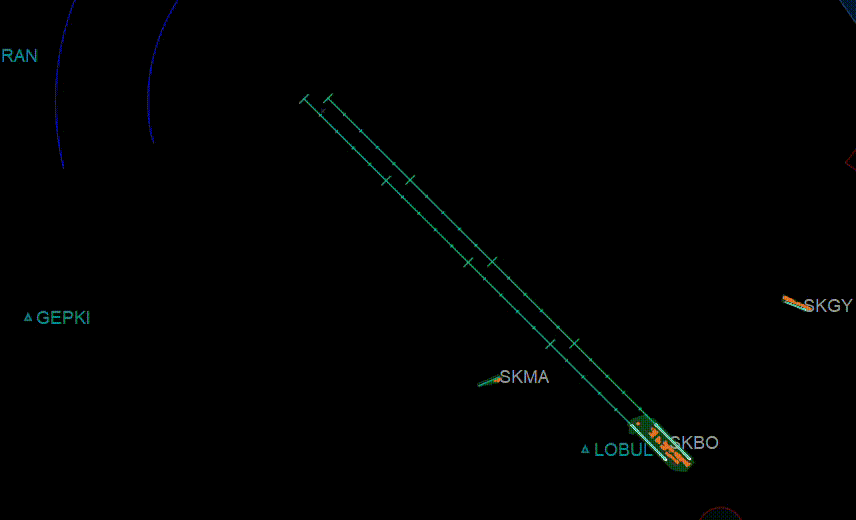
- Show or Hide Runway Approach Centerlines. (These lines only appear when you select active runways)
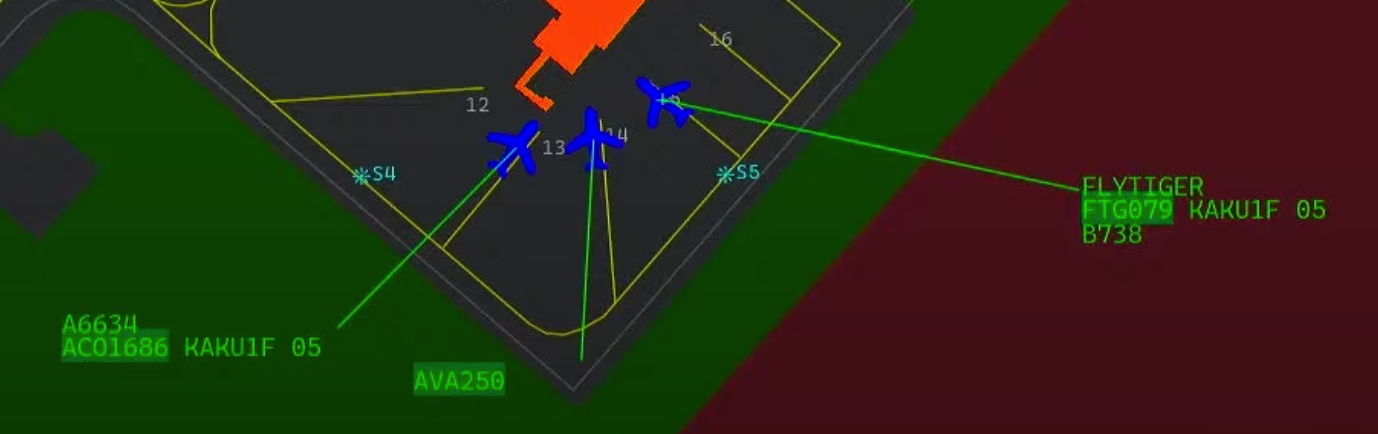
- When RWC is underlined, this means the actual centerline of the runway is turned ON. In the image it can be seen when the runway centerline is displayed on the actual runway.
¶ GTS (CTRL + SHIFT + D)
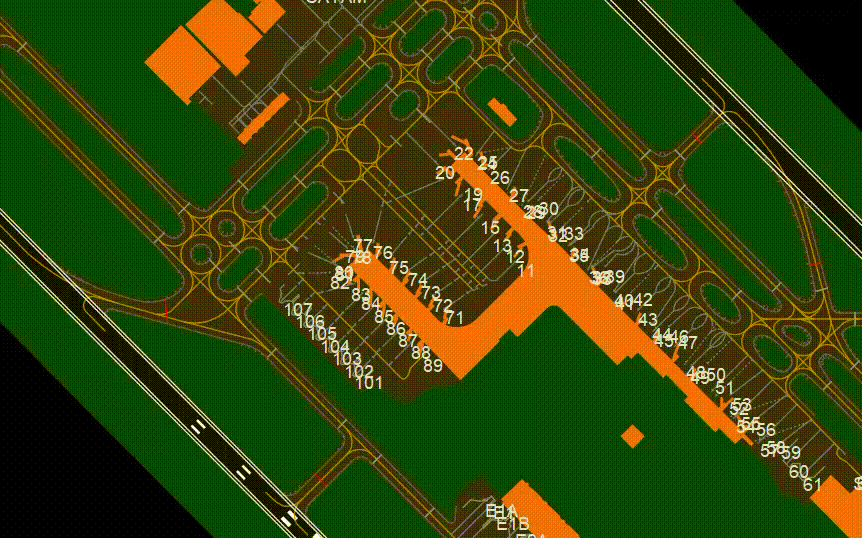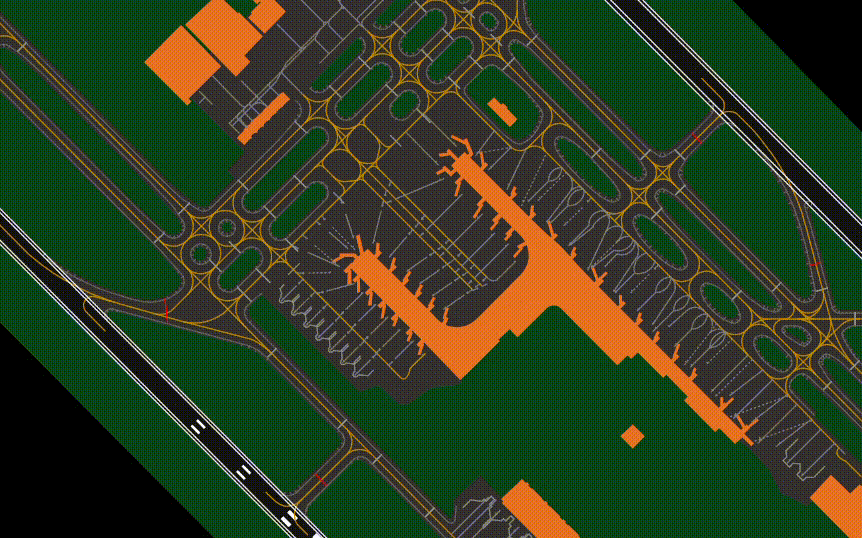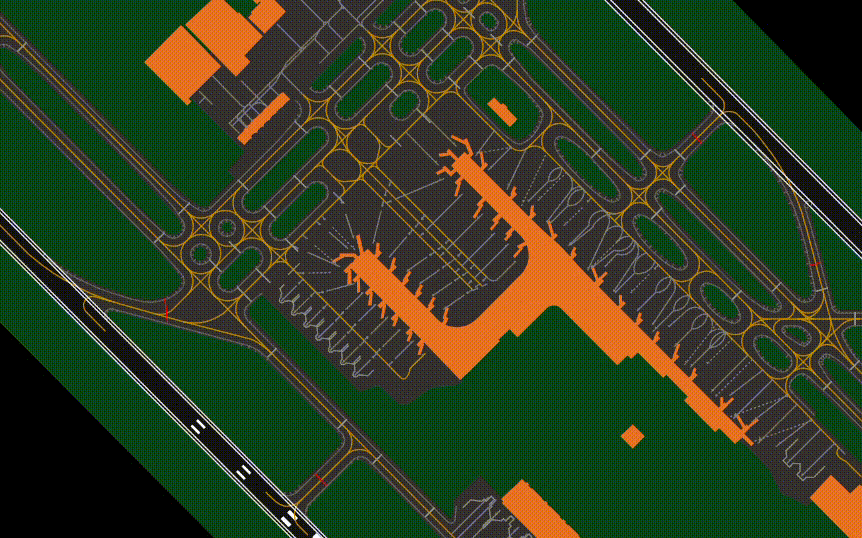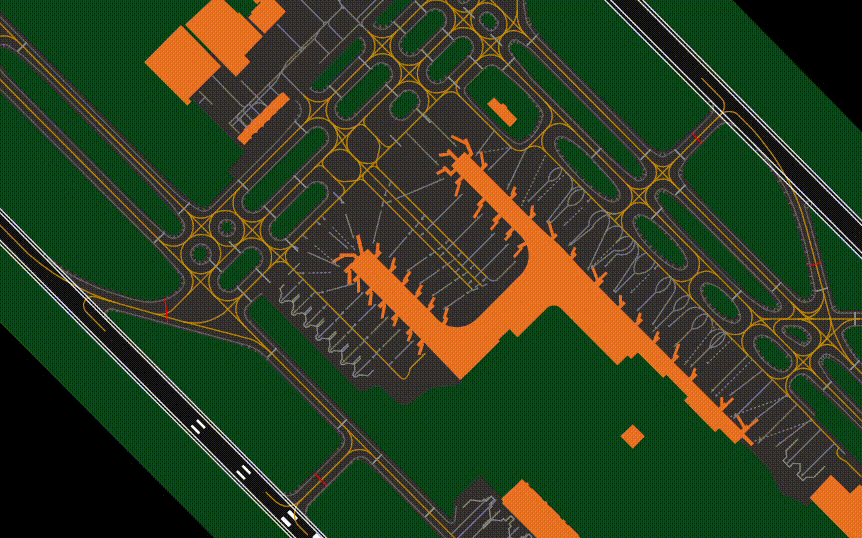
- Shows or Hides Gates
¶ TXL

- Shows or Hides Taxiway labels
¶ TXI
- Shows or Hides Taxiways
¶ TXC
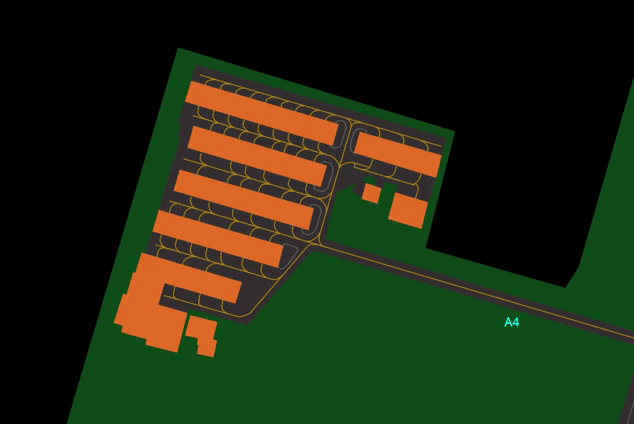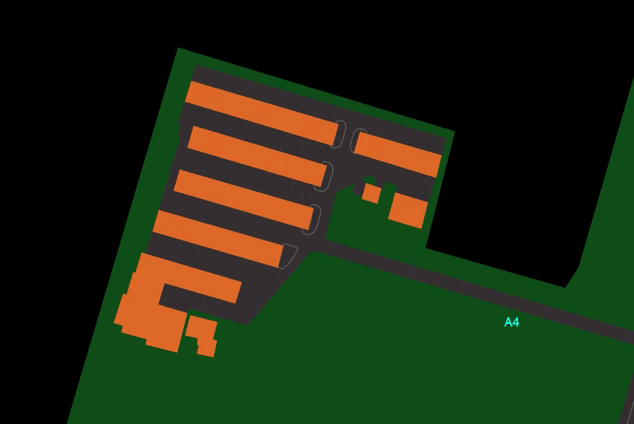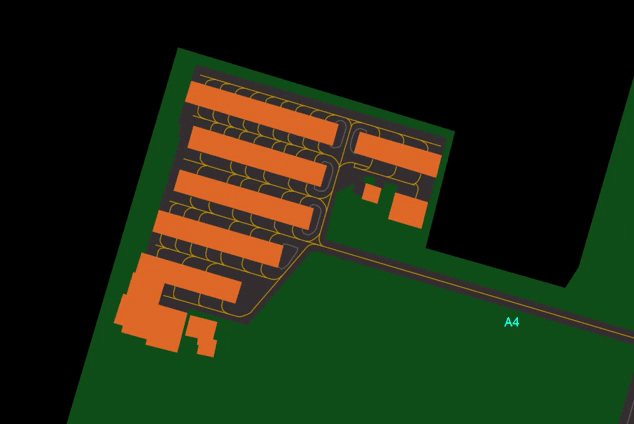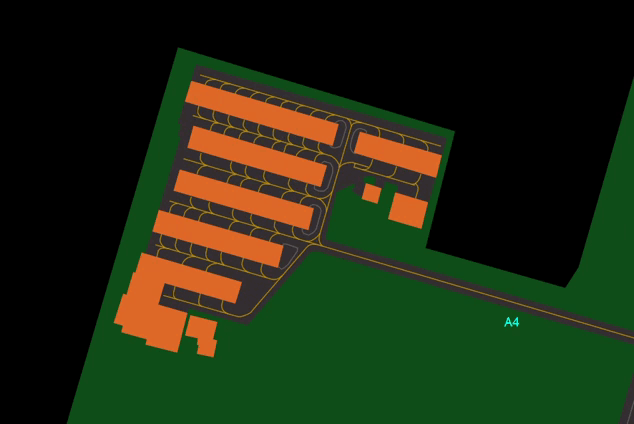
- Shows or Hides Taxiway Centerlines
¶ STP
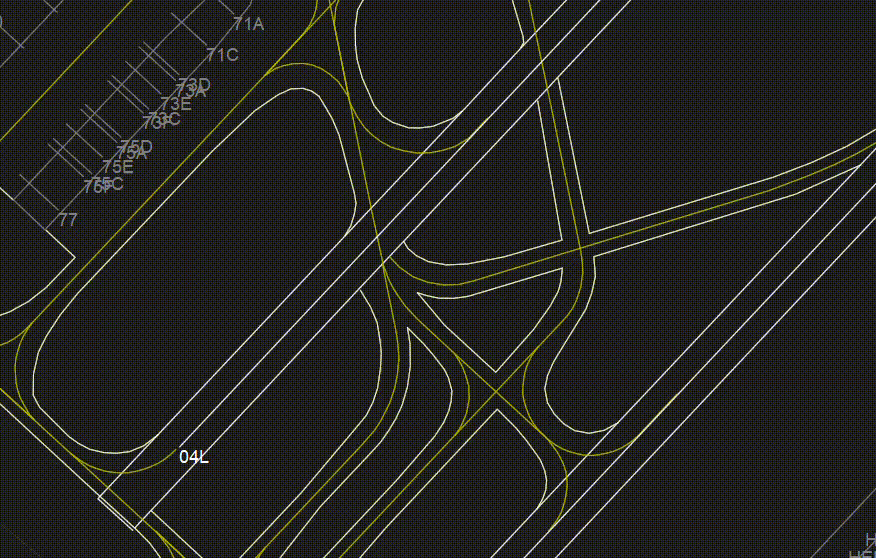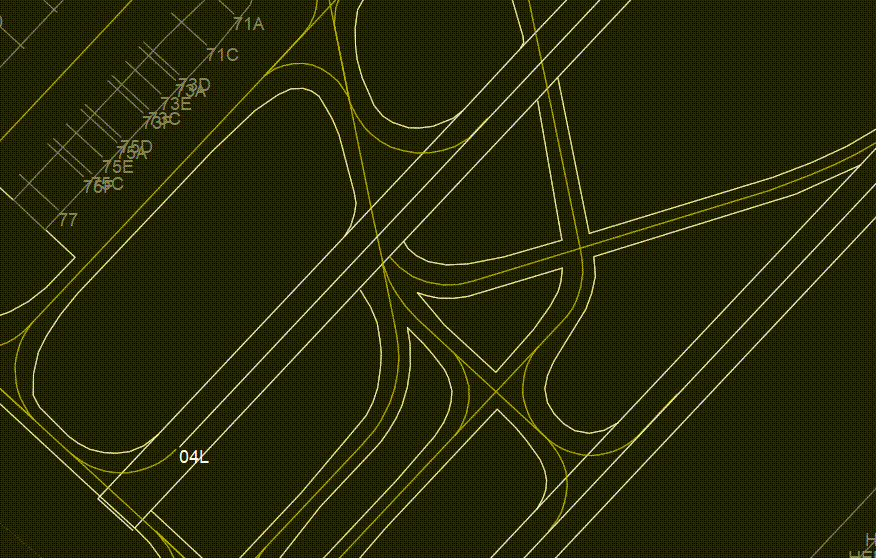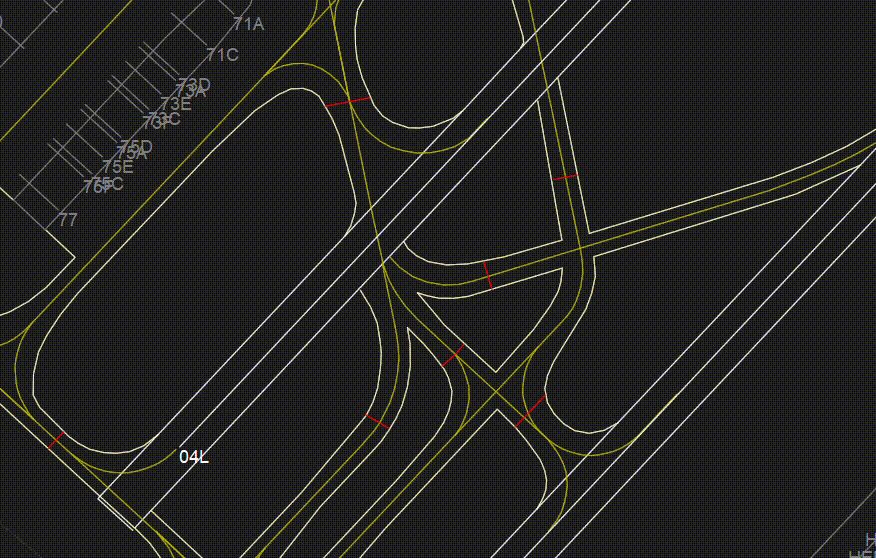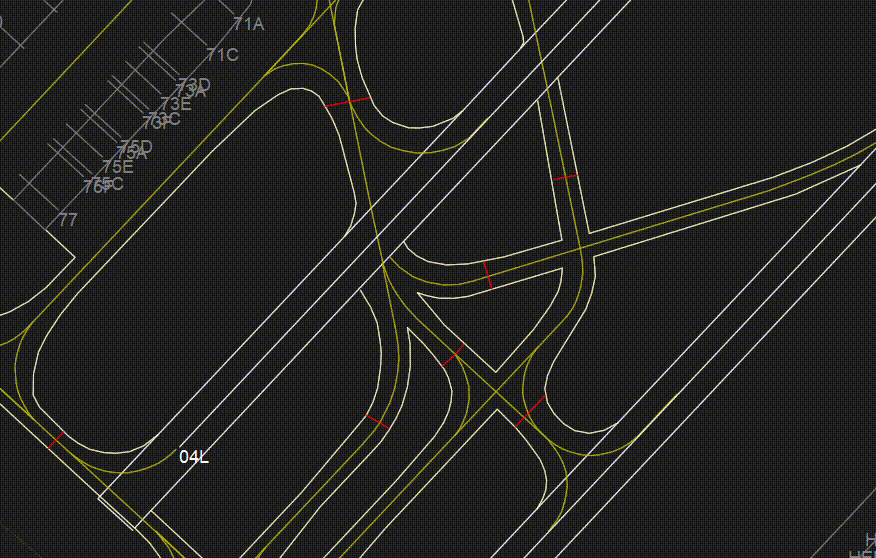
- Shows or Hides Stop lines
¶ APR
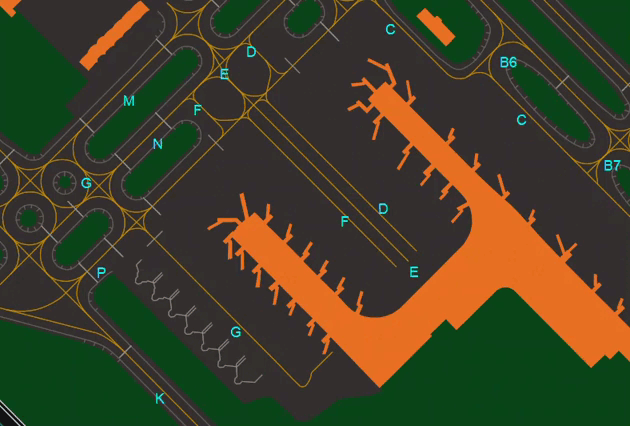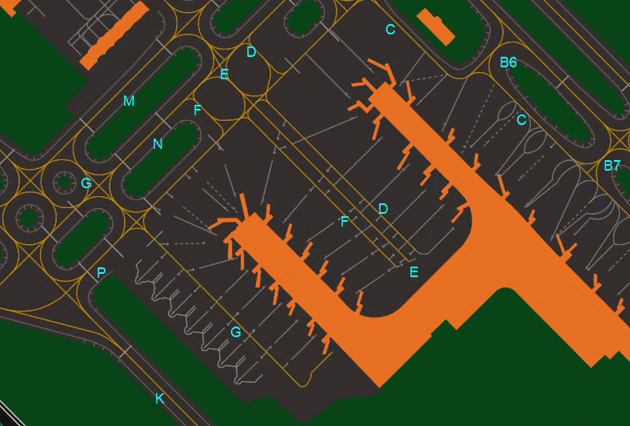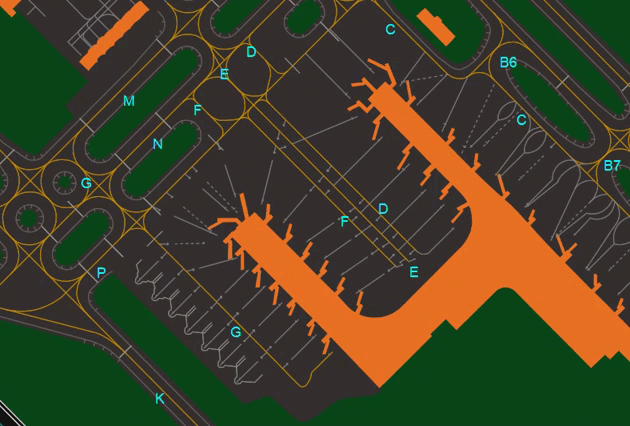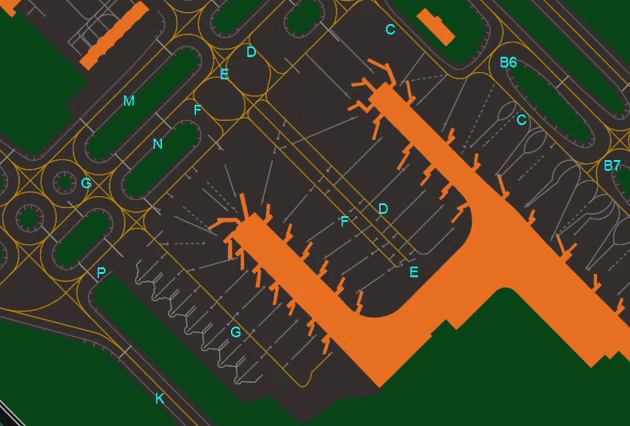
- Shows or Hides Aprons
¶ PIER
- Shows or Hides Airport Piers
¶ BLD
- Shows or Hides Buildings
¶ DA, PA and RA
Stand for:
- DA: Danger Areas
- PA: Prohibited Areas
- RA: Restricted Areas
All of them can be SHIFT + Click to reveal a sub window that allows you to individually select the areas you want to display or hide.
¶ DA (ALT + Q)
- Shows or Hides Danger Areas
- Press SHIFT + DA to choose one by one.
¶ PA (ALT + W)
- Shows or Hides Prohibited Areas
- Press SHIFT + PA to choose one by one.
¶ RA (ALT + E)
- Shows or Hides Restricted Areas
- Press SHIFT + RA to choose one by one.
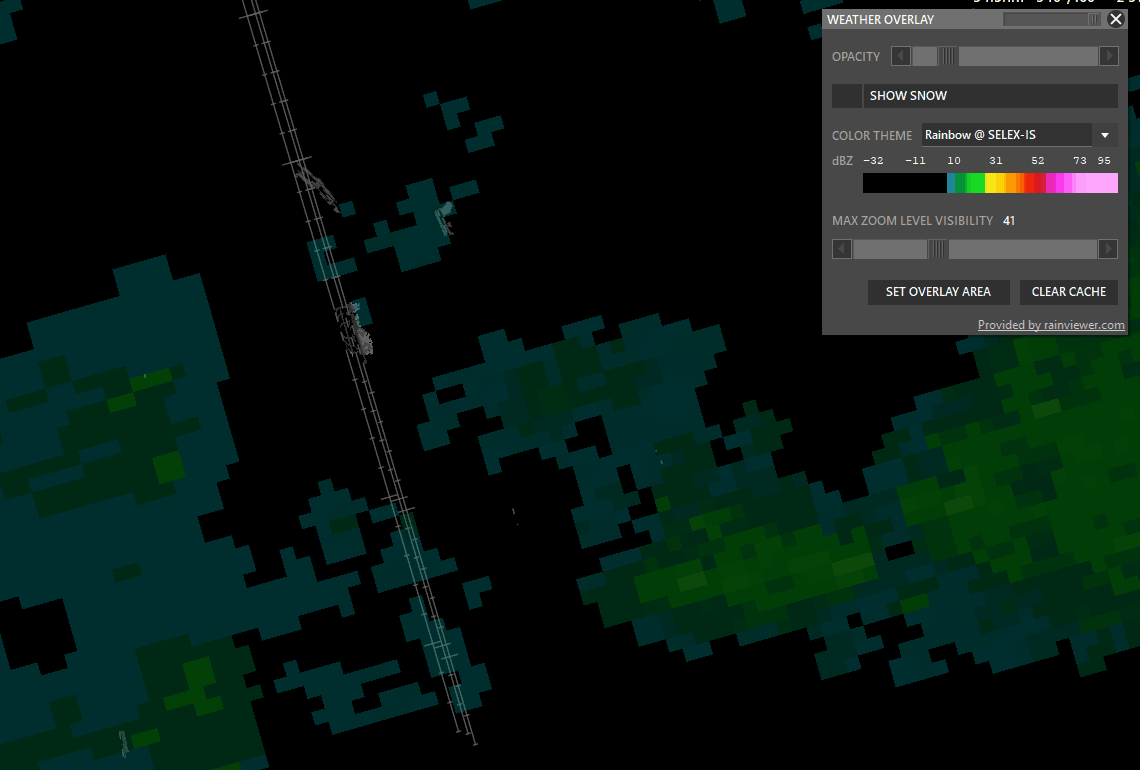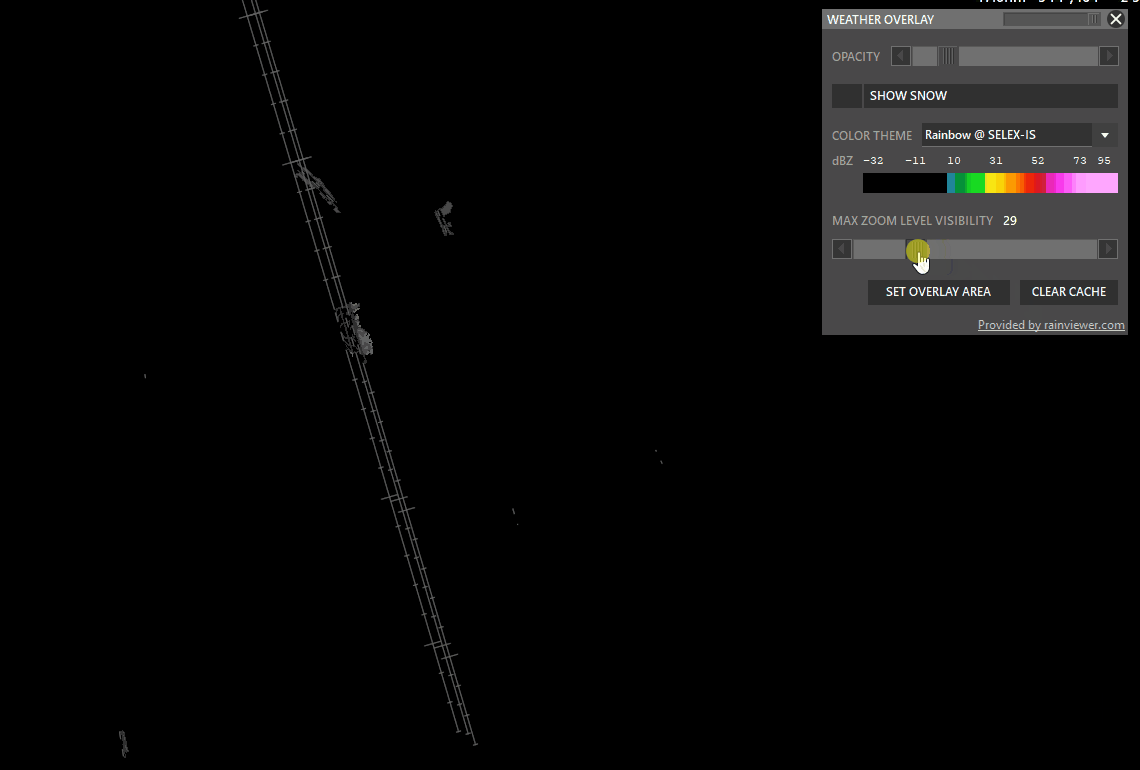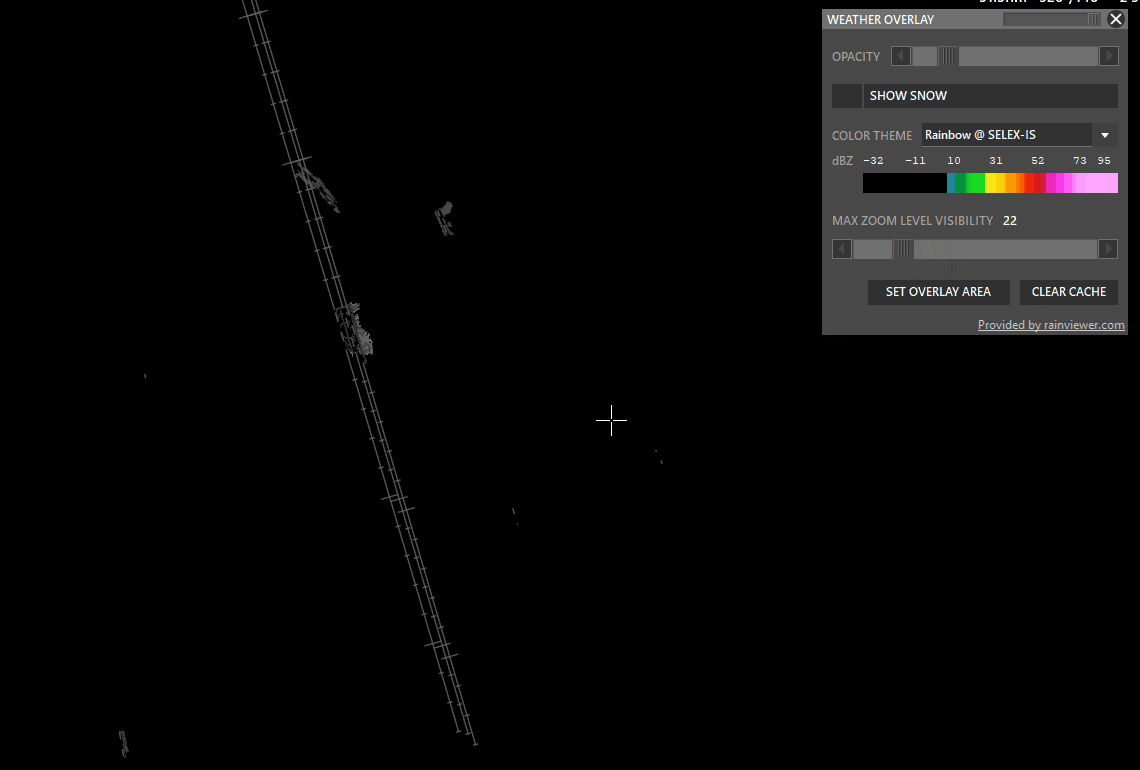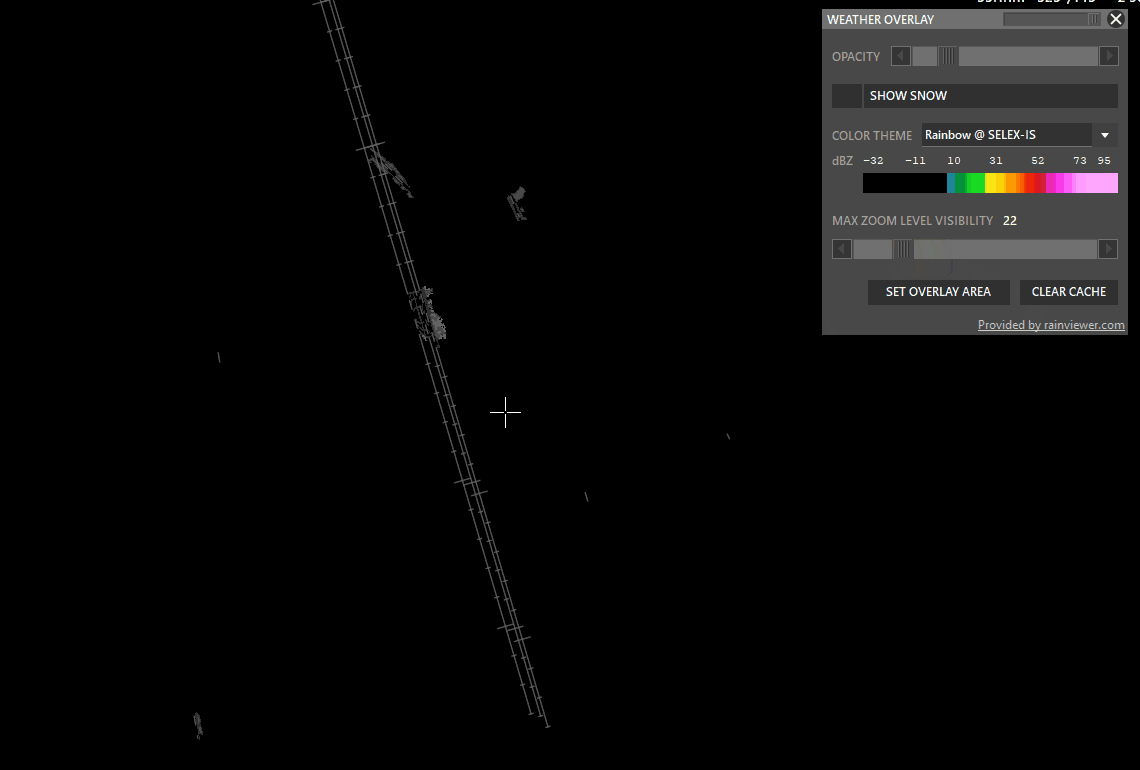
¶ WXR (Weather Radar)
The WXR button has 3 states:
-
WXR off (grey)
-
WXR on (white) → Shows precipitation.
-
SAT on (white) → Shows clouds
Shift + WXR → Open Weather overlay panel
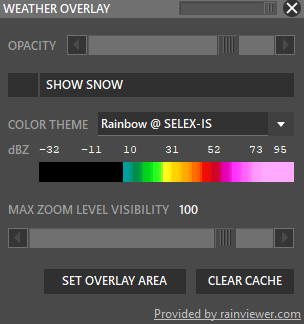
To enable weather maps, select Set Overlay Area, hold shift and left-click drag a rectangle. Aurora will download overlay tiles to cover your selected area.
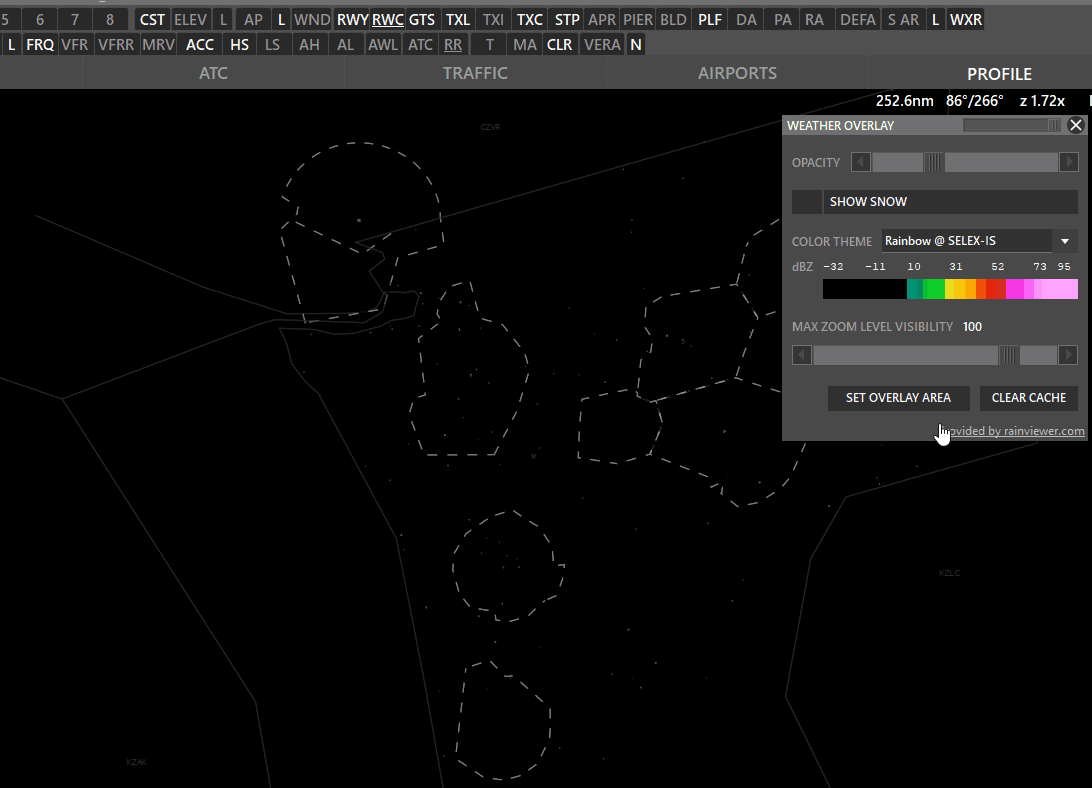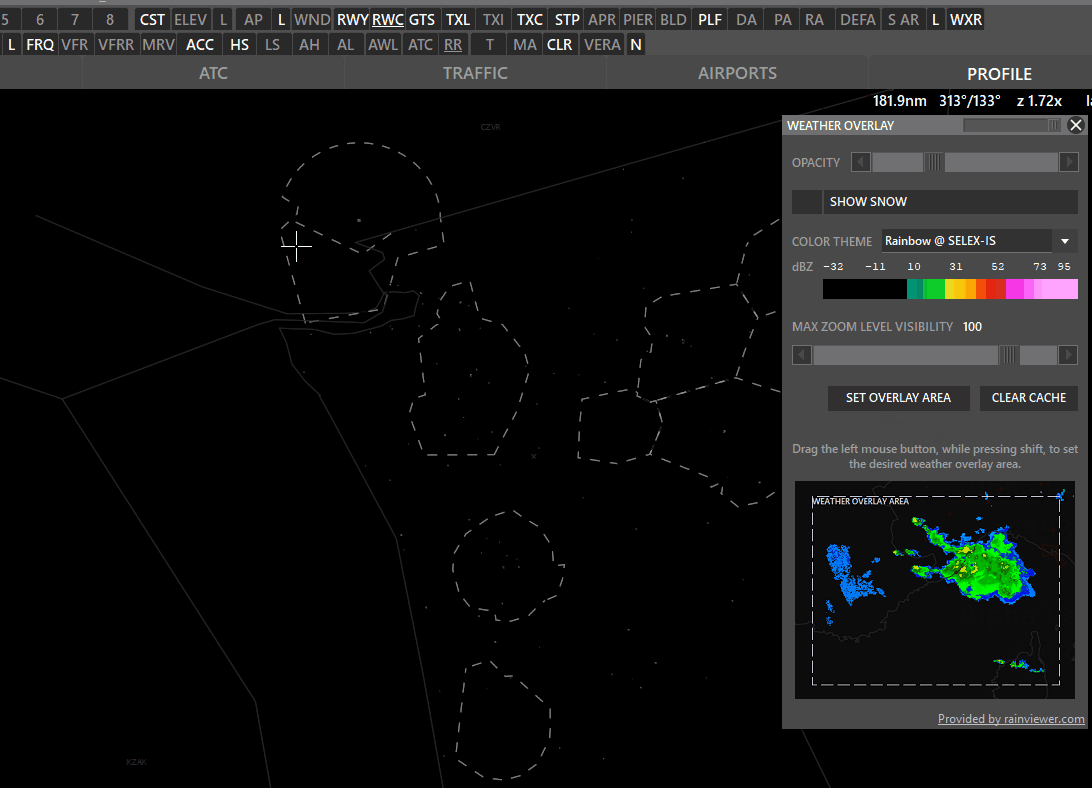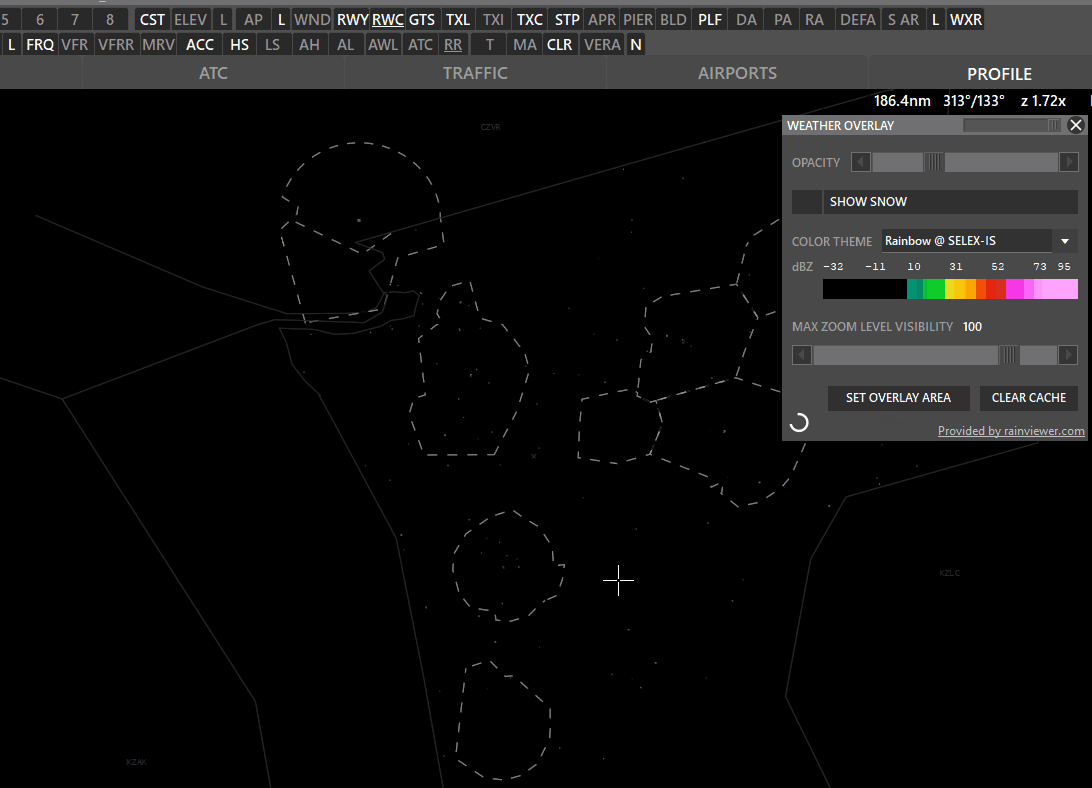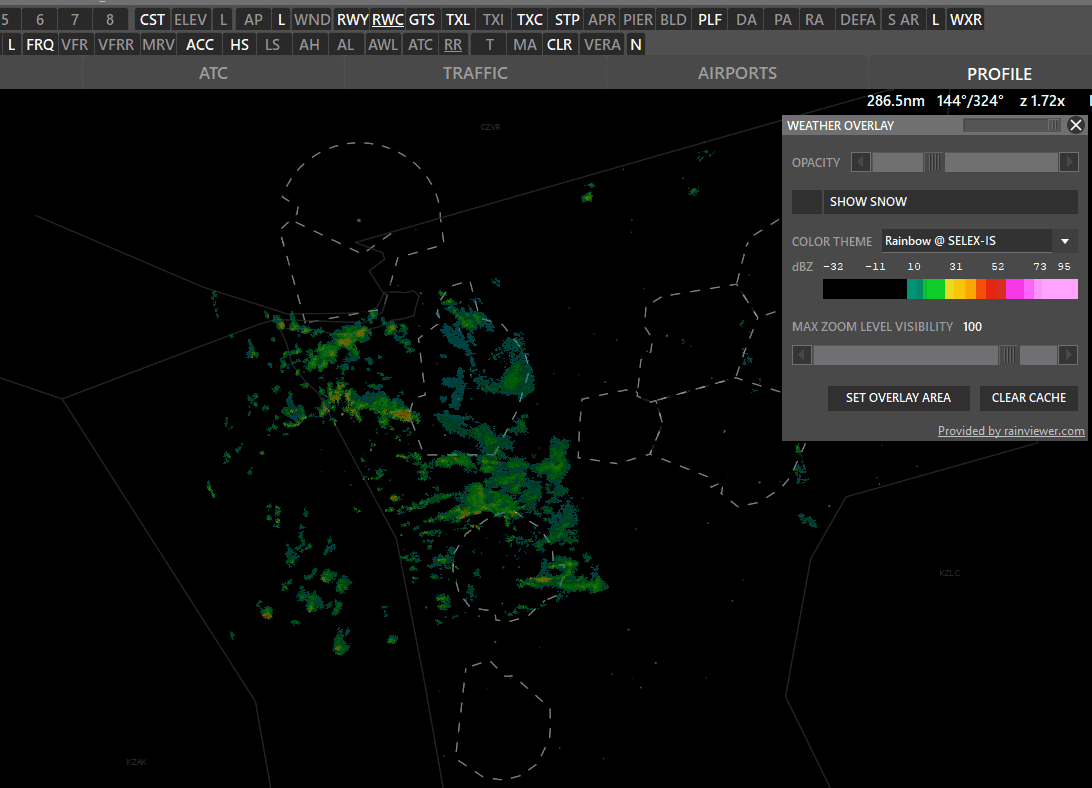
- Color theme: Select different overlay sources.
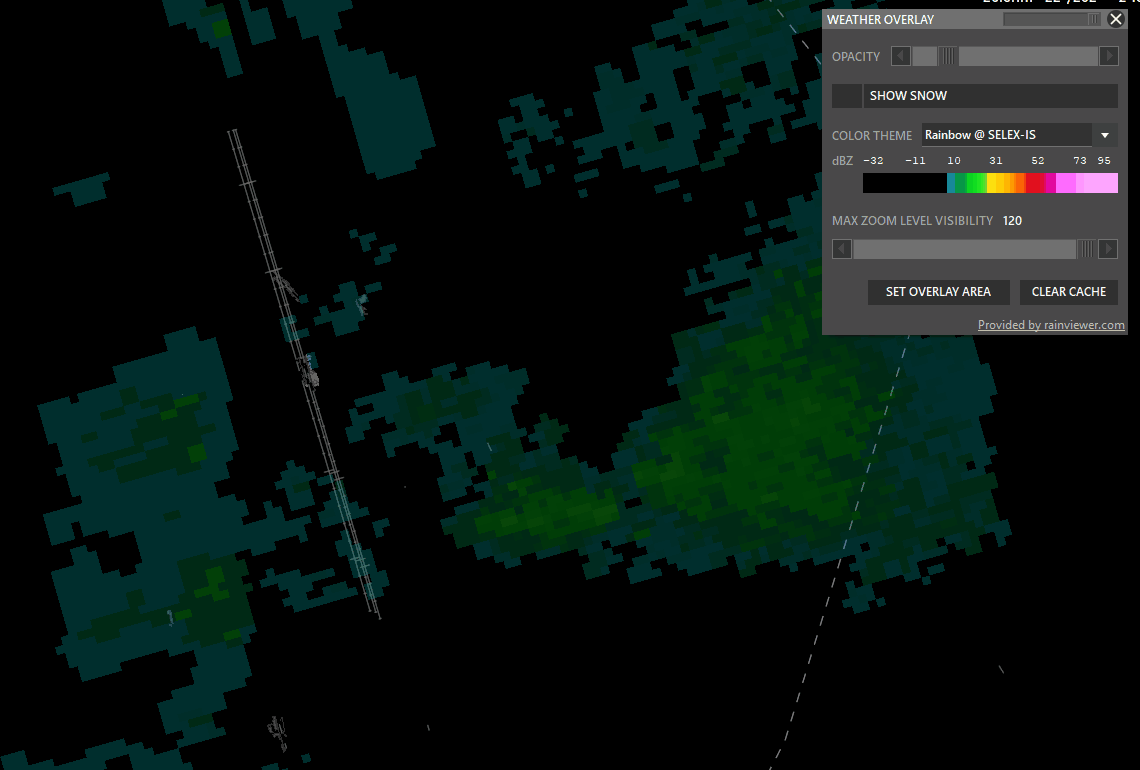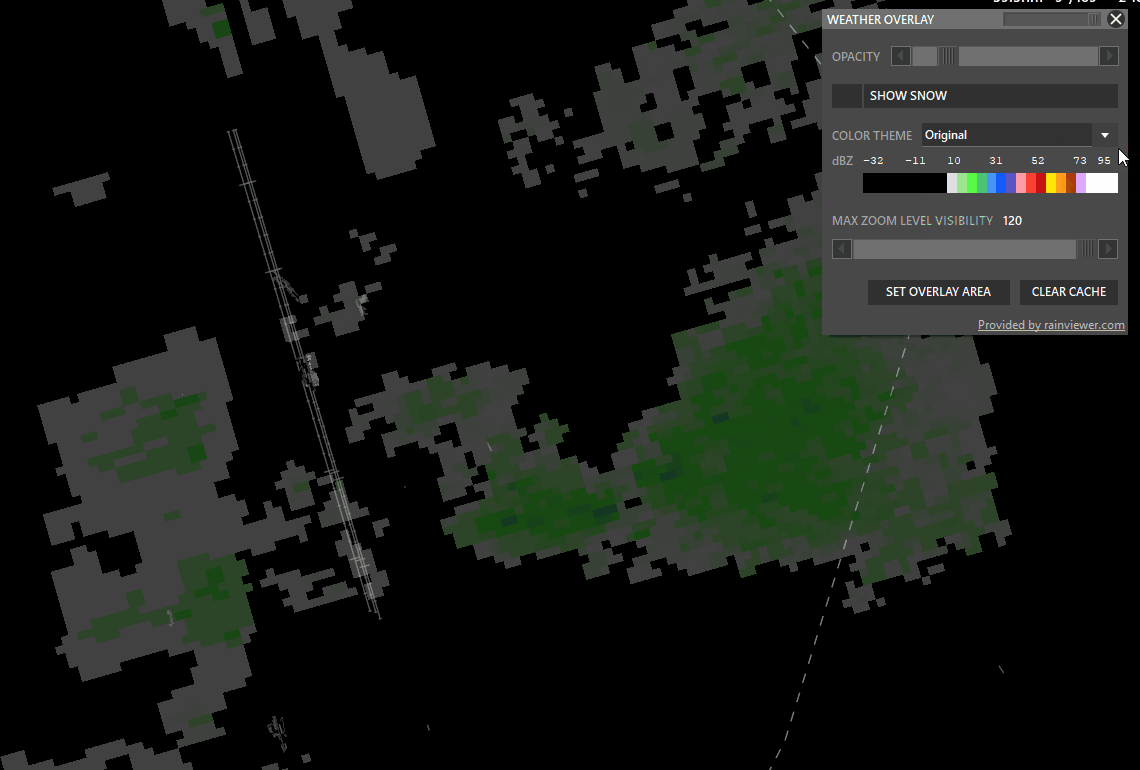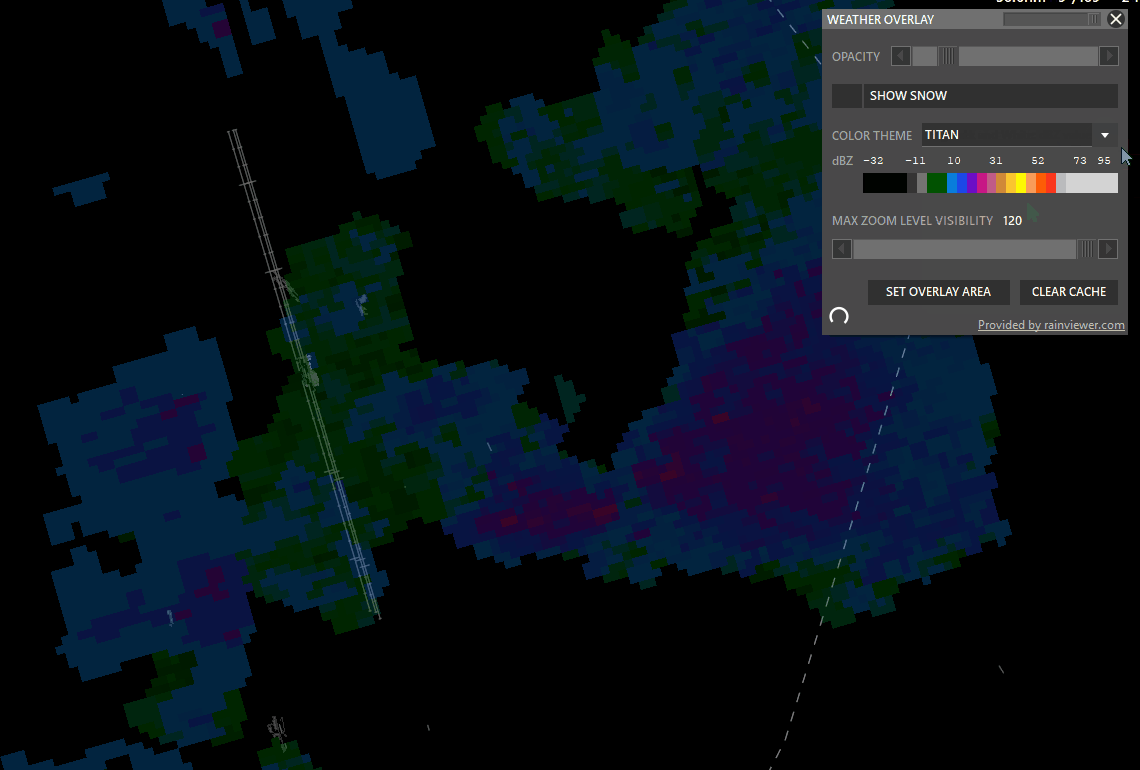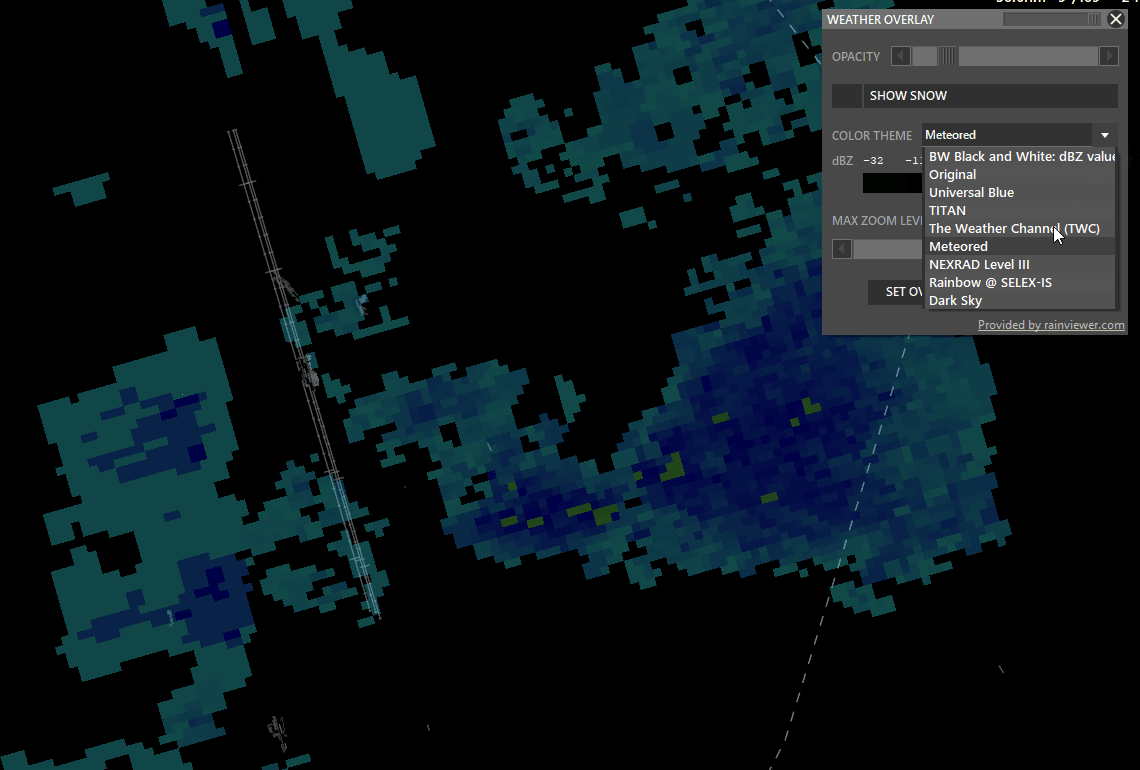
- Opacity: Adjust how transparent the overlay should be.
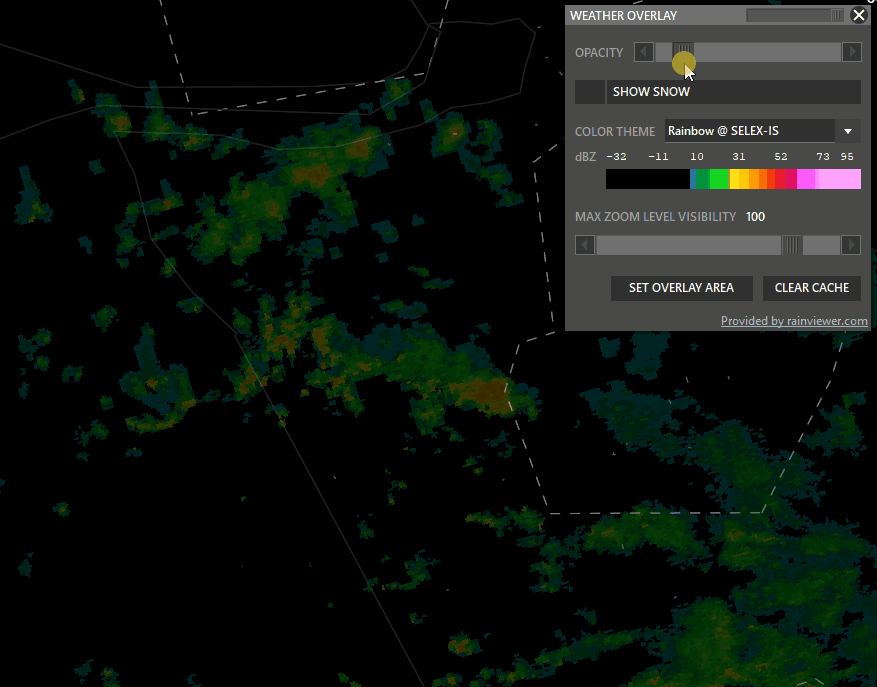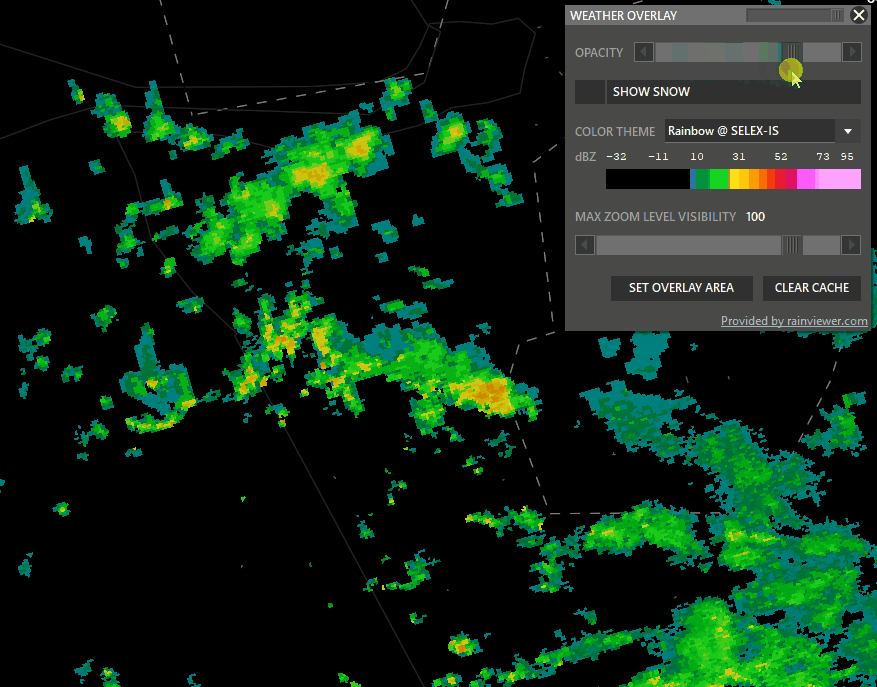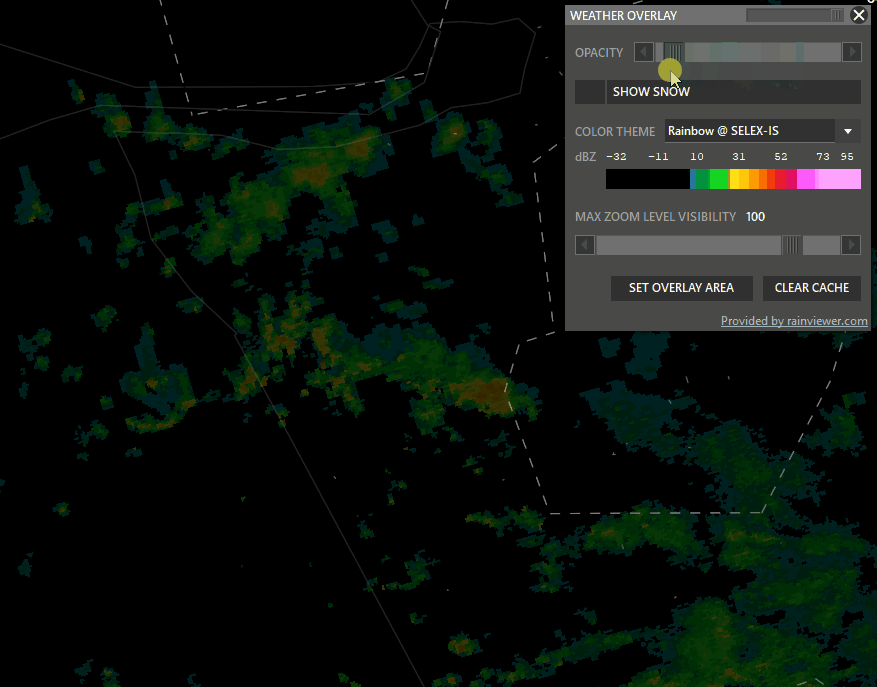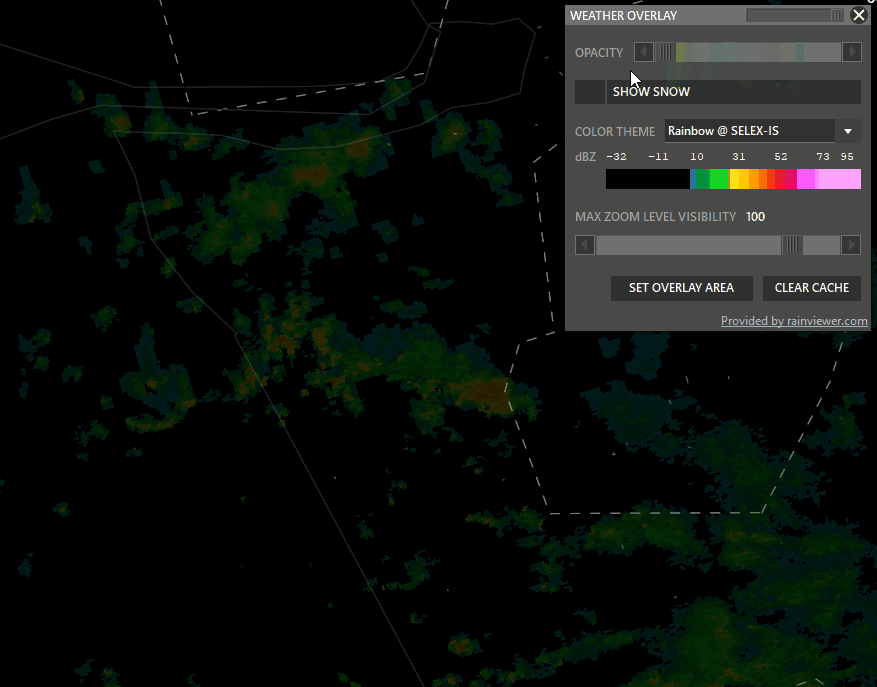
- Snow: taggle snow overlay
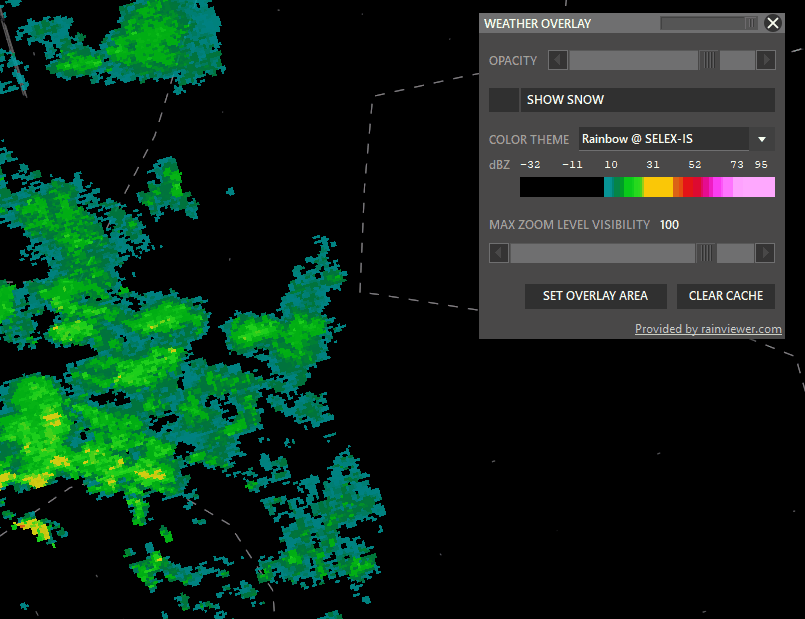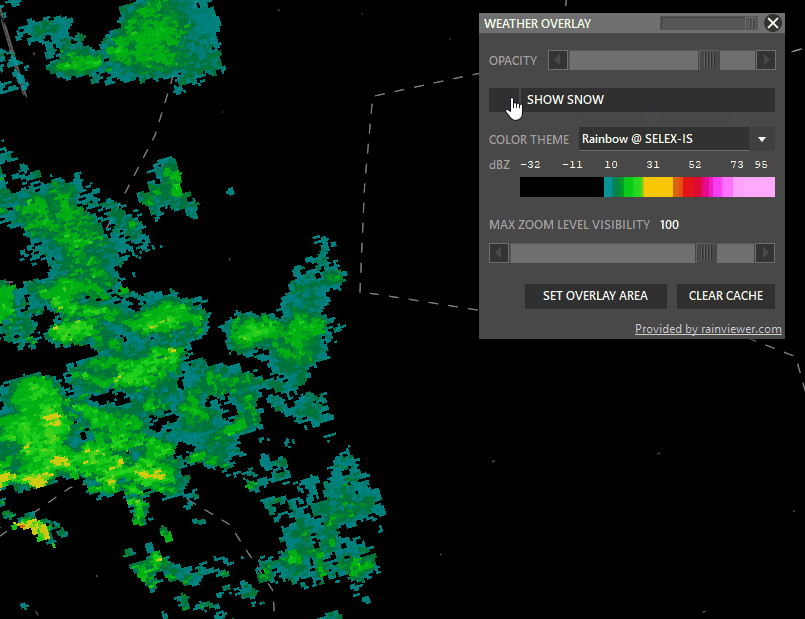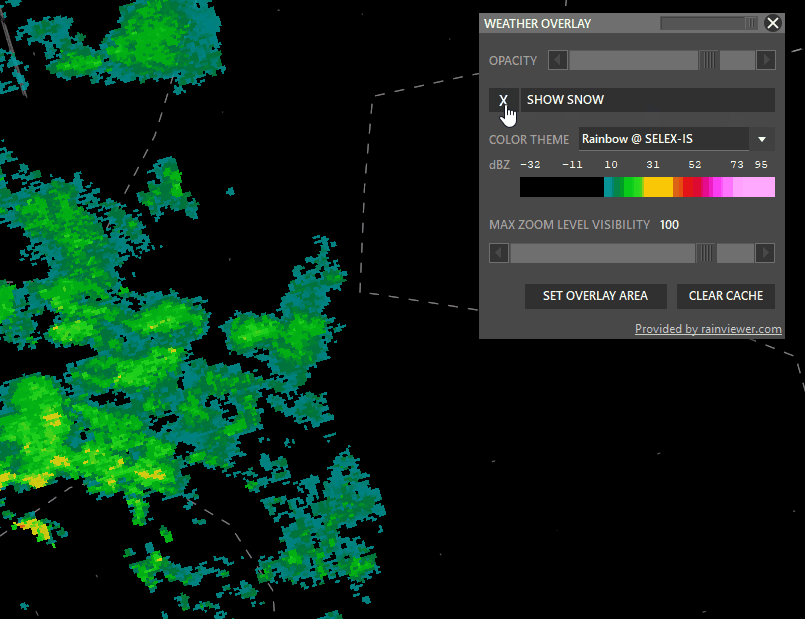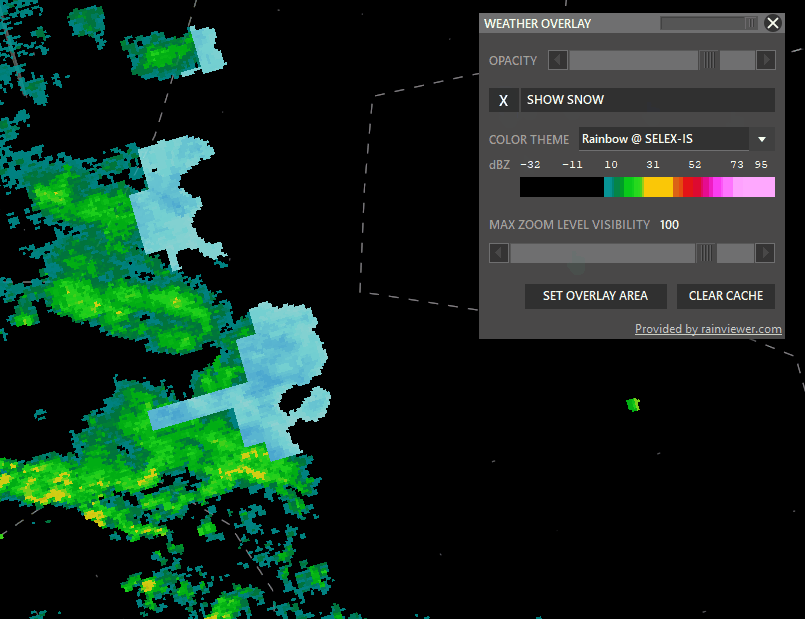
- SAT: Left click to switch to satellite cloude coverage mode.
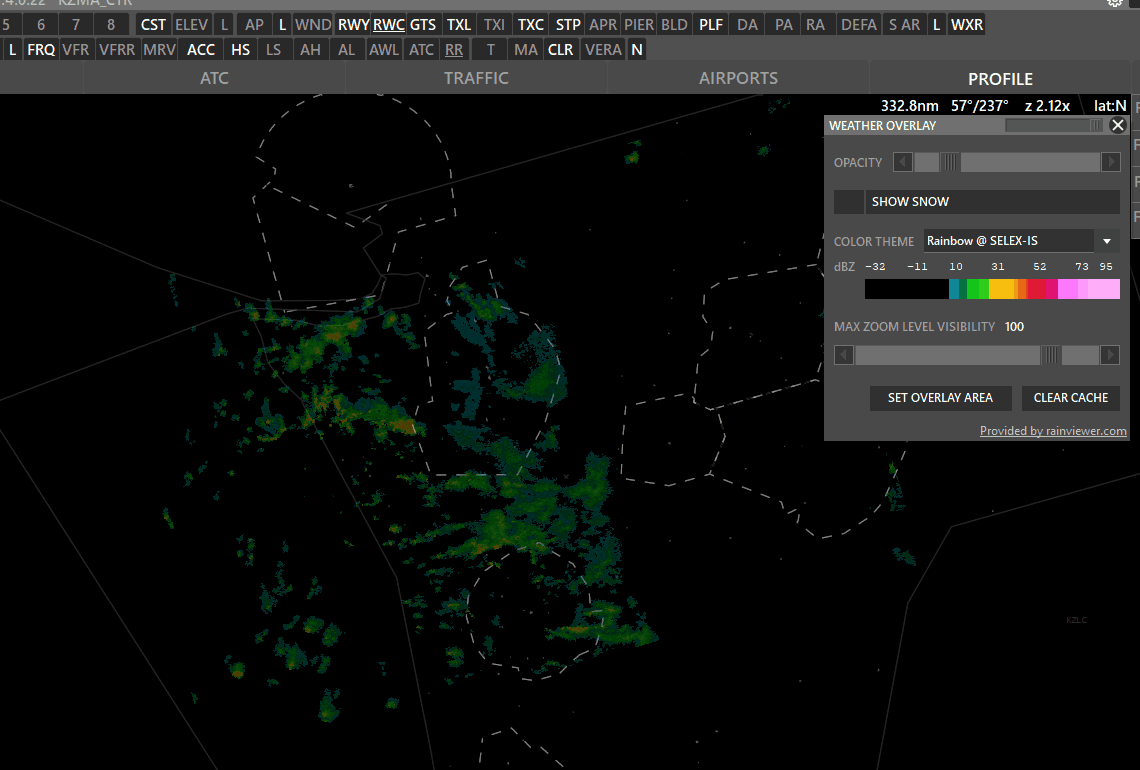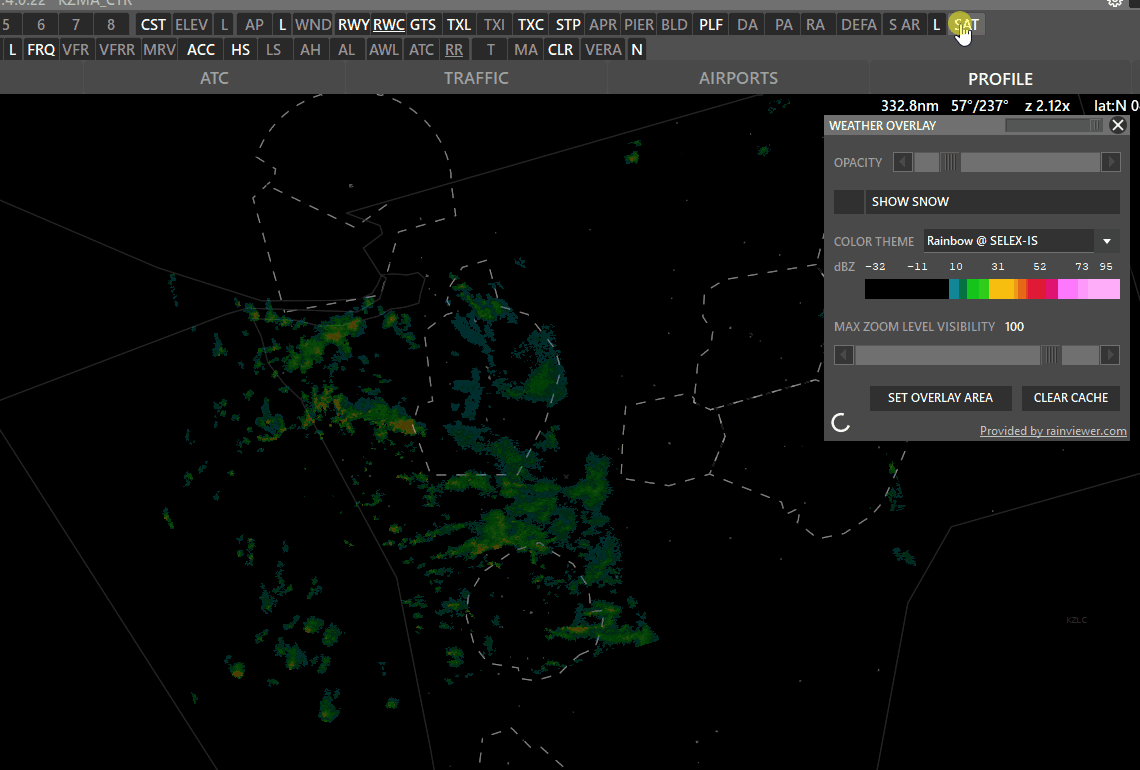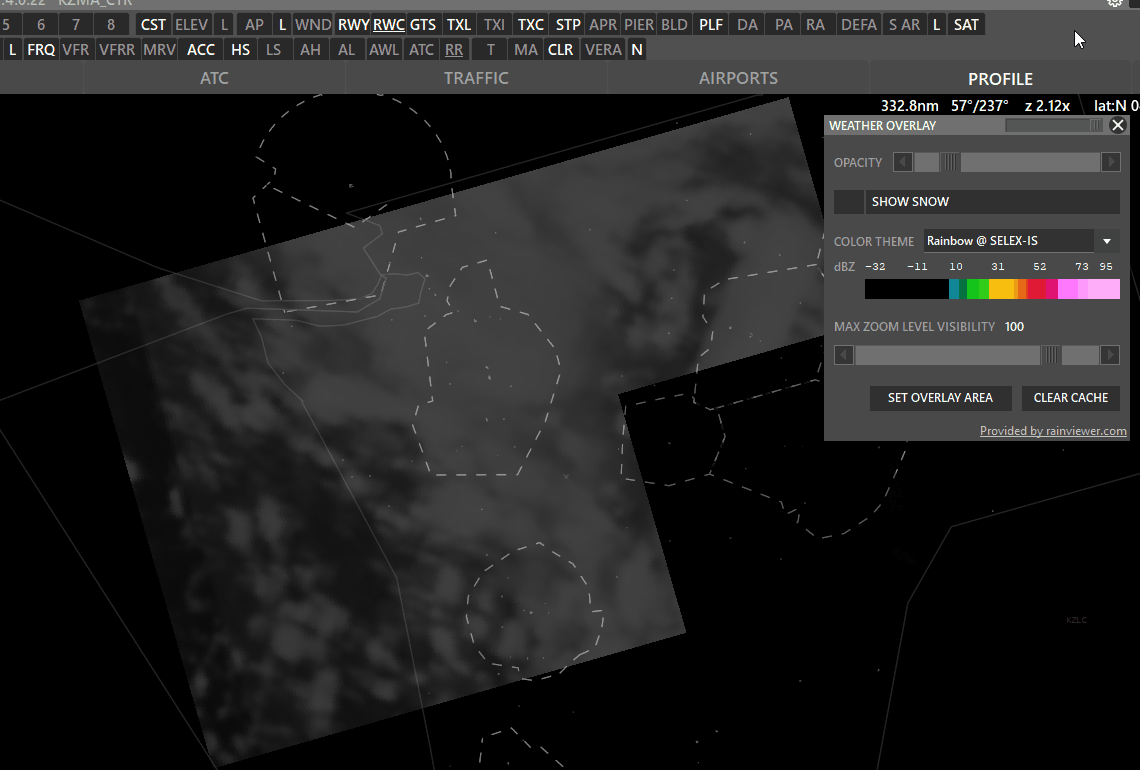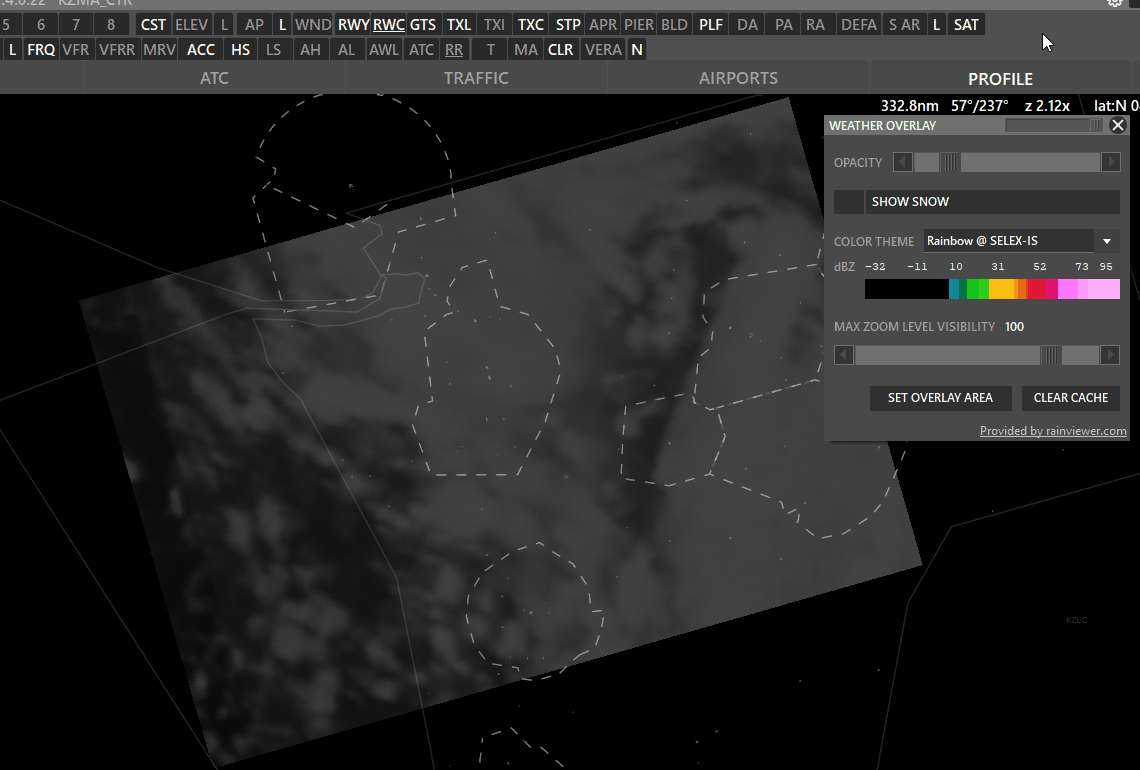
- Max Zoom Level Visibility: Set zoom level where the overlay should not be shown.
¶ NAV (CTRL + N)
This button, when enabled (BOLD), lets you display or hide some information of the Sector File (radar screen content) related to Navigation, like VORs, FIXs, Frequencies, Airways, etc.

¶ VOR (CTRL + Q)
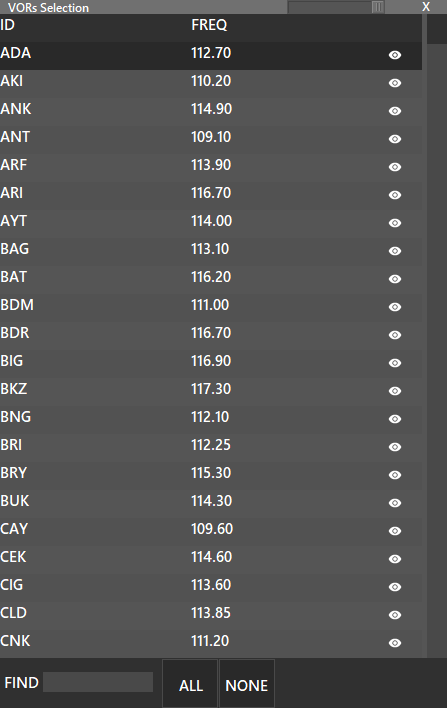
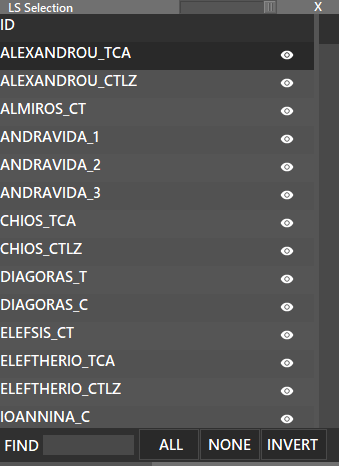
Show, Hide or Manage VORs. If you press the shift key and press the VOR button, a list with all the available VOR’s will be displayed, where you can enable or disable each one to be displayed, clicking on the “eye” icon. Also, you can enable or disable all by pressing the buttons at the bottom of the window.
¶ NDB (CTRL + W)
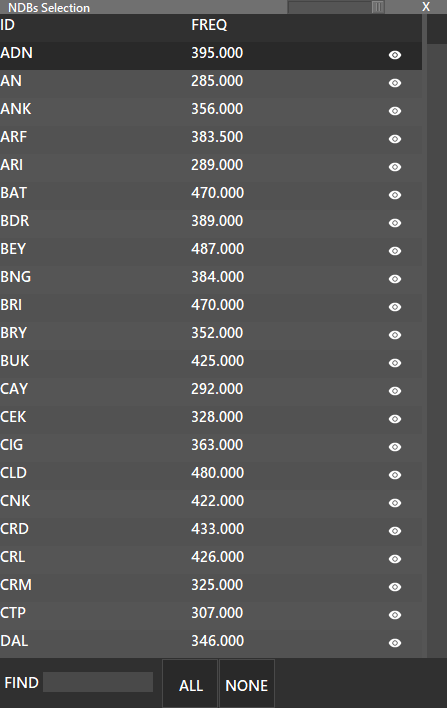
Show, Hide or Manage NDBs. If you press the shift key and press the NDB button, a list with all available NDBs will be displayed, where you can enable or disable each one to be displayed, clicking on the “eye” icon. Also, you can enable or disable all by pressing the buttons at the bottom of the window.
¶ FIX (CTRL + E)
Show, Hide or Manage FIXs. If you press the shift key and press the FIX button, a list with all available FIXs will be displayed, where you can enable or disable each one to be displayed, clicking on the “eye” icon. Also, you can enable or disable all by pressing the buttons at the bottom of the window.
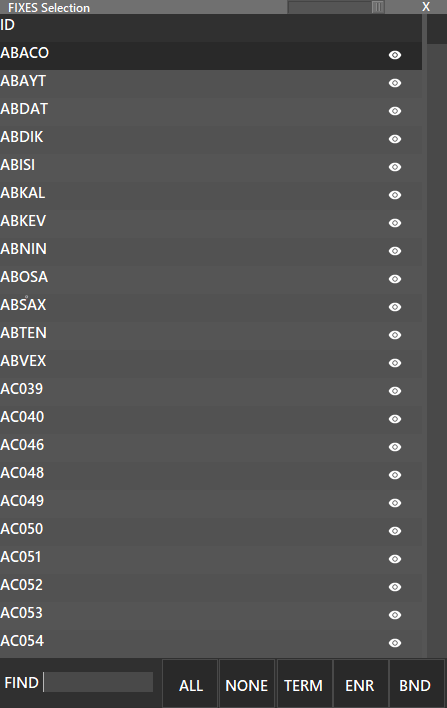
You can use the buttons on the bottom to filter FIXES.
- TERM: Terminal Fixes
- ENR: Enroute Fixes
- BND: Boundary Fixes
Also fixes can be filtered by using the FIND box.
¶ FRQ (CTRL + F)
- Show or Hide Frequencies next to VOR/NDB names.
¶ VFR (CTRL + V)
- Show or Hide VFR Waypoints.
¶ VFRR (CTRL + SHIFT + V)
- Show or Hide VFR Routes.
¶ MRV (CTRL + M)
- Show or Hide Minimum Radar Vectoring Altitudes.
- MRV's can also be enabled/disabled from Airports Menu.
¶ ACC
- Show or Hide ARTCC
- Press SHIFT + ACC to choose one by one.

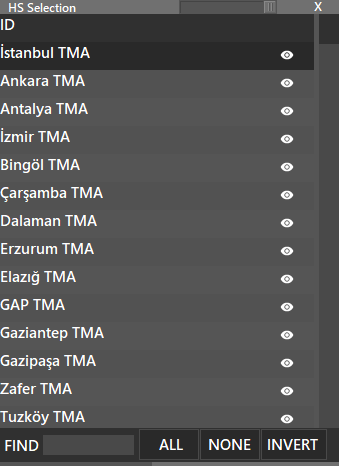
¶ HS
- Show or Hide High Sectors
- Press SHIFT + HS to choose one by one.
¶ LS
- Show or Hide Low Sectors
- Press SHIFT + LS to choose one by one.
¶ H (CTRL + H)
- Show or Hide High Airways.
¶ L (CTRL + L)
- Show or Hide Low Airways.
¶ ATC (ALT + A)
- Show or Hide ATC Online.
¶ N (CTRL + S)
- Show or Hide Name labels for all objects.
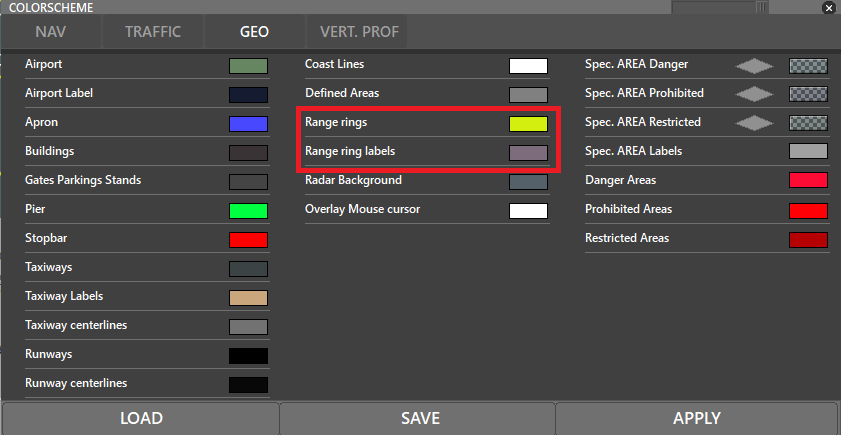
¶ RR (CTRL + R)
- Show or Hide Range Rings.
- SHIFT + RR will bring up the range labels.
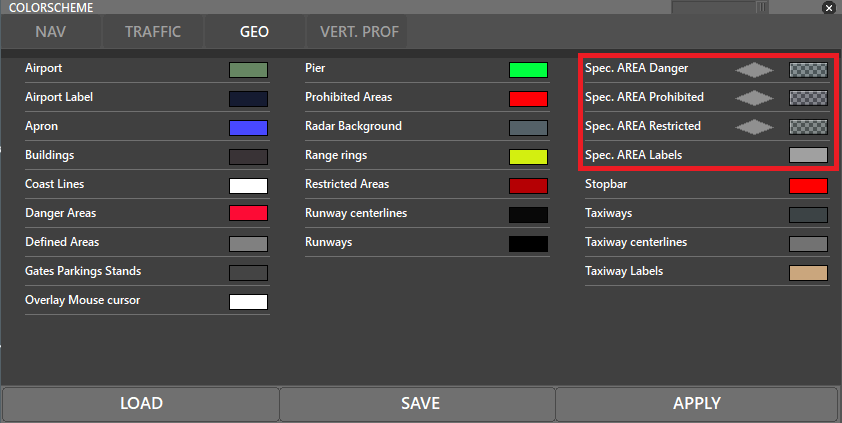
Range rings' and labels' colour can be edited via the COLORS (F5) menu:
¶ T (ALT + T)
- Show or Hide Vectoring Ts.
¶ MA (CTRL + X)
- Show NAVAID Labels only in the area of the mouse.
¶ CLR
- Clears Displayed Routes / SIDs / STARs
¶ S AR
- Show/Hide Special Areas which are implemented.
- To view the special areas, you must be connected to the network. After becoming online, make sure that S AR is white and you will see special areas on your radar if there are any.

- To view their details, press the S AR button while holding the “SHIFT” key from the keyboard.
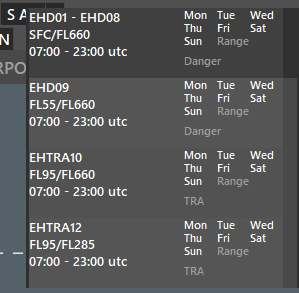
- There, you can see their names, altitude restrictions, date/time restrictions, and their type (Danger/Prohibited/Restricted)
- On the radar, they can be seen with their names, labels or just as an area.
- Click to L/N on the right of the S AR to switch between viewing modes.
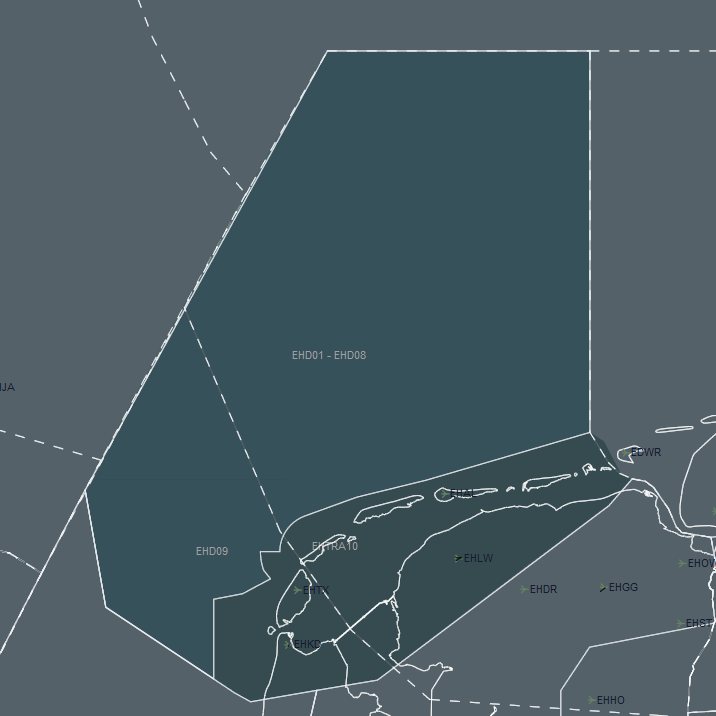
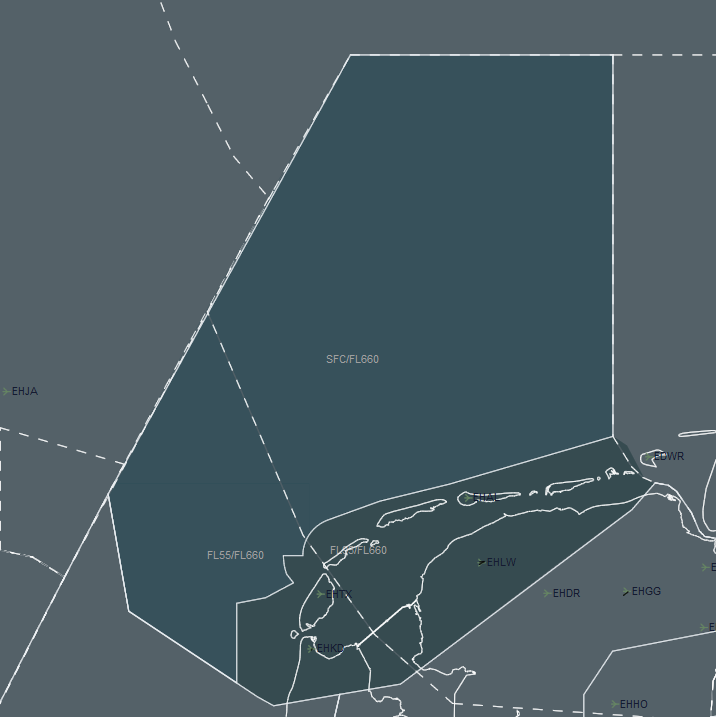
- Colors of the special areas can also be changed via Colors menu for each type (Danger/Prohibited/Restricted)
¶ NOTAMs
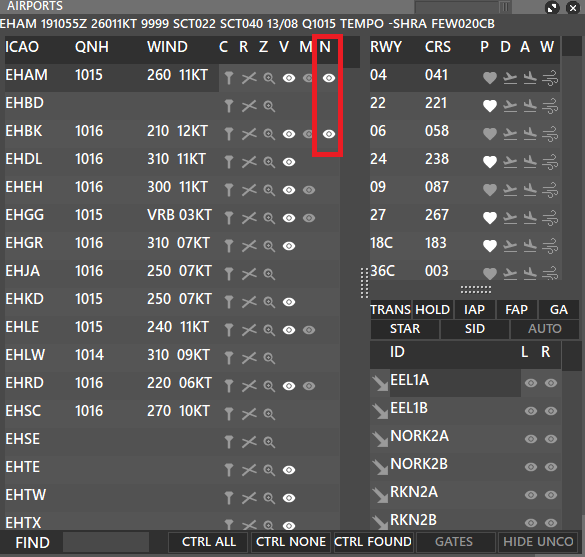
- To view the NOTAMs, open the Airports Menu from the Menu bar, and click the “eye icon” on the relevant row of the N column.
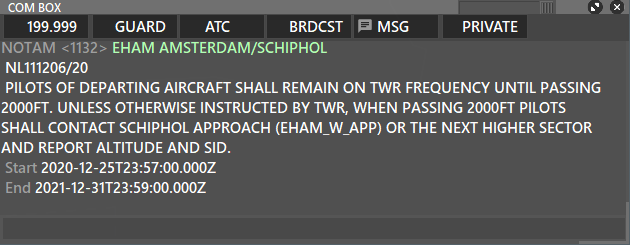
- Details of the NOTAM will appear in your MSG tab of the COM BOX.
¶ Aircraft Context Menu
¶ Types of Context Menus
The first context menu will appear is when you right-click any part of your radar
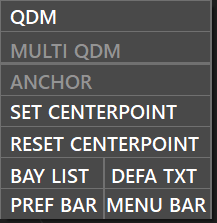
The second context menu will apear when you right-click a non assumed aircraft
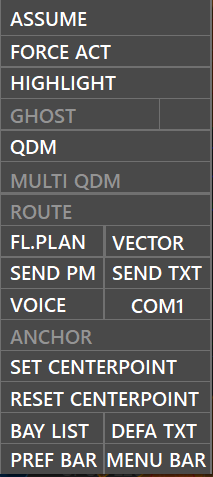
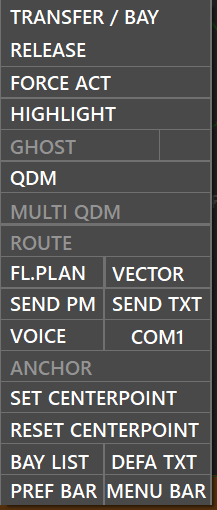
The third context menu will apear when you right-click an assumed aircraft
¶ Actions
¶ Assume
- Indicates taking control of an aircraft by you as ATC unit.
¶ Transfer
- shows list of ATC to transfer aircraft to, set as Next Frequency, or make Bay requests.
- double-clicking an ATC will initiate the transfer.
- If other ATC has auto-accept enabled then the transfer will completed instantly
- If other ATC has manual-accept enabled ithen the tranfer is pending until accepted.
¶ Release
- Release control and send aircraft to unicom frequency 122.8
- By default will also send a text message on primary frequency to pilot: "Switch to UNICOM 122.8, good day"
¶ Force Act
- Sends an automated contact-me message to the pilot including your frequency.
If you have an CPDLC ID, It will also be sent when using Force ACT function:
Good day, please contact CZQX_CTR on 199.999 CPDLC ID CZQX
¶ Highlight

- Highlights the selected field for adjacent ATC to see.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| ALT | Current Altitude |
| ALT A | Assigned Altitude |
| ALT C | Assigned Cruising Altitude |
| SPD | Current Speed |
| SPD A | Assigned Speed |
| VS | Vertical Speed (Rate of climb/descend) |
| DEST | Destination |
| WP | Waypoint |
| AIRCR | Aircraft Type Designator |
¶ Ghost
The purpose is to displaye a ghost target of specific aircraft on a runway centerline. This function is made to be used at converging runways or converging arrival flows to the same or parallel runways.
This functionality is based on CRDA (Converging Runway Display Aid) which is mainly used to help ATC sequence aircraft effectively.
The Ghost function displays the position of a certain aircraft on a selected RCL (Runway Center Line) by plotting a ghost label (including altitude) by using the remaining distance of the aircraft from airport.
Requirements
- The arrival airport of the aircraft must be selected as Controlled in the Airports Manager.
- The runways must be marked as Arrival for the Airport in the Airports Manager.
- Must be done for each aircraft.
How to use it
- In the aircraft context menu activate or deactivate GHOST.
- In the aircraft context menu activate left click on the runway label next to the ghost button to cycle the runway center line.
- If a RNAV approach procedure has been entered in the WP field of the selected aircraft then the ghost target will follow that specific path as well.
Example
AAL22 is approaching runway 08R at ~6NM final. A ghost target of this aircraft has been created for runway 09 centerline. This allows ATC to exactly see the distance from AAL22 ghost label to LAN502 which is intercepting ILS runway 09.

The GHOST symbol can also be changed in the Defined Labels Section, see the Aurora Advanced Functions Manual for more information.
¶ QDM
- Creates a vector line to your mouse courser.
- 1st line = heading
- 2nd line = distance
- 3rd line = time
QDM can also be created by double-clicking an aircraft label or anywhere on your PVD.
A second double-click pins the QDM line.
A third double-click deletes the QDM.
¶ Multi-QDM
- If enabled it allows to created multie QDM lines which can be edited by the QDM manager.
- Disabled Multi-QDM deletes all QDM lines.
¶ Route
Displays the FPL route of the aircraft selected on the radar.
This action can also be done by selecting the traffic in question and pressing TAB
¶ FL.PLAN - Flight Plan
Pops up the Flight Plan of the selected aircraft.
This action can also be done by selecting the traffic in question and pressing F8
¶ Vector
More info soon.
¶ Send PM
Directly opens a PM window directed to the selected traffic.
¶ Send TXT
Directly opens the COM window directed to the selected traffic on the ATC Position frequency.
¶ Voice
Tags the traffic as VOICE or NO VOICE.
¶ COM1
More info soon.
¶ Anchor
More info soon.
¶ Set Centerpoint
- Sets the centerpoint for range rings (your ATC visibilty)
- Automatically set to the airport for DEL/GND/TWR/APP ATC
- CTR centerpoints have a default value specified in the .isc file.
¶ Reset Centerpoint
- Resets centerpoint.
¶ Bay List
- Shows incoming strip bay requests.
¶ DEFA TXT
- Creates custom text labels on your PVD screen. Refer to Aurora Advanced Functions Manual for more information.
¶ Pref bar
- Toggles preference bar
¶ Menu bar
- Toggles menu bar
¶ Session Recorder
Aurora allows ATC to record their session. You can enable/disable Session Recorder from PVD → Settings → Other. To learn more, please check Settings.
You can view your previous ATC/Observer sessions by pressing REPLAY on the Title Bar.
- First, click on the small arrow pointing down to select the session you want to view.
- Sessions names are stored in the following format:
YearMonthDayHourMinuteSecondse.g.20211020180422 - After selecting the session, press REPLAY and options will come up.

- From left to right:
- Day, month and year
- Play, pause and playback speed
- Time adjustment slider
- Zulu time which the playback is playing at
- On the radar screen the information you will see includes, but is not limited to:
- Aircrafts' locations
- Aircrafts' labels which you see during ATC/Observer sessions (Callsign, altitude, speed, ATC filled labels, etc.)
- Aircrafts' speed vectors and history dots
- After every adjustment in time slider, please wait up to 5 seconds for Aurora to refresh.
Each session is recorded automatically once you disconnect or close the Aurora.
¶ Shortcuts
Currently Aurora has the following functional shortcuts:
¶ Aurora's Menu Shortcuts
- F1 : Open Sector Definition List
- F2 : Reset Zoom place to profile's saved zoom
- F3 : Supervisor module
- F4 : Save Profile
- F5 : Open Colorscheme editor
- F6 : Open Soundscheme editor
- F7 : Open Settings editor
- F8 : Show Flightplan window
- + / - : Zoom in / out
¶ Selected Traffic Shortcuts
- z : Assume/Release (selected label)
- q : Request SSR Code
- w : Add Waypoint (selected label)
- a : Add Altitude (selected label)
- s : Add Speed (selected label)
- t : Transfer (selected label)
- x : Send Text (selected label)
- TAB: View the route of the selected aircraft
¶ MENU Shortcuts
- CTRL + I : INSET Bar
- CTRL + T : TRAFFIC Bar
- CTRL + G : GEO Bar
- CTRL + N : NAV Bar
¶ NAV Shortcuts
- CTRL + Q : Show / Hide VOR's
- CTRL + W : Show / Hide NDB's
- CTRL + E : Show / Hide Fixes
- CTRL + F : Show / Hide Frequencies
- CTRL + V : Show / Hide VFR Fixes
- CTRL + SHIFT + V : Show / Hide VFR Route
- CTRL + M : Show / Hide MRVA
- CTRL + H : Show / Hide High Airway
- CTRL + L : Show / Hide Low Airway
- CTRL + S : Show / Hide All Labels
- CTRL + R : Show / Hide Range Rings
- CTRL + T : Show / Hide Vectoring T
- CTRL + X : Show / Hide Mouse Area
- CTRL + A : Show / Hide Aiports
- CTRL + SHIFT + C : Show / Hide Coastlines
- CTRL + SHIFT + D : Show / Hide Gates
- CTRL + C : Copy mouse coordinates
¶ GEO Shortcuts
- ALT + A : Show / Hide ATC Online
- ALT + Q : Show / Hide Danger Areas
- ALT + W : Show / Hide Prohibited Areas
- ALT + E : Show / Hide Restricted Areas
- ALT + R : set SSR MAX TOP
- ALT + F : set SSR MIN FLOOR
¶ INSET Shortcuts
- CTRL + 1 : Open INSET 1
- CTRL + SHIFT + 1: Open INSET 1 at Main Screen Zoom level
- CTRL + 2 : Open INSET 2
- CTRL + SHIFT + 2: Open INSET 2 at Main Screen Zoom level
- CTRL + 3 : Open INSET 3
- CTRL + SHIFT + 3: Open INSET 3 at Main Screen Zoom level
- CTRL + 4 : Open INSET 4
- CTRL + SHIFT + 4: Open INSET 4 at Main Screen Zoom level
- CTRL + 5 : Open INSET 5
- CTRL + SHIFT + 5: Open INSET 5 at Main Screen Zoom level
- CTRL + 6 : Open INSET 6
- CTRL + SHIFT + 6: Open INSET 6 at Main Screen Zoom level
- CTRL + 7 : Open INSET 7
- CTRL + SHIFT + 7: Open INSET 7 at Main Screen Zoom level
- CTRL + 8 : Open INSET 8
- CTRL + SHIFT + 8: Open INSET 8 at Main Screen Zoom level
¶ COMBOX Shortcuts
- .c : Find navaids and airports
- .x : Close chat
- .t CALLSIGN : Find traffic
- .wx ICAO : Receive METAR
- .taf ICAO : Receive TAF
- .chat CALLSIGN : Open chat in PRIVATE tab
- .a CALLSIGN : Add to chat group
- .r CALLSIGN : Remove from chat group
¶ Authors
- VID 193103 - Creation
- VID 425236 - Update
- VID 150259 - Wiki integration
- VID 274235 - Edits and Updates
- VID 573229 - Reformatting and Updates
- VID 545587 - Updates
- VID 190881 - Updates
- VID 657678 - Updates
- VID 644626 - Updates
- VID 657678 - Reformatting and Updates